Team:University College London/LabBook/Week7
From 2012.igem.org



Contents |
Monday (23.7.12)
Aim - Picking colonies: On Friday 20.7.12 we found that the transformation for BBa_J23119, BBa_1750016, BBa_B0015, and BBa_B0034 all produced colonies and were suitable for colony picking.
Step 2 - Inoculating Colonies into a Selective Broth:: Add Yul of antibiotic to reach desired antibiotic concentration.
(For Ampicillin this is 50ug/ml, For Kanamycin it is 25ug/ml, for Tetracycline it is 15ug/ml, and for Chloramphenicol it is 25ug/ml)
Step 4 – Selecting a Colony: Select a clear, isolated colony and using an inoculation hoop scoop up a colony onto the tip. Deposit in the falcon tube
Step 5 - Culture: Culture your falcon tubes overnight at a temperature of 37 oC. Leave for no longer than 16 hours.
Step 2 – Inoculating Colonies into a Selective Broth: The table below indicates the volume of broth and the concentration of antibiotic required for each BioBrick.
| Samples | Volume Inoculated | Broth (ml) | Antibiotic (ug/ml) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioBrick | BBa_J23119 | 10ul | Lysogeny Broth (5) | Ampicillin(50ug/ml) |
| 90ul | ||||
| BBa_I750016 | 10ul | |||
| 90ul | ||||
| BBa_B0015 | 10ul | |||
| 90ul | ||||
| BBa_B0034 | 10ul | |||
| 90ul | ||||
Tuesday 24.7.12
Aim – Results from Colony Picking
Results: The table below indicates whether there was growth for the BioBricks
| Samples | Volume Inoculated | Growth | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioBrick | BBa_J23119 | 10μl | Yes |
| 90μl | Yes | ||
| BBa_I750016 | 10μl | No | |
| 90μl | No | ||
| BBa_B0015 | 10μl | Yes | |
| 90μl | Yes | ||
| BBa_B0034 | 10μl | No | |
| 90μl | No | ||
Conclusion: We concluded that the failure of BBa_I750016 and BBa_B0034 is not necessarily due to failed transformation, as there was an unusual degree difficulty Picking the colonies 23.7.12. From this, it is possible that colonies were not properly inoculated, and so this requires a repeat. BBa_J23119 and BBa_B0015 however appeared sufficient for the protocol to be continued
Miniprep of Samples
(LOGO) Miniprep Protocol ?
The above protocol was done only for J23119 and B0015 – three stocks of each, originating from each of the three replicate falcon tubes
Restriction Digest and Gel Electrophoresis of Samples
Step 1 - Thawing cells: Thaw all materials on ice
Step 2 - Adding Ingredient: Add the following ingredients to autoclaved/sterile eppendorf tubes
| Component | Amount (ul) (one enzyme used) | Amount (ul) (two enzymes used) |
|---|---|---|
| dH20 | 2.5 | 1.5 |
| Buffer 1x | 1 | 1 |
| DNA template | 5 | 5 |
| BSA | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Enzyme 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Enzyme 2 | N/A | 1 |
Step 3 - Addition of BioBrick: Flick contents gently and centrifuge.
Step 4 - Centrifuge:
RPM: 14000
Time: 1 minute
Temperature: 18oC
Step 5 - Digest Program: Place the samples on a thermocycler under the following conditions:
RPM: 550
Time: 2.5 hours
Temperature: 37oC
Step 6 - Denaturing Enzymes: If you are not running the samples on a gel immediately, denature the restriction enzymes by running the samples on a thermocycler under the following conditions:
RPM: 550
Time: 25 minutes
Temperature: 65oC
Step 2: Set up Reaction 1(Plasmid) and Reaction 2 (Control) for both the miniprepped BioBricks.
| Samples | Recipe | Enzymes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioBrick | BBa_J23119 | Digested Plasmid | Xba1 & Spe1 |
| Undigested Plasmid (Control) | None | ||
| BBa_B0015 | Digested Plasmid | Xba1 & Spe1 | |
| Undigested Plasmid (Control) | None | ||
Results: The gel demonstrated no bands for the plasmid and the uncut DNA, which would suggest that there is a low concentration of the plasmid. Therefore we undertook a Nanodrop of the sample.
Software ND-1000 Model:
Step 1: Initialise the spectrophotometer by pipetting 1 µ of clean water onto lower optic surface, lowering the lever arm and selecting ‘initialise’ in the ND-1000 software
Step 2: Wipe and add elution buffer as negative control. Click blank in ND-1000 software
Step 3: Wipe and add 1 µl sample
Step 4: On the software set lambda to 260nm
Step 5: Lower the lever arm and click measure in ND-1000 software
Step 6: Take readings for concentration and purity
Step 7: Once measurement complete, wipe surface
Results
| BioBrick | λ260 | λ 280 |
|---|---|---|
| BBa_J23119 (ng/μl) | 24.8 | 26.1 |
| BBa_B0015 (ng/μl) | 41.7 | 56.6 |
Conclusion: The concentration of these plasmids is very low

Monday 23.7.12
Aim - Transformation of TetR BBa_C0040 BioBrick
Step 1 - Thawing Cells: Thaw competent cells on ice.
Step 2 - Adding cells: Add 50 µL of thawed competent cells into pre-chilled 2ml tube.
Step 3 - Addition of BioBrick: Add 1 - 2 µL of the resuspended DNA to the 2ml tube. Pipette up and down a few times, gently. Make sure to keep the competent cells on ice.
Step 4 - Incubation: Close tube and incubate the cells on ice for 30 minutes.
Step 5 - Heat Shock: Heat shock the cells by immersion in a pre-heated water bath at 42ºC for 60 seconds.
Step 6 - Incubation: Incubate the cells on ice for 5 minutes.
Step 7 - Add media: Add 200 μl of SOC media or LB broth
Step 8 - Incubation: Incubate the cells at 37ºC for 2 hours while the tubes are rotating or shaking.
Step 9 - Label plates: Label two petri dishes with LB agar and the appropriate antibiotic(s) with the part number, plasmid backbone, and antibiotic resistance. Plate 20 µl and 200 µl of the transformation onto the dishes, and spread. This helps ensure that you will be able to pick out a single colony.
Step 10 - Culture:Incubate the plate at 37ºC for 12-14 hours, making sure the agar side of the plate is up. If incubated for too long the antibiotics start to break down and un-transformed cells will begin to grow. This is especially true for ampicillin - because the resistance enzyme is excreted by the bacteria, and inactivates the antibiotic outside of the bacteria.
Step 11 - Colony Picking: You can pick a single colony, make a glycerol stock, grow up a cell culture and miniprep.
Step 1 – Thawing Cells: Use W3100 cell line created in Week 2 (Expt 2.1)
Step 3 – Addition of BioBrick: To a 2ml eppendorf, add 1ul of the following BioBricks. Note: we have changed the protocol for our positive control. Previously it contained no BioBrick, but it has been recommended to us that we transform our positive control such that there is one for each BioBrick – this will tell us if the BioBrick has in any way affected cell viability. This will be used from this point onwards. Include an extra tube as a negative control, with no BioBrick added
| Samples | Function | Module | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioBrick | BBa_C0040 | Tetracycline Repressor | Buoyancy |
| Control | Positive (Contains BioBrick BBa_C0040) | ||
| Negative (No Biobrick) | |||
Step 9 - Plating samples on Agar Plates: The table below indicates the chosen inoculation volume (two for each BioBrick) and the correct gel antibiotic concentration for all samples.
| Samples | Volume Inoculated | Antibiotic in Gel (μg/ml) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioBrick | BBa_C0040 | 10μl | Ampicillin(50ug/ml) |
| 90μl | |||
| Control | Positive (Contains BioBrick BBa_C0040) | 36μl | No Antibiotic |
| Negative (No BioBrick) | 36μl | 2x Ampicillin(50μg/ml) | |
Tuesday 24.7.12
Aim - Results of Transformation
Result: The table below indicates that there was growth for this transformation.
| Samples | Volume Inoculated | Colony Formation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioBrick | BBa_C0040 | 10ul | Yes |
| 90ul | Yes | ||
| Control | Positive (Contains BioBrick BBa_C0040) | 36ul | Yes |
| Negative (No BioBrick) | 36ul | No | |

Monday 23.7.12
Aim - Repeat Restriction Digest for BioBricks in Expt 4.1 and 5.1, where the gel previously was inconclusive: This is intended to diagnose whether the correct plasmid had been transformed into our bacteria, by measuring the size of the digested products against a DNA ladder. In previous gel attempts, K540000 has produced a band of the correct size, but we are repeating it because of the presence of other unexpected bands, which we expect are contaminants from the reaction. A previous restriction digest of BBa_I13522 has failed to produce a band of the correct size, so we are repeating the digest before considering another transformation. For the same reason, we are repeating the digest of BBaK398108, which produced bands of incorrect size, which is suggestive of contamination.
Step 1 - Thawing cells: Thaw all materials on ice
Step 2 - Adding Ingredient: Add the following ingredients to autoclaved/sterile eppendorf tubes
| Component | Amount (ul) (one enzyme used) | Amount (ul) (two enzymes used) |
|---|---|---|
| dH20 | 2.5 | 1.5 |
| Buffer 1x | 1 | 1 |
| DNA template | 5 | 5 |
| BSA | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Enzyme 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Enzyme 2 | N/A | 1 |
Step 3 - Addition of BioBrick: Flick contents gently and centrifuge.
Step 4 - Centrifuge:
RPM: 14000
Time: 1 minute
Temperature: 18oC
Step 5 - Digest Program: Place the samples on a thermocycler under the following conditions:
RPM: 550
Time: 2.5 hours
Temperature: 37oC
Step 6 - Denaturing Enzymes: If you are not running the samples on a gel immediately, denature the restriction enzymes by running the samples on a thermocycler under the following conditions:
RPM: 550
Time: 25 minutes
Temperature: 65oC
Step 2: Set up as follows
| Samples | Recipe | Enzymes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioBricks | BBa_ K540000 (Expt 4.1) | Digested | Xbar 1 & Spe1 |
| BBa_ I13522 (Expt 4.1) | Digested | Xbar 1 & Spe1 | |
| BBa_ K398108 (Expt 5.1) | Digested | Xbar 1 & Spe1 | |
| BBa_ KI32003 (Expt 5.1) | Digested | Xbar 1 & Spe1 | |
Preparing the Gel
Step 1: Within a conical flask, add 3ml 50X TAE, 1.5g Agarose, and 150ml RO water
Step 2: Heat for 1 min in microwave. Swirl. Heat again for 30s. If solution is clear stop. Else repeat.
Step 3: Cool solution under running cold water.
Step 4: Add 20ul ethidium bromide (normal concentration of EB solution is 500ug/ul)
Step 5: Pour into a sealed casting tray in a slow steady stream, ensuring there are no bubbles
Running a gel
Step 6: Add 1 part loading buffer to five parts of loading sample
Step 7: Position the gel in the tank and add TAE buffer, enough to cover the gel by several mm
Step 8: Add 5ul of DNA ladder to lane 1
Step 9: Add samples to the remaining wells
Step 10: Run at 100 volts for 1hour and 15 minutes
Imaging the Gel
Step 11: Place gel in GelDoc 2000 chamber
Step 12: Turn GelDoc 2000 chamber on
Step 13: From computer: Quantity One > Scanner > Gel_Doc_Xr>Manuqal Acquire
Step 14: Alter the exposure/settings to give a clear image.
TAE - Tris-acetate-EDTA
EDTA - ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
Results: The image below shows a 1% Agarose Gel of an Analytical Restriction Enzyme Digest for Expt 7.2. Visible in Lane 1 is a product of the correct size for the BBa_K540000 insert (3123bp), as indicated by A. Also shown is a correct sized product for the backbone PSB1C3 (2070bp), as indicated by B. Lane 2 shows a product corresponding to the size of the BBa_I13522 insert (937bp) as indicated by C. Also present is a product corresponding to the size of the PSB1A3 backbone (2155bp) as indicated by D. Lane 3 has a product corresponding to the expected size of insert BBa_K398108 (844bp) as indicated by E, and a product of the expected size for the plasmid backbone PSB1C3 (2070bp) as indicated by F. Lane 4 shows no products, where we would expect a product of size 1849bp (indicated by G) and a product of 2155 (indicated by H).

Conclusion: Plasmids Bba_k540000 (3123), Bba_I13522 (937) and Bba_K391108 (844) have produced bands of the correct size. The band at 2000 is the plasmid backbone. The failure of Bba_K123003 to produce a band is not of great concern, as we do not expect we will require this BioBrick. However, we may repeat it at a later date.
Friday 3.8.12
Aim - Check results of Transformation: The table below indicates whether there was growth on the Agar Plates after Transformation. Included below are images of the Agar Plates for each BioBrick.
| Samples | Volume Inoculated | Colony Formation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioBrick | BBa_J23100 | 10ul | Yes |
| 90ul | Yes | ||
| BioBrick | BBa_J23106 | 10ul | Yes |
| 90ul | Yes | ||
| BioBrick | BBa_B0030 | 10ul | Yes |
| 90ul | Yes | ||
| BioBrick | BBa_I750016 | 10ul | Yes |
| 90ul | Yes | ||
| Control | Positive | 36ul | Yes |
| Negative (No BioBrick) | 36ul | Yes | |
Conclusion:

Tuesday 24.7.12
Aim - Colony Picking from unsuccessful colonies for Expt 7.1 and 6.3
Step 2 - Inoculating Colonies into a Selective Broth:: Add Yul of antibiotic to reach desired antibiotic concentration.
(For Ampicillin this is 50ug/ml, For Kanamycin it is 25ug/ml, for Tetracycline it is 15ug/ml, and for Chloramphenicol it is 25ug/ml)
Step 4 – Selecting a Colony: Select a clear, isolated colony and using an inoculation hoop scoop up a colony onto the tip. Deposit in the falcon tube
Step 5 - Culture: Culture your falcon tubes overnight at a temperature of 37 oC. Leave for no longer than 16 hours.
Step 2 – Inoculating Colonies into a Selective Broth: The table below indicates the volume of broth and the concentration of antibiotic required for each BioBrick.
| Samples | Number of Falcons | Broth | Antibiotic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biobrick | BBa_C0040 | 3 | Lysogeny Broth (5ml) | Ampicillin(50ug/ml) |
| BBa_I750016 | 4 | |||
| BBa_B0034 | 5 | |||
| BBa_B0015 | 3 | |||
| BBa_J23119 | 2 | |||
Wednesday 23.7.12
Aim - Results from Colony Picking
Results:
| Samples | Number of Falcons | Growth | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioBrick | BBa_C0040 | 3 | None |
| BBa_I750016 | 4 | None | |
| BBa_B0034 | 5 | Growth in one | |
| BBa_B0015 | 3 | Growth | |
| BBa_J23119 | 2 | Growth | |
Conclusion: We are beginning to consider other possibilities for the failure of Colony Picking in Expt 7.1 and Expt 6.3. Foremost, we believe it may be due to the addition of Ampicillin to the Agar before it has cooled sufficiently, leading to degradation of the antibiotic. This would reduce the selective pressure, and allow growth of colonies that are not Ampicillin-resistant. Subsequent inoculation into Amipicillin positive LB broth leads to failed growth. Those BioBricks that have worked will undergo Miniprep, Restriction Enzyme Digests and Nanodrop.
Method
Miniprep:
Step 2 - Resuspend Cells: Resuspend pelleted bacterial cells in 250ul Buffer P1 and transfer to a microcentrifuge tube
Step 3 - Puncturing Cell Membrane: Add 250ul Buffer P2 and mix thoroughly by inverting the tube 4-6 times until the solution becomes clear. Do not allow the lysis reaction to proceed for more than 5 min.
Step 4 - Neutralising buffer P2: Add 350ul Buffer N3 and mix immediately and thoroughly by inverting the tube 4-6 times.
Step 5 - Centrifuge:
RPM: 13000
Time:10 minutes
Temperature: 18oC
Step 6 - Centrifuge: Apply the supernatant from step 5 to the QIAprep spin column by decanting or pipetting. Centrifuge for 30-60s and discard the flow-through.
Step 7 - Remove Endonucleases from Sample: Wash the QIAprep spin column by adding 500ul of Buffer PB. Centrifuge for 30-60s and discard flow-through.
Step 8 - Remove salts from sample: Wash the QIAprep spin column by adding 750ul of Buffer PE. Centrifuge for 3-60s and discard flow through.
Step 9 - Centrifuge:
RPM: 13000
Time:1 minute
Temperature: 18oC
Step 10 - Elute DNA: Place the QIAprep column in a clean 1.5ml microcentrifuge tube. To elute DNA, add 50ul Buffer EB to the centre of the spin column, let it stand for 1 min, and centrifuge for 1 min.
Step 1: Set up an eppendorf as follows
Step ?: Used 2mls
Step ?: Step ? had to be missed because we realised too late we had too little PE? buffer remaining.
Restriction Digest:
Step 1 - Thawing cells: Thaw all materials on ice
Step 2 - Adding Ingredient: Add the following ingredients to autoclaved/sterile eppendorf tubes
| Component | Amount (ul) (one enzyme used) | Amount (ul) (two enzymes used) |
|---|---|---|
| dH20 | 2.5 | 1.5 |
| Buffer 1x | 1 | 1 |
| DNA template | 5 | 5 |
| BSA | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Enzyme 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Enzyme 2 | N/A | 1 |
Step 3 - Addition of BioBrick: Flick contents gently and centrifuge.
Step 4 - Centrifuge:
RPM: 14000
Time: 1 minute
Temperature: 18oC
Step 5 - Digest Program: Place the samples on a thermocycler under the following conditions:
RPM: 550
Time: 2.5 hours
Temperature: 37oC
Step 6 - Denaturing Enzymes: If you are not running the samples on a gel immediately, denature the restriction enzymes by running the samples on a thermocycler under the following conditions:
RPM: 550
Time: 25 minutes
Temperature: 65oC
Step 2 - Setting up Digests and Controls: The protocol describes the recipe for (i) Digested Plasmid and (ii) Uncut Control. The table below indicates that an uncut and an Xcar1/Spe1 digested sample be set up for each BioBrick. Set up Eppendorfs as follows
| Samples | Recipe | Enzymes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioBrick | BBa_J23119 | Digested Plasmid | Xba1 & Spe1 |
| Undigested Plasmid (Control) | None | ||
| BBa_B0015 | Digested Plasmid | Xba1 & Spe1 | |
| Undigested Plasmid (Control) | None | ||
| BBa_B0034 | Digested Plasmid | Xba1 & Spe1 | |
| Undigested Plasmid (Control) | None | ||
Preparing the Gel
Step 1: Within a conical flask, add 3ml 50X TAE, 1.5g Agarose, and 150ml RO water
Step 2: Heat for 1 min in microwave. Swirl. Heat again for 30s. If solution is clear stop. Else repeat.
Step 3: Cool solution under running cold water.
Step 4: Add 20ul ethidium bromide (normal concentration of EB solution is 500ug/ul)
Step 5: Pour into a sealed casting tray in a slow steady stream, ensuring there are no bubbles
Running a gel
Step 6: Add 1 part loading buffer to five parts of loading sample
Step 7: Position the gel in the tank and add TAE buffer, enough to cover the gel by several mm
Step 8: Add 5ul of DNA ladder to lane 1
Step 9: Add samples to the remaining wells
Step 10: Run at 100 volts for 1hour and 15 minutes
Imaging the Gel
Step 11: Place gel in GelDoc 2000 chamber
Step 12: Turn GelDoc 2000 chamber on
Step 13: From computer: Quantity One > Scanner > Gel_Doc_Xr>Manuqal Acquire
Step 14: Alter the exposure/settings to give a clear image.
TAE - Tris-acetate-EDTA
EDTA - ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
Results: The image below shows a 1% Agarose Gel of an Analytical Restriction Enzyme Digest for Expt 7.2. Visible in Lane 1 is a band corresponding to the Plasmid Backbone PSB1A2 (2079bp) as show by A, but it is not possible to detect our BBa_J23119 insert on this gel, as it is just 35bp long. Lane 2 shows the uncut plasmid for BBa_J23119 (shown by B) but the size difference between A and B appears to large for Bba_J23119 to have been the insert. This will require further investigation. Lane 3 shows a product 129bp long (indicated by C) which is the correct size for our insert BBa_B0015. A stronger band is also visible, indicated by D, which corresponds to the plasmid backbone PSB1AK3 (3189bp). Lane 4 displays a product which is somewhat larger than the expected size for the uncut plasmid (3318bp) as indicated by E. Lane 5 displays the correct product for the PSB1A2 backbone (2079bp) as indicated by F, but the extremely small size of the Bba_B0034 insert (12bp) means that it cannot be detect on this gel. Lane 6 indicates a band larger than expected, and does not correspond to the size of the uncut plasmid (2091bp) as shown by G.

Conclusion: The BBa_B0015 transformation was a success. However, with regard BBa_J23119, we feel that the difference in the product size of A (PSB1A2 plasmid backbone) and B (uncut plasmid) raises concerns as to whether the insert could be as short as 35bp. However, we must also consider the secondary effects had by the conformation of an uncut plasmid on its migration through the gel. It is possible this is sufficient to misplace the plasmid, such that its position does not represent its size. Even without this possibility, however, it would not be possible to determine whether there was a 35bp difference on such a crude scale of ladder. Instead we will reattempt the Analysis against a 25bp ladder, with the intention of detecting the insert. (See Expt 8.1). We have similar concerns for BBa_B0034, and so this too will be run against a 25bp ladder.
Nanodrop:
Software ND-1000 Model:
Step 1: Initialise the spectrophotometer by pipetting 1 µ of clean water onto lower optic surface, lowering the lever arm and selecting ‘initialise’ in the ND-1000 software
Step 2: Wipe and add elution buffer as negative control. Click blank in ND-1000 software
Step 3: Wipe and add 1 µl sample
Step 4: On the software set lambda to 260nm
Step 5: Lower the lever arm and click measure in ND-1000 software
Step 6: Take readings for concentration and purity
Step 7: Once measurement complete, wipe surface
| BioBrick | λ260 | λ 280 |
|---|---|---|
| BBa_J23119 (ng/μl) | 77.6 | 71.8 |
| BBa_B0034 (ng/μl) | 70 | 71.2 |
| BBa_B0015 (ng/μl) | 128.9 | 128 |

Thursday 26.7.12
Aim - Transformation of previously failed BioBricks: BBa_I750016 was previously grown on an Agar Plate (Expt 6.3) but failed to produce growth after colony picking. BBa_C0040 was previously grown on an Agar Plate (Expt 7.1) but also failed to produce growth after colony picking. R0040 failed to produce colonies in Expt 5.1.
Method:
Step 1 - Addition of BioBrick: To the still frozen competent cells, add 1 - 5 µL of the resuspended DNA to the 2ml tube.
Step 4 - Incubation: Close tube and incubate the cells on ice for 45 minutes.
Step 5 - Heat Shock: Heat shock the cells by immersion in a pre-heated water bath at 37ºC for 10 minutes.
Step 6 - Incubation: Incubate the cells on ice for 2 minutes.
Step 7 - Add media: Add 1.5ml of Lysogeny Broth and transfer to a falcon tube.
Step 8 - Incubation: Incubate the cells at 37ºC for 1 hour at RPM 550.
Step 9 - Transfer: transfer the solution back into a 1.5ml Eppendorf and centrifuge
RPM: 14000
Time: 2 minutes
Temperature (18-25oC)
Step 10 - Resuspend:Remove supernatant and resuspend in 100ul LB
Step 11 - Plating: Spread the resuspended cell solution onto a selective nutrient agar plate. Place the plates in a 37°C static incubator, leave overnight (alternatively a 30°C static incubator over the weekend)
Step 1 – Thawing Cells: Use W3100 cell line created in Week 2 (Expt 2.1)
Step 3 – Addition of BioBrick: To each 2ml eppendorf, add 1ul of the following BioBricks. Include an extra tube as a control, with no BioBrick added
| Function | Module | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| BioBrick | BBa_I750016 | Gas Vesicle Polycistronic Cluster | Buoyancy |
| BBa_C0040 | Tetracycline Repressor | Buoyancy | |
| BBa_R0040 | TetR Repressible Promoter | Buoyancy | |
| Control | Positive (one for each of the above BioBricks) | ||
| Negative (No BioBrick) | |||
Step 9 – Plating samples on Agar Plates: The table below indicates the chosen inoculation volume (two for each BioBrick) and the correct gel antibiotic concentration for all samples.(Extra caution was taken to allow agar to cool before adding Ampicillin, in case this is the cause of difficulty).
| Samples | Volume Inoculated | Antibiotic in Gel (ug/ml) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioBrick | BBa_I750016 | 10ul | Ampicillin(50ug/ml) |
| 90ul | |||
| BBa_C0040 | 10ul | ||
| 90ul | |||
| BBa_R0040 | 10ul | ||
| 90ul | |||
| Control | Positive (Contains BioBrick BBa_C0040) | 36ul | No Antibiotic |
| Negative (No BioBrick) | 36ul | 1x Ampicillin(50ug/ml) | |
Friday 27.7.12
Aim - Check results of Transformation: The table below indicates whether there was growth on the Agar Plates after Transformation. Included below are images of the Agar Plates for each BioBrick.
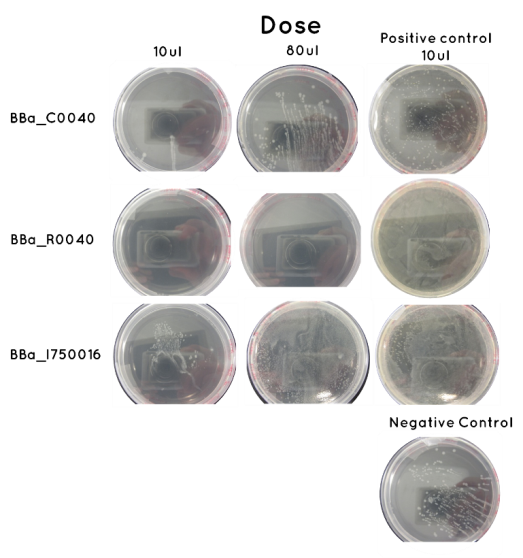
| Samples | Volume Inoculated | Colony Formation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioBrick | BBa_I750016 | 10ul | No |
| 90ul | No | ||
| BioBrick | BBa_C0040 | 10ul | Yes |
| 90ul | Yes | ||
| BioBrick | BBa_R0040 | 10ul | Yes |
| 90ul | Yes | ||
| Control | Positive (Contains BioBrick BBa_C0040) | 36ul | Yes |
| Negative (No BioBrick) | 36ul | No | |
Conclusion: Given there was growth on the negative control we are wary of our results. We feel the contamination was not a result of any of our materials, but rather the pattern of spread on the agar is suggestive of a contaminant entering during spreading. A similar pattern is seen on our BBa_C0040 plates, and so it is likely we will repeat these. A very different pattern was observed on the BBa_I750016 agars, and so we will carry out an analytical digest to determine whether it has been transformed correctly.
 "
"