Team:Calgary/Project/DataPage
From 2012.igem.org
Emily Hicks (Talk | contribs) |
Emily Hicks (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
<li><p> An existing <i>xylE</i> gene in the registry (<a class="blue" href= "http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J33204">BBa_J33204</a>) was constructed with a constitutive promoter instead of the glucose-repressible part available within the registry. This allows for increased output in media containing glucose, making it more suitable for a variety of applications such as our own. We validated the functionality of this part which can be found on our <a class="blue" href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Calgary/Project/OSCAR/CatecholDegradation">Decatecholization</a> page. In addition, we documented a novel application for this part, by using it in conjunction with Washington's PetroBrick (<a class="blue" href="http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K590025">BBa_K590025</a>) to degrade catechol into a further break-down product. </p></li> | <li><p> An existing <i>xylE</i> gene in the registry (<a class="blue" href= "http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J33204">BBa_J33204</a>) was constructed with a constitutive promoter instead of the glucose-repressible part available within the registry. This allows for increased output in media containing glucose, making it more suitable for a variety of applications such as our own. We validated the functionality of this part which can be found on our <a class="blue" href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Calgary/Project/OSCAR/CatecholDegradation">Decatecholization</a> page. In addition, we documented a novel application for this part, by using it in conjunction with Washington's PetroBrick (<a class="blue" href="http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K590025">BBa_K590025</a>) to degrade catechol into a further break-down product. </p></li> | ||
| + | <li><p>An <I>E. coli</i> catalase gene from the registry (<a class="blue" href= "http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K137068">BBa_K137068</a>) was also tested in conjunction with a lacI inducible promoter as a new composite part (<a class="blue" href= "http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K902060">BBa_K902060</a>) . This part was characterized in TOP10 <i> E. coli<i> for its ability to allow cells to survive in higher concentrations of hydrogen peroxide. This data can be found on our <a class="blue" href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Calgary/Project/OSCAR/Desulfurization">Desulfurization</a> page. | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
<p><a href="#top">Back to Top</a></p> | <p><a href="#top">Back to Top</a></p> | ||
Revision as of 23:40, 26 October 2012


Hello! iGEM Calgary's wiki functions best with Javascript enabled, especially for mobile devices. We recommend that you enable Javascript on your device for the best wiki-viewing experience. Thanks!
Detect and Destroy: Data Page
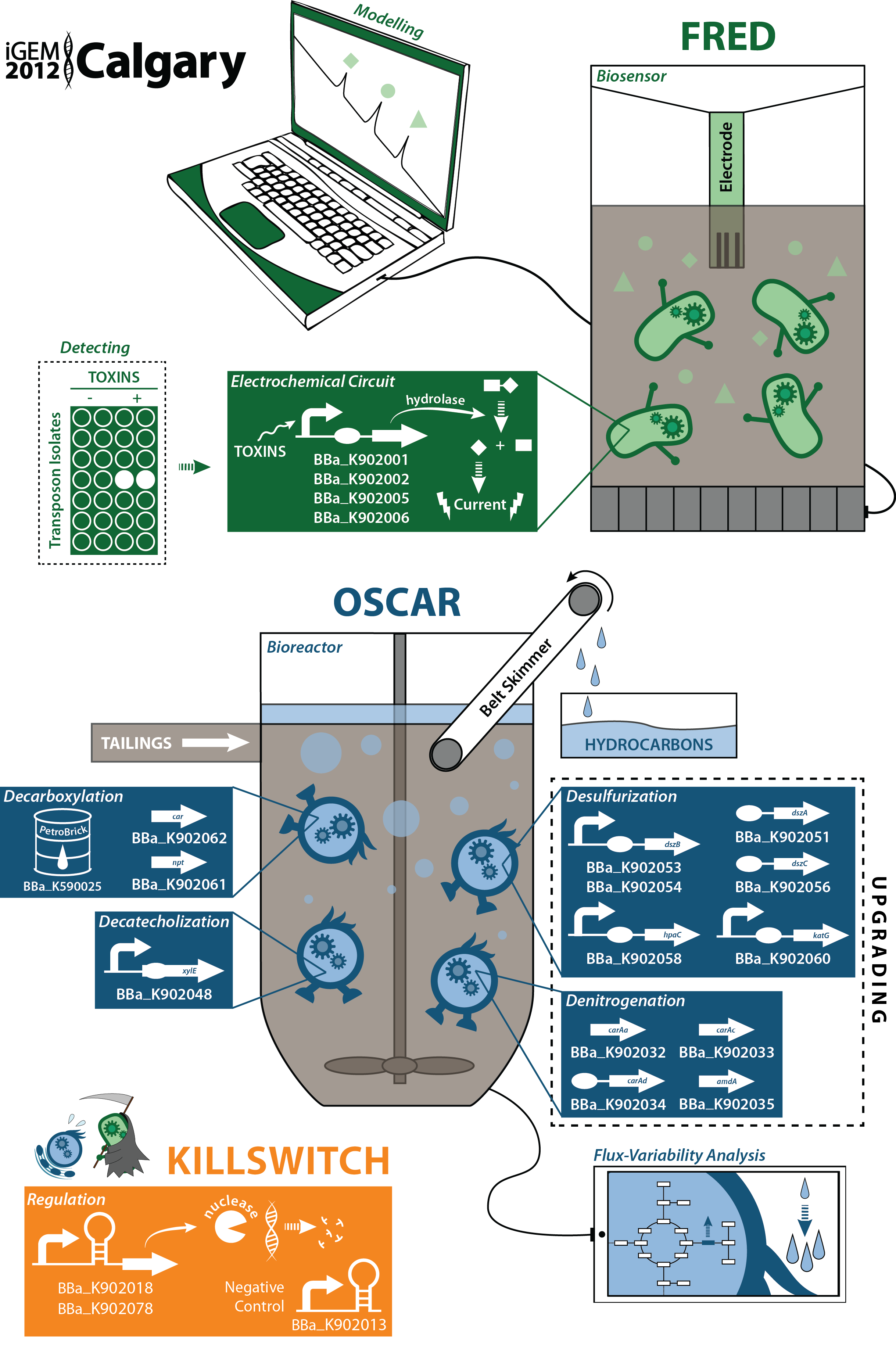
Characterization of new parts submitted to the Registry
(BBa_K902000) and (BBa_K902004): two novel hydrolase enzymes were submitted to the registry for the hydrolysis of two different sugar-conjugated electroactive compounds: PNPG and PDPG. Used in conjunction with the existing lacZ part in the registry (BBa_I732005) which hydrolyzes CPRG, this allows for the electrochemical detection of three compounds with a single electrode. A uidA inducible generator (BBa_K902002) was submitted and characterized electrochemically. This data can be found on our Electroreporting page.
(BBa_K902008),(BBa_K902023) and (BBa_K902074): three novel riboswitches sensitive to magnesium, molybdate, and manganese were submitted along with two associated promoters (BBa_K902009 and BBa_K902073) in addition to a rhamnose inducible, glucose repressible promoter (BBa_K902065). One of these riboswitches (BBa_K902008) was tested with GFP and a constitutive promoter using this construct, (BBa_K902021), with its promoter and GFP using this construct (BBa_K902017) and with its promoter and the S7 kill gene using this construct (BBa_K902018). This data can be found on our killswitch Regulation page.
Genes for denitrogenation and desulfurization were biobricked and submitted. The amdA, amidase gene (BBa_K902041) was biobricked and characterized shown to be able to remove primary amines from a variety of compounds. A novel oxidoreductase part (BBa_K902058) was also submitted and its functionality characterized for use in the desulfurization project. This data can be found on our upgrading Desulfurization page.
Further characterization of parts already present within the registry
The IPTG inducible lacI regulated promoter (BBa_R0010) was tested electrochemically to demonstrate its leakiness when not used in conjunction with strong expression of regulatory elements. This data can be found on our Electroreporting page.
(BBa_K590025), the PetroBrick, submitted by the Washington team in 2011, was characterized for a novel function: the conversion of naphthenic acids and 2-hydroxymuconate- a catechol break-down product from from the xylE gene (BBa_J33204) into hydrocarbons and potential value added products. This data can be found on both the Decarboxylation page and the Decatecholization page. We feel that these new and meaningful applications of this part present a distinct improvement on its usefulness for other teams.
The output of (BBa_K590025) was also optimized thorugh a program we developed in MATLAB for the optimization of metabolic pathways in synthetic biology metabolic networks. The program allows you to build an artificial synthetic biology network in E. coli and predicts substrates that should be fed to the organism to increase production of the compound. This was characterized and validated in the wetlab with the Petrobrick. This data can be found on our Flux Analysis page.
An existing xylE gene in the registry (BBa_J33204) was constructed with a constitutive promoter instead of the glucose-repressible part available within the registry. This allows for increased output in media containing glucose, making it more suitable for a variety of applications such as our own. We validated the functionality of this part which can be found on our Decatecholization page. In addition, we documented a novel application for this part, by using it in conjunction with Washington's PetroBrick (BBa_K590025) to degrade catechol into a further break-down product.
An E. coli catalase gene from the registry (BBa_K137068) was also tested in conjunction with a lacI inducible promoter as a new composite part (BBa_K902060) . This part was characterized in TOP10 E. coli for its ability to allow cells to survive in higher concentrations of hydrogen peroxide. This data can be found on our Desulfurization page.
Additional Work and Characterization
Developed and tested both hardware and software for a biosensor using an electrochemical sensor. The software is available on our wiki as are the results fom the hardware. These are on our Device Prototype page
Characterized one of our constitutively expressed transposon clones to test the lacZ gene electrochemically. This data can be found on our Electroreporting page.
Submitted novel parts involved in decarboxylation and validated the functionality of an additional enzyme (oleT), capable of converting fatty acids into alkenes by itself. This was done in its host organism. This data can be found in our Decarboxylation section, however this gene has not yet been submitted due to problems cloning it.
Designed and prototyped a physical bioreactor for which we obtained both qualitative and quantitative data for its functionality. This is outlined on our Bioreactor page.
Characterized the biodegradation of carbazole and various sulfur-containing compounds resembling naphthenic acids in the organisms from which we got our genes. This data can be found on our (Desulfurization) and (Denitrogenation)
Resubmitted (BBa_K26009) an inconsistent registry composite part that we had to construct from basic parts, resubmitting as the sequence-verified (BBa_K902016)
 "
"