Team:University College London/LabBook/Week16
From 2012.igem.org



Monday (24.09.12)
1. Prepare 11-16 plates (DNAse - Agar + CMP)
2. Streak cells onto all plates at the same time
3. Incubate at 37°C
4. Apply HCl to the first plate before putting in the incubator (set time as zero)
5. Take a second reading after four hours, followed by six readings every 3 hours, and a final three readings every two hours.
6. When the reading is taken, observe the following: a. Diameter of the colony (once the diameter of the colony is measured, pick the colony and put it to grow in LB for nine hours) b. Diameter of the halo that is achieved once HCL is applied c. OD from a) d. Estimate of the depth of the colony on the agar plate
| Sample/time | Colony diameter/mm | Halo diameter/mm | Absorbance at 600 OD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (12.30 noon) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 (16.30pm) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 (19.30 pm) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 (22.30 pm) | 0.5 | 1 | 0.002 |
| 5 (01.30 am) | 1 | 3.5 | 0.182 |
| 6 (04.30 am) | 1.5 | 7 | 0.238 |
| 7 (07.30 am) | 2 | 9 | 0.297 |
| 8 (10.30am) | 2.5 | 11 | 0.518 |
| 9 (12.30noon) | 3 | 12.5 | 0.701 |
| 10 (2.30pm) | 3.5 | 14 | 0.811 |
| 11(4.30pm) | 4 | 15 | 0.906 |
 " />
" /></html>
Monday (24.09.12)
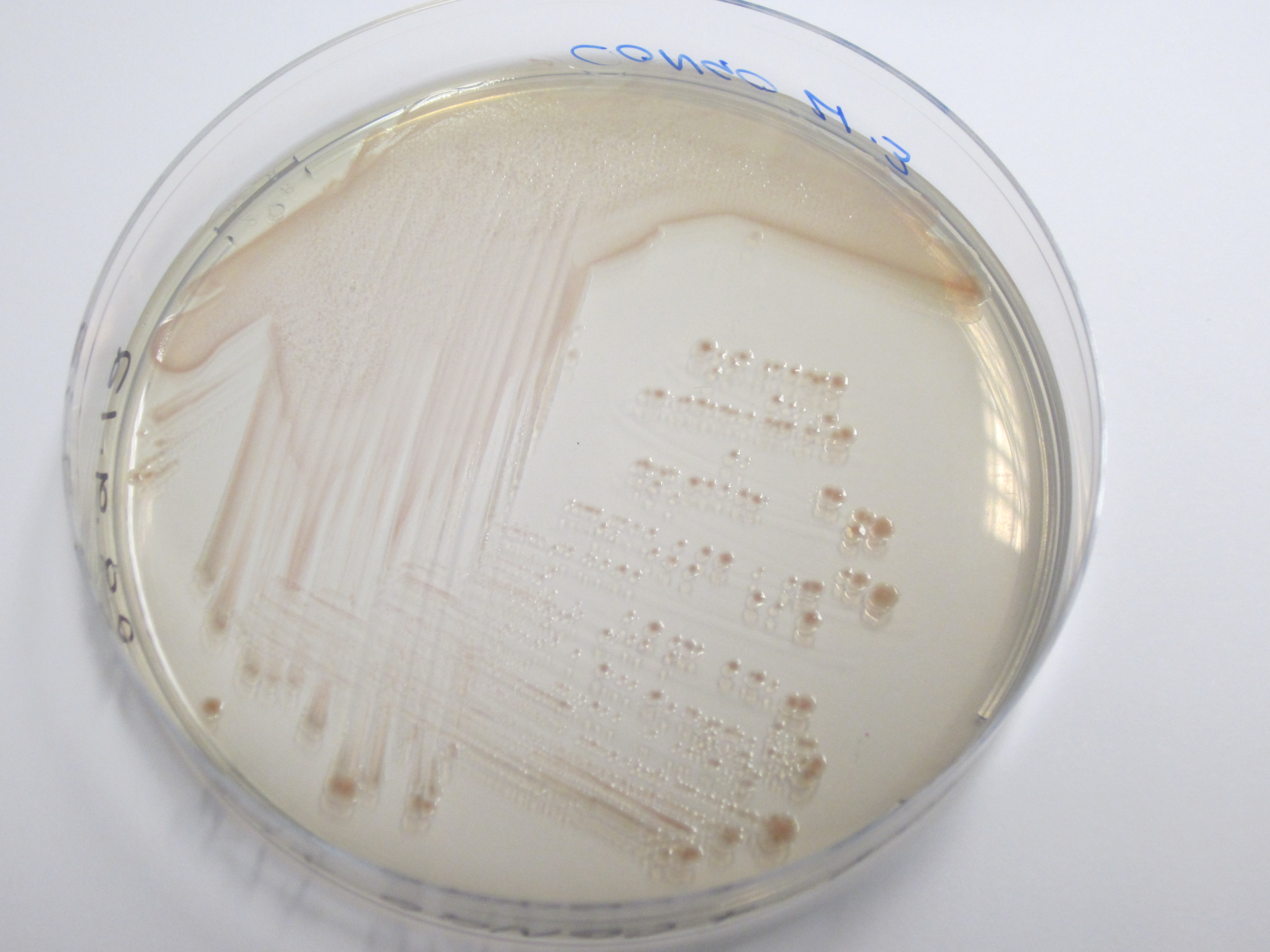
Congo red binding assay, Preparation of Congo red supplemented agar:
20uL.ml-1 Congo Red Dye 10ug.ml-1 Coomassie brilliant blue dye G-250 LB Agar (No salt)
Plates subsequently streaked. Uptake of red pigment indicative of amyloid fiber expression.
Results: First photo represents control which is W3110 that does not have curli cluster insert. Second represents BL21 strain that has T7 + curli cluster. As we can see from the photos above the control sample does not obtain red colour.
| Control | BBa_K729017 |
|---|---|
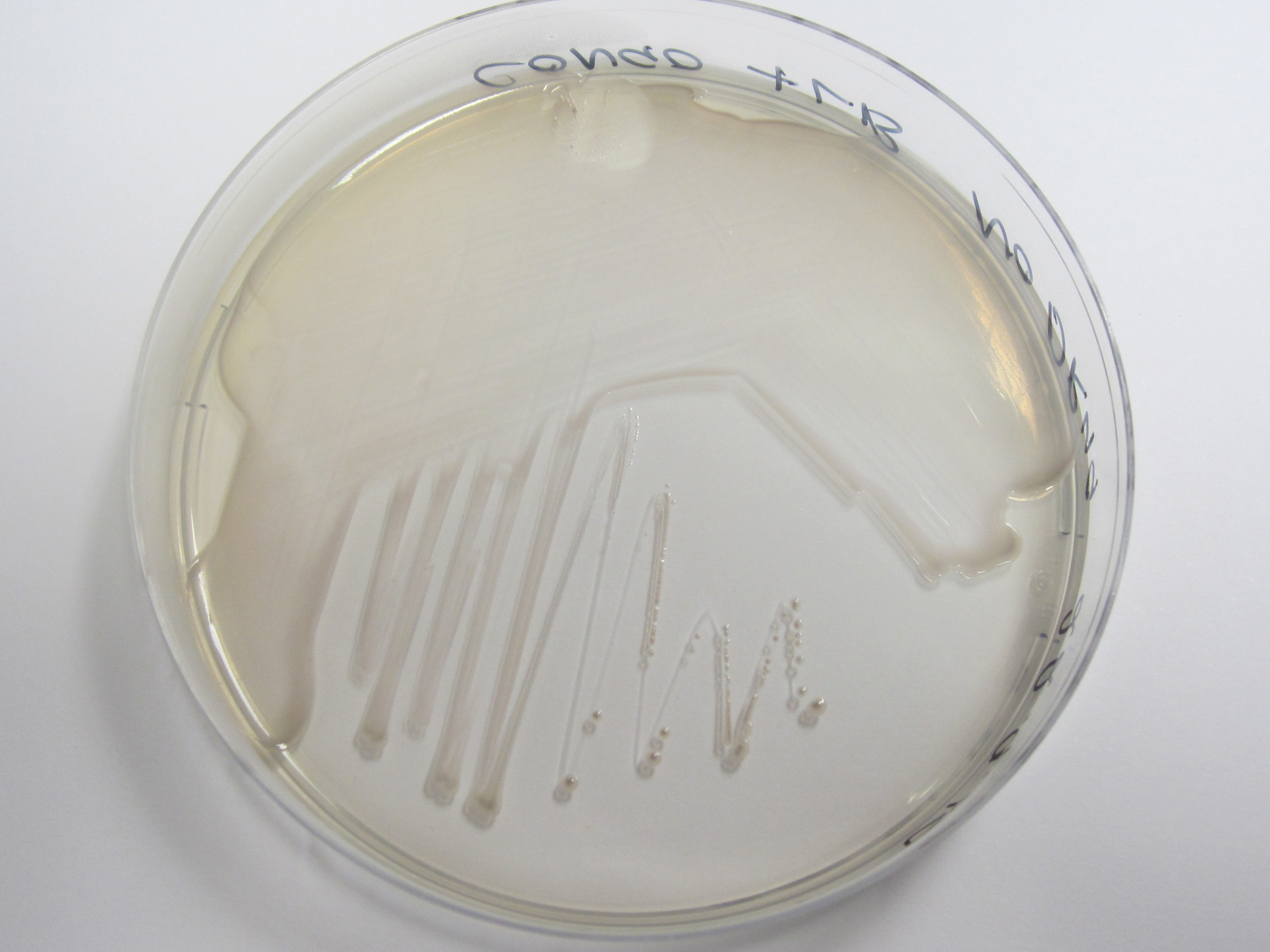 | 
|
Conclusion: We can conclude that our ligation T7+curli worked, and our cells are expressing curli fibrils.

Wednesday (26.09.12)
Aim – We would like to determine if our curli producing BBa_K729018 is capable of producing shear resistant biofilms.
1) Cells are grown overnight in 10ml of LB media at 37˚C, 200rpm.
- a) BBa_K729006
- b) W3110 Control
2) Shake flasks are inoculated with 5 ml of cells into LB media (100ml)
- a) Shake flasks contain pre-sterilised polycarbonate discs
3) Shake flasks are run at 37˚C, 200rpm, for 7 hours.
4) Shake flasks are run at 30˚C, 50rpm, for 14 hours.
5) PC discs are removed from flasks, dried, and stained with crystal violet.
6) Discs are sheared with the small scale shear device, using water as the buffer. Rotaion speed varies from 50rpm to 700rpm.
7) Critical shear radius is measured from diameter of shear resistant area.
Conclusion - Our transformed cells are producing shear resistant biofilm, with double the shear resistance of untransformed biofilms, indicating that our BioBrick is working as intended and is capable of producing shear resistant curliated biofilms.
 "
"