Team:Valencia Biocampus/Achievements
From 2012.igem.org
Cristina VS (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
[[Image:Achievements_vlc.png|700 px||center]] | [[Image:Achievements_vlc.png|700 px||center]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | We have successfully talked to microorganisms. Our dialogues with yeast are still in progress, but they already talk to us when they are hungry (fluorescence is emitted when there is no glucose in the medium). Moreover, we achieved true dialogues with <i>E. coli</i>. All our biobricks worked as expected in <i>E. coli</i>, and allowed it to answer the following questions: <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Valencia_Biocampus/Results1#ARE_YOU_HOT?"><b>“Are you hot?”</b></a></html> (thermal shock sensitivity); <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Valencia_Biocampus/Results1#ARE_YOU_HUNGRY?"><b>“Are you hungry?”</b></a></html> (glucose); <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Valencia_Biocampus/Results1#DO_YOU_HAVE_ENOUGH_NITROGEN?"><b>“Do you have enough nitrogen?”</b></a></html>; and <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Valencia_Biocampus/Results1#CAN_YOU_BREATHE?"><b>“Can you breathe?”</b></a></html>. We did so by encoding the questions into light wavelenghths that excite reporter proteins, which were cloned under the control of environment-sensitive promoters. Emitted light pulses were encoded back into the answers “I am cool”, “I am hungry”, etc. We could even make <i>E. coli</i> obey our orders by encoding the <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Valencia_Biocampus/Results1#EXPRESS_YOUR_GENE!"><b>“Express your gene”</b></a></html> sentence into a promoter-activation wavelenghth. | + | <b>We have successfully talked to microorganisms. Our dialogues with yeast are still in progress, but they already talk to us when they are hungry (fluorescence is emitted when there is no glucose in the medium). Moreover, <b>we achieved true dialogues</b> with <i>E. coli</i>. All <b>our biobricks worked as expected</b> in <i>E. coli</i>, and allowed it to answer the following questions: <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Valencia_Biocampus/Results1#ARE_YOU_HOT?"><b>“Are you hot?”</b></a></html> (thermal shock sensitivity); <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Valencia_Biocampus/Results1#ARE_YOU_HUNGRY?"><b>“Are you hungry?”</b></a></html> (glucose); <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Valencia_Biocampus/Results1#DO_YOU_HAVE_ENOUGH_NITROGEN?"><b>“Do you have enough nitrogen?”</b></a></html>; and <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Valencia_Biocampus/Results1#CAN_YOU_BREATHE?"><b>“Can you breathe?”</b></a></html>. We did so by encoding the questions into light wavelenghths that excite reporter proteins, which were cloned under the control of environment-sensitive promoters. Emitted light pulses were encoded back into the answers “I am cool”, “I am hungry”, etc. We could even make <i>E. coli</i> obey our orders by encoding the <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Valencia_Biocampus/Results1#EXPRESS_YOUR_GENE!"><b>“Express your gene”</b></a></html> sentence into a promoter-activation wavelenghth. |
| - | We submitted seven <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Valencia_Biocampus/Biobricks">biobricks</a></html> to the registry and fulfilled all other requirements listed at the judging form. Most of our constructions did also work on another bacterial species, <i>Citrobacter freundii</i>: We collaborated with the <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Edinburgh">Edimburg iGEM team</a></html> sending them our bacterial biobricks (BBa_K763000, BBa_K763001, BBa_K763002, BBa_K763003 & BBa_K763004). They have tested them and the results obtained are collected in <html><a href="https://docs.google.com/document/d/1VykqxS47mSIi9IAc_yiWsosNOt7zBnoxPOEItSdaCTU/edit">this</a></html> link. | + | We submitted <b>seven <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Valencia_Biocampus/Biobricks">biobricks</a></html></b> to the registry and fulfilled all other requirements listed at the judging form. Most of our constructions did also work on another bacterial species, <i>Citrobacter freundii</i>: We <b>collaborated with the <html><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Edinburgh">Edimburg iGEM team</a></html></b> sending them our bacterial biobricks (BBa_K763000, BBa_K763001, BBa_K763002, BBa_K763003 & BBa_K763004). They have tested them and the results obtained are collected in <html><a href="https://docs.google.com/document/d/1VykqxS47mSIi9IAc_yiWsosNOt7zBnoxPOEItSdaCTU/edit">this</a></html> link. |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
== '''Had we to highlight one feature of Talking Life…''' == | == '''Had we to highlight one feature of Talking Life…''' == | ||
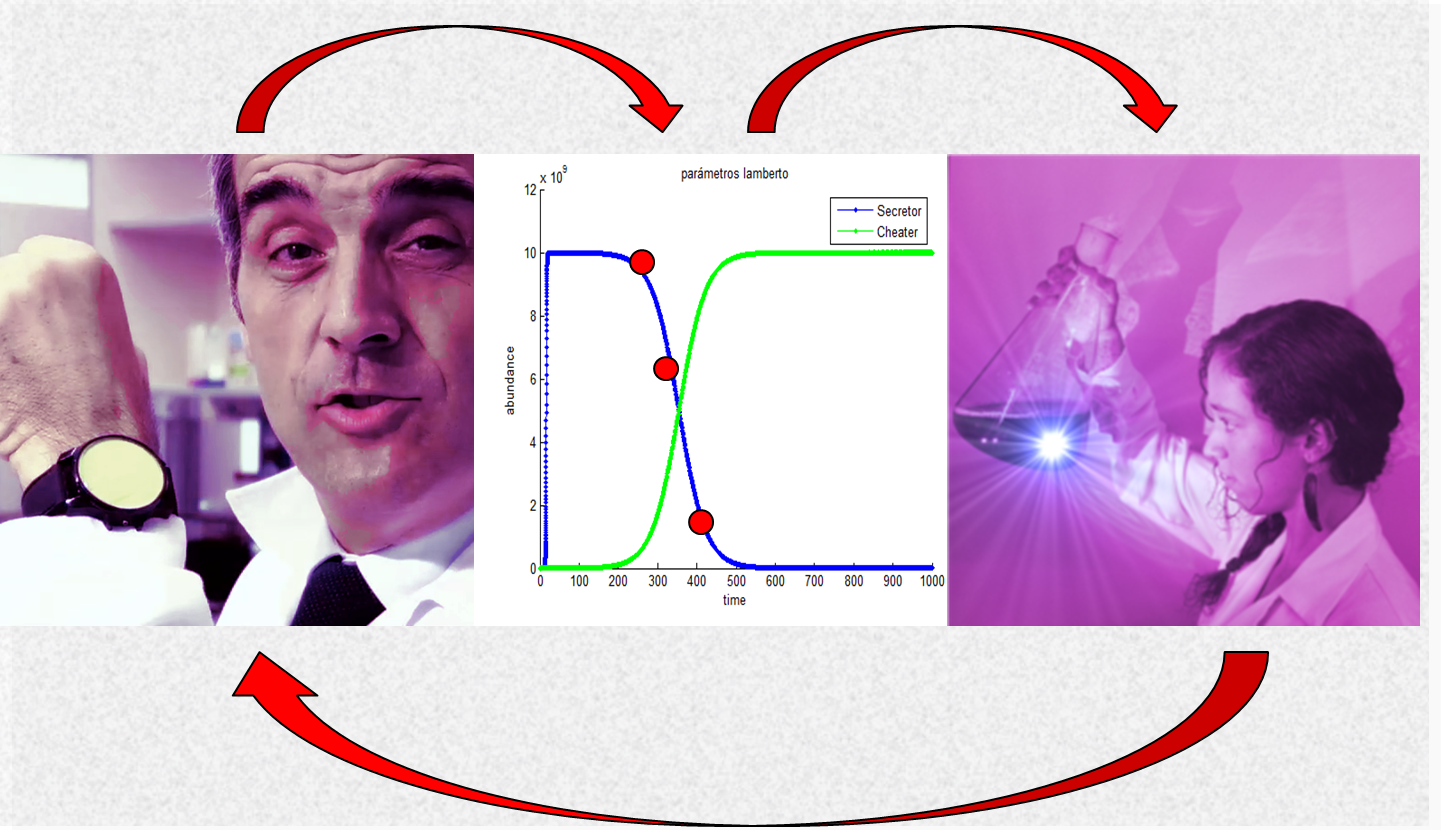
| - | …it would be its holistic nature. In our project, there was a constant flow between dry- and wetlabs, modeling and Human Practices sub-teams. For Human Practices, we shot a short film to show to several audiences and analyze their opinion on ethical subjects and we forecasted the risk of cheater mutants. We carefully modeled such risk and finally end up by discovering that mutant cheaters were in fact among our cultures! We characterized such mutants, performed adaptive evolution tests and found them to behave as expected/modeled/feared: mutants actually display an evolutionary advantage on “honest”, heterologous protein-expressing clones. The consequences of all this were already anticipated in the script of our movie, one of the first things we attempted in this challenging project, and maybe the best way to close it: | + | …it would be its <b>holistic</b> nature. In our project, there was a </b>constant flow between dry- and wetlabs, modeling and Human Practices</b> sub-teams. For Human Practices, we shot a short film to show to several audiences and analyze their opinion on ethical subjects and we forecasted the risk of cheater mutants. We carefully modeled such risk and finally end up by discovering that mutant cheaters were in fact among our cultures! We characterized such mutants, performed adaptive evolution tests and found them to behave as expected/modeled/feared: mutants actually display an evolutionary advantage on “honest”, heterologous protein-expressing clones. The consequences of all this were already anticipated in the script of our movie, one of the first things we attempted in this challenging project, and maybe the best way to close it: |
Revision as of 19:00, 24 September 2012

Achievements
We have successfully talked to microorganisms. Our dialogues with yeast are still in progress, but they already talk to us when they are hungry (fluorescence is emitted when there is no glucose in the medium). Moreover, <b>we achieved true dialogues with E. coli. All our biobricks worked as expected in E. coli, and allowed it to answer the following questions: “Are you hot?” (thermal shock sensitivity); “Are you hungry?” (glucose); “Do you have enough nitrogen?”; and “Can you breathe?”. We did so by encoding the questions into light wavelenghths that excite reporter proteins, which were cloned under the control of environment-sensitive promoters. Emitted light pulses were encoded back into the answers “I am cool”, “I am hungry”, etc. We could even make E. coli obey our orders by encoding the “Express your gene” sentence into a promoter-activation wavelenghth.
We submitted seven biobricks to the registry and fulfilled all other requirements listed at the judging form. Most of our constructions did also work on another bacterial species, Citrobacter freundii: We collaborated with the Edimburg iGEM team sending them our bacterial biobricks (BBa_K763000, BBa_K763001, BBa_K763002, BBa_K763003 & BBa_K763004). They have tested them and the results obtained are collected in this link.
Had we to highlight one feature of Talking Life…
…it would be its holistic nature. In our project, there was a </b>constant flow between dry- and wetlabs, modeling and Human Practices</b> sub-teams. For Human Practices, we shot a short film to show to several audiences and analyze their opinion on ethical subjects and we forecasted the risk of cheater mutants. We carefully modeled such risk and finally end up by discovering that mutant cheaters were in fact among our cultures! We characterized such mutants, performed adaptive evolution tests and found them to behave as expected/modeled/feared: mutants actually display an evolutionary advantage on “honest”, heterologous protein-expressing clones. The consequences of all this were already anticipated in the script of our movie, one of the first things we attempted in this challenging project, and maybe the best way to close it:
 "
"