Team:Calgary/Project/Synergy
From 2012.igem.org


Hello! iGEM Calgary's wiki functions best with Javascript enabled, especially for mobile devices. We recommend that you enable Javascript on your device for the best wiki-viewing experience. Thanks!
Synergy: Putting it all Together

Incorporating Human Practices in the Design of our System
In the earlier stages of our project, we realized that in order to give our project the best chance of being implemented, we needed to do it in a way that was in line with both industry’s wants and needs. To ensure that we did this, we established a dialogue with several experts in order to get their opinions on how we should approach our project. This led to an informed design of our system, in which we emphasized the need for both physical and genetic containment devices.
Have we accomplished our goal?
Nearing the end of our project however, we wanted to see if we had accomplished what we set out to do. So we decided to go back to the experts, this time taking the progress we had made on our project with us. We got a variety of different perspectives from suggestions on the scale up of our project, to the cost and environmental impact of our numerous components. The results of all of these can be found on our Interviews page. One major concern was scale-up. One expert wanted to know how feasible this system would actually be. We have some FRED components, OSCAR components, and killswitch components, but how functional are these parts, and how do they work together? Our next major goal was therefore to establish synergy: to put these pieces together in order to assess how far we have actually gotten.
Here we demonstrate that we can develop a comprehensive kill switch consisting of both an auxotroph and an inducible kill switch which work together to contain FRED and OSCAR. With FRED, we show that we can detect toxins selectively in tailing ponds using our identified transposon. Finally, with OSCAR we show that our killswitch auxotroph dramatically increases the production of hydrocarbons in the system and that we are capable of scaling up OSCAR's bioreactor and selectively collect hydrocarbons with our belt skimmer device.
Putting our Killswitch Together
Testing the Requirement of Glycine With our Auxotroph
Our flux-based analysis allowed us to realize the potential for glycine to be used not only as a way to increase the yield of OSCAR, but also as an auxotrophic killswitch. This allowed our model to be used not only to inform our wetlab, but also our human practices. We wanted to see how this auxotrophic marker system could work with one of our inducible killswitch constructs. We procured a Keio Knockout Collection Strain which deleted glyA an important enzyme in glycine metabolism making it auxotrophic for this compound. We wanted to identify the concentration of glycine required for its growth as shown below.
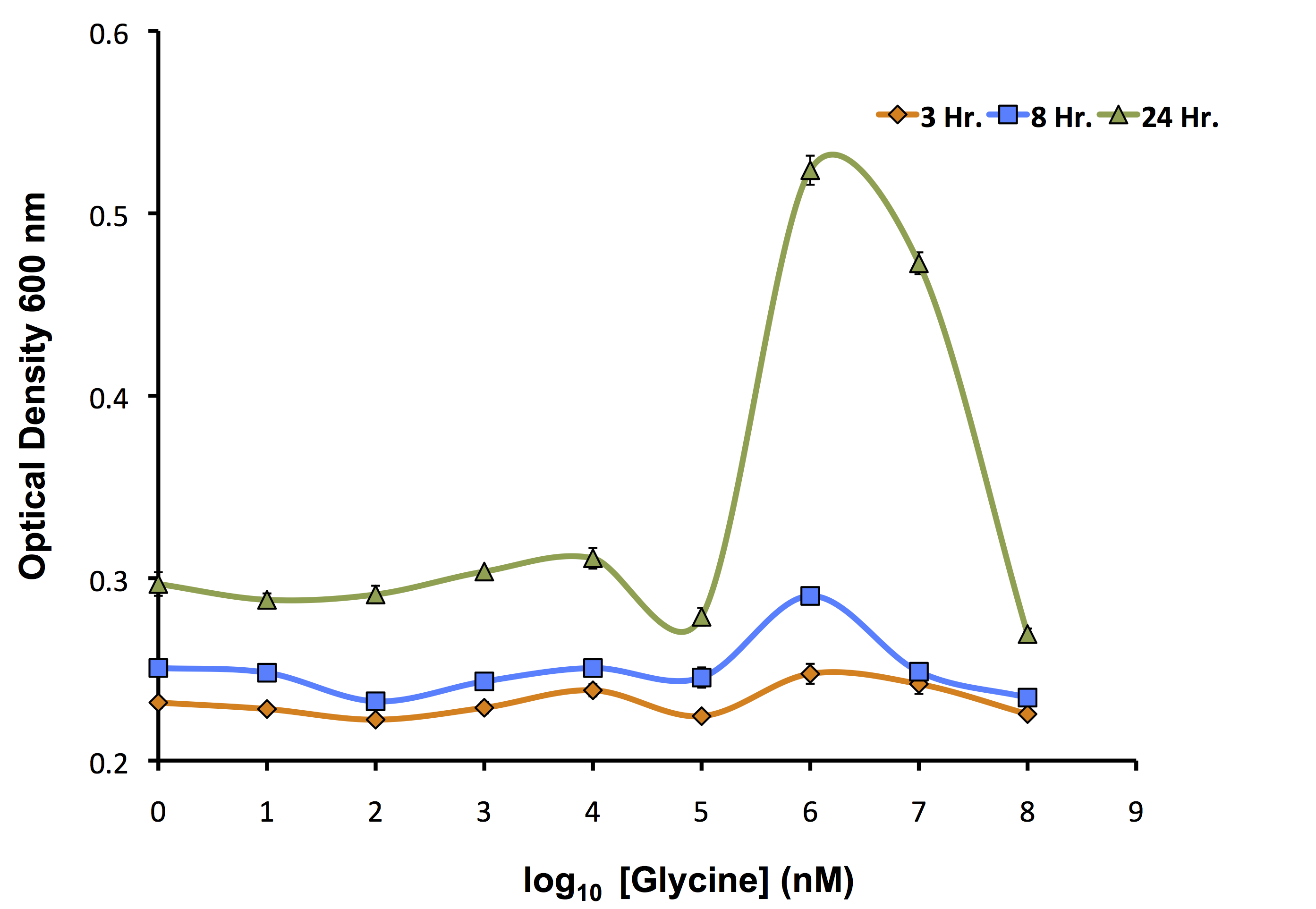
As identified by the growth assay, the glycine knockout is not capable of completely preventing growth of the strain even at very low concentrations of glycine. This identifies that it is important to continue to use our kill switch mechanism in combination with the auxotroph to control the cells. Now, with the concentrations ideal for glycine growth determined, we transformed our rhamnose inducible killswitch construct containing S7 (BBa_K902084) into our glycine knockout strain and attempted to characterize cell death over a variety of conditions.
Testing the Auxotrophic Marker as a Kill Switch
To test if using the glyA knockout strain in conjunction with our kill switch was effective, we transformed our Prha-S7 construct into the knockout strain as shown in Figure 2.
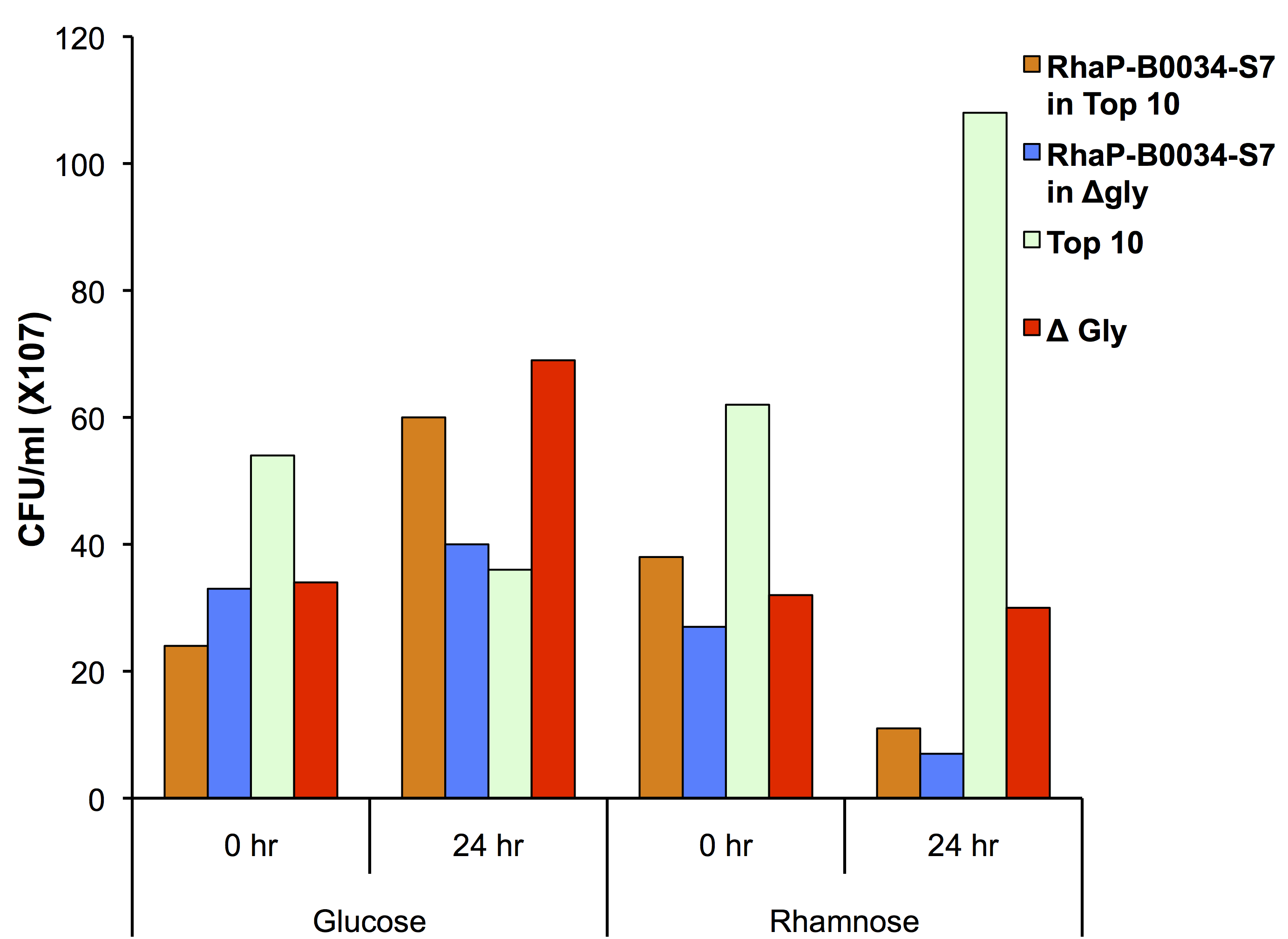
This data suggests that our killswitch system can act synergistically with the glycine auxotroph. In the prescence of glucose you see growth of both TOP10 and glyA knockout cells showing that our system is repressed. There is less growth in our glycine knockout as there was not a significant amount of glycine used in the media. The TOP10 control cell line did not show growth over 24 hours which was likely due to error in the read. In the presence of rhamnose, the kill switch is capable of being induced in both TOP10 and glycine knockout strains as shown by the decrease in CFU counts. This demonstrates a functional kill switch mechanism with the Prha promoter and auxotroph.
Putting FRED together
Can we sense toxins?
Now that we’ve been able to show that we can indeed sense three compounds electrochemically and simultaneously using our hydrolase system, and characterized genetic circuits for two of these outputs, our next goal was to actually try to sense toxins. Despite the fact that we have encountered significant difficulty in trying to sequence our transposon clones, given that we designed our transposon library to use lacZ, we could actually use our transposon directly in our electrochemical reporter system without actually knowing the identity of the sensory element. Although we do plan to BioBrick this in the future, for now, we grew up cultures of our transposon and tested the ability of our FRED system to sense toxins. We didn't just want to sense toxins however, we wanted to be able to sense toxins in tailings ponds. To do this, we grew up our transposon clone in media, aspirated the media and then placed it in tailings pond water samples. Upon addition of our sugar-reporter conjugate, CPRG, we monitored the formation of CPR electrochemically, which would be indicative of LacZ production, indicating activity of our toxin sensory element. The results of this assay can be shown below.
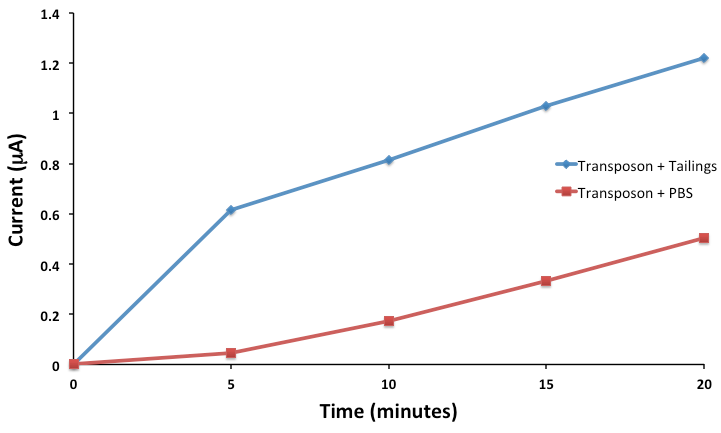
This result was extremely exciting for us, as we see clear induction of the system in the presence of tailings, as compared to the control. Although we don't know exactly what we are sensing, (remember that our transposon is sensitive to 3 different toxins: DBT, Carbazole and NAs),we are definitely sensing something! This shows that FRED is functional and more than that, FRED is functional in the application for which he was designed! The next step will be to quantify toxins present in tailings pond water samples in order to calibrate our reporter.
Taking FRED out to the field!
Once we knew that we had a promoter/reporter system that could actually detect toxins found in tailings ponds within the laboratory, the next challenge was to detect tailings pond toxins with our FRED prototype on site. Unfortunately, there are very strict regulations surrounding tailings ponds, and the publication of information pertaining to their contents. As such, obtaining permissions for a tailing pond field test was not possible within the time frame of our project. Because we did want to perform a kind of field test with FRED to show that the prototype that we built is feasible and easy to use, we investigated whether it would be permissable or advisable to try FRED outside of the lab. We performed a literature search to look for any regulations that might exist. Nothing pertaining to our province could be found, so we looked to Ontario and the United States. The concise guide to U.S. federal guidelines, rules and regulations for synthetic biology outlined the rules pertaining to field tests and indicated that in cases where organisms are going to be released into the environment, the EPA (environmental protection agency) requires a TSCA (Toxic Substances Control Act) Experimental Release Application (TERA) to be completed 60 days before the trial begins and the APHIS (Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service) requires a permit or notification. Although we specifically designed FRED to not release the microbes but rather to contain them, the prototype is too much in its infancy to remove it from the lab and be absolutely assured that it won’t be released. What we did instead, was took our prototype without bacteria in it to collect a water sample in a nearby river in Calgary. The video of this experience can be found below.
Putting our Killswitch into OSCAR - Can we use our Auxotroph with the Petrobrick?
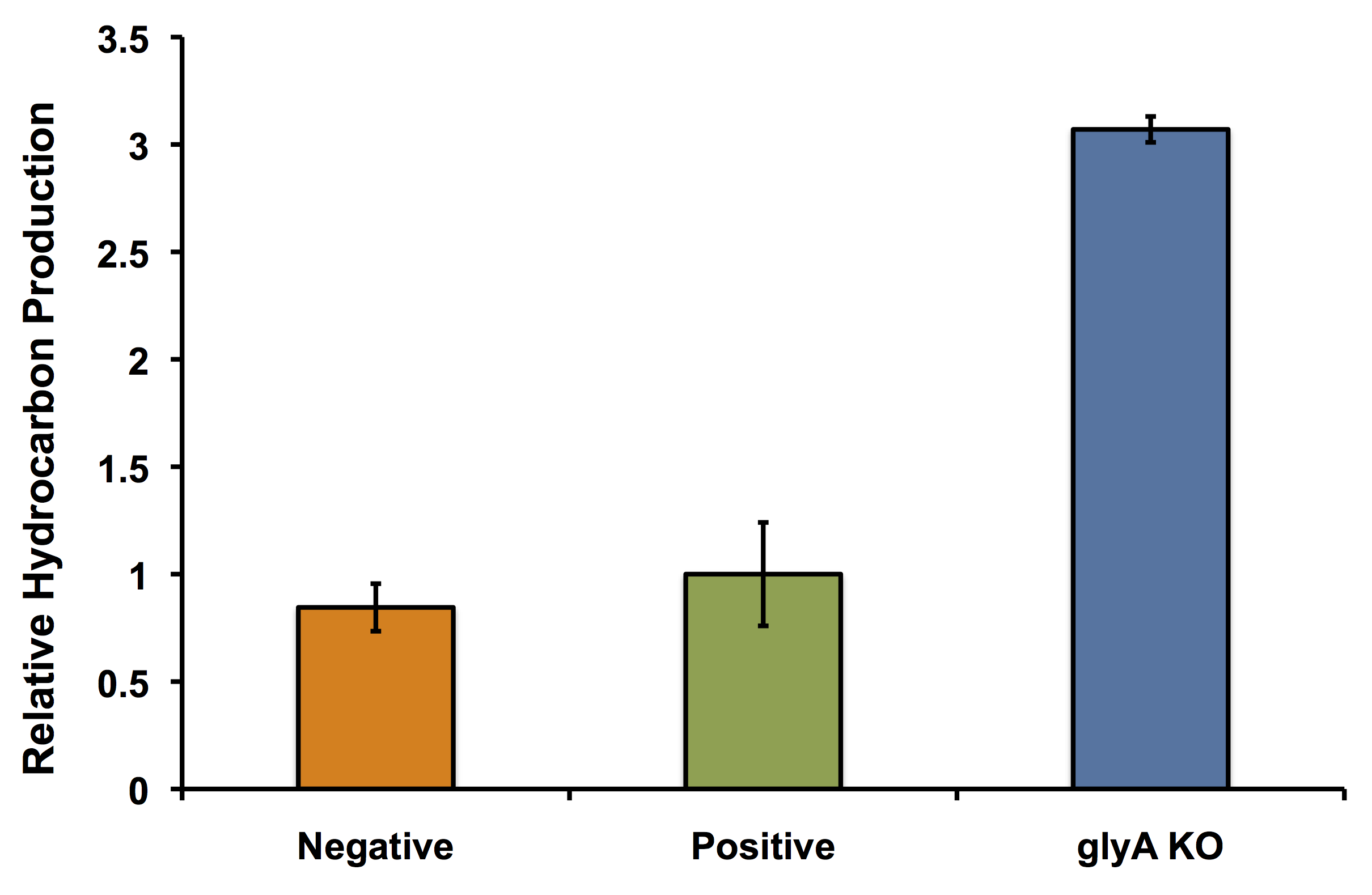
In fact it's better! The glycine auxotroph will be used as a second layer of regulation with our kill switch in the event that our bacterium is capable of escaping the bioreactor. However in order to ensure that the glycine knockout we are using does not compromise the production of hydrocarbons and we can continue to see the high yield of hydrocarbons as predicted with our flux balance modelling, we performed an experiment to look at the relative amount of hydrocarbon production as in the flux balance analysis model. As seen in the figure below, using the glyA knockout greatly increased the output of hydrocarbons much higher than in the wild type E. coli strain. This was extremely exciting showing that our system could not only be safe, with a second layer of control for safety, and an increase in output.
Putting OSCAR into Action!
Once we had tested FRED and shown that we could use him to detect toxins in tailings samples we wanted to put OSCAR into action in his home the bioreactor. By the end of the summer, we had designed and built a lab scale prototype of our bioreactor system. However, to better understand the needs of the oil sands industry we approached Kelly Roberge, an oil sands consultant specializing in tailings ponds. Through speaking with Mr. Roberge, we were able to better understand the concerns that the oil sands industry has with the use and building synthetic biology systems to solve the challenges they face. In particular, Mr. Roberge had questions that surrounded the feasibility of scaling up our bioreactor to an industrial scale. As it turns out there are a number of considerations that should be made when moving from the lab scale to industrial scale. Particularly, because these transitions can be an imperfect when moving from the lab scale to industrial scale (>1000L tanks). Therefore we thought it would be important to test the feasibility of using our bioreactor, belt skimmer, and Petrobrick, to demonstrate we can produce and isolate hydrocarbons. These results are illustrated in the video below!
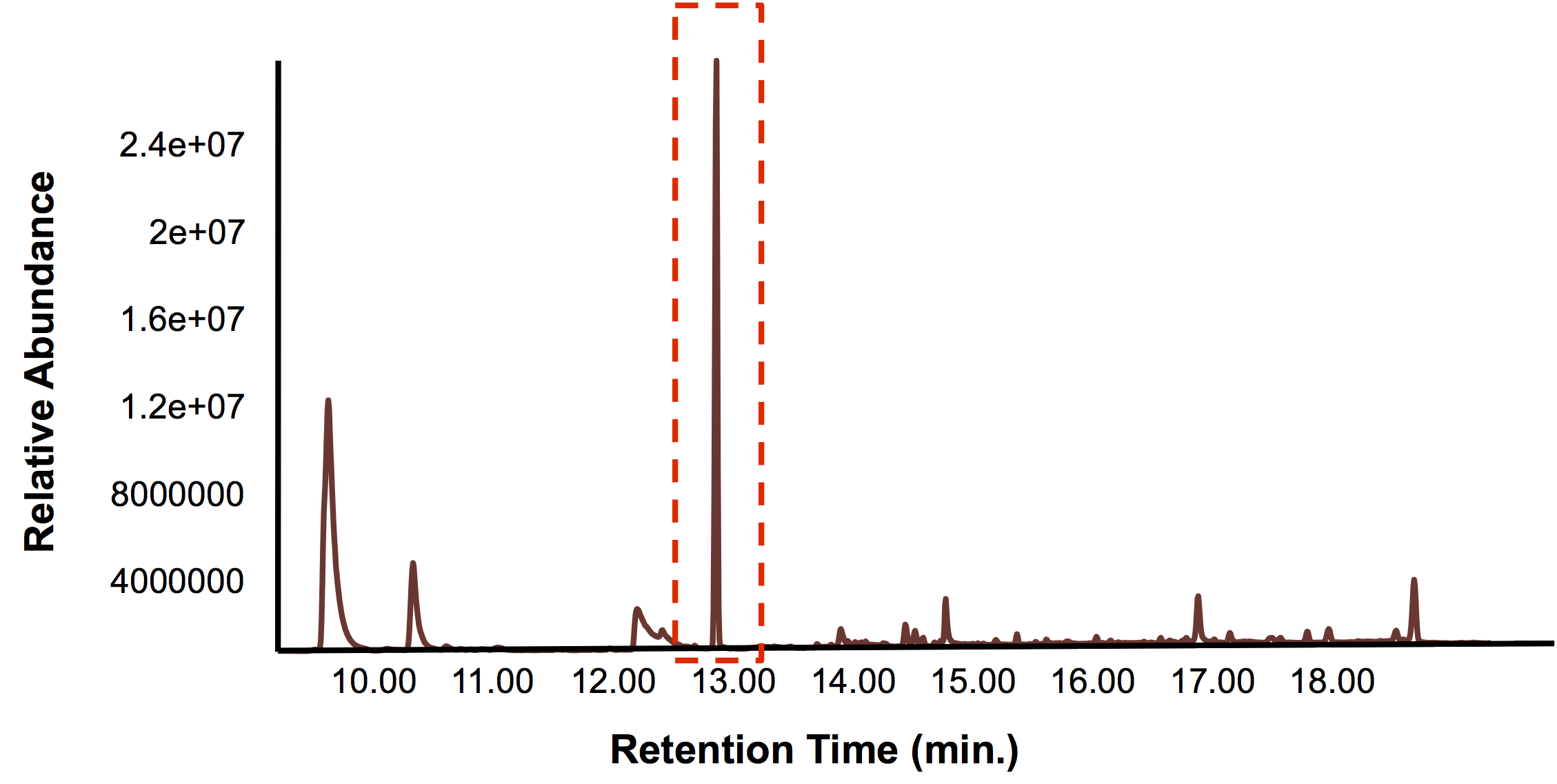
In short, the bioreactor was filled with 50:50 LB:Washington Production Media and we allowed the Petrobrick to grow over a 72 hour period. Afterwards, we demonstrated how our belt skimmer could be used for removal of the hydrocarbons. Because the hydrocarbons need to be extracted, we added ethyl acetate to allow for extraction, and demonstrated that our belt skimmer could selectively pick up the organic layer. Finally we ensured that this organic phase contained hydrocarbons by running this segment on the GC/MS as illustrated below.
With these experiments we have been able to demonstrate that both FRED and OSCAR are functional and can work on their respective applications even in the context of a large scale! By listening to professionals and bringing an informed design to our project we have been able to provide systems with real world applications. FRED can detect compounds in tailings ponds and we have been able to scale up and optimize OSCAR through our bioreactor and flux balance analysis work. Additionally, we have connected our projects together by providing a double kill switch system with both an auxotroph and inducible exonuclease system that increases the production of hydrocarbons in OSCAR! With these systems in place and a clear concept of the value of what our project has to offer, we look forward to seeing what the future holds for FRED and OSCAR!
 "
"