Team:Groningen/Modeling
From 2012.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
m |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{|align="center" | {|align="center" | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | |[[File:Groningen2012 JP | + | |[[File:Groningen2012 JP 20120611 NH4-TnrA Relationship.png|680px|center]] |
|- | |- | ||
| - | + | {|align="center" | |
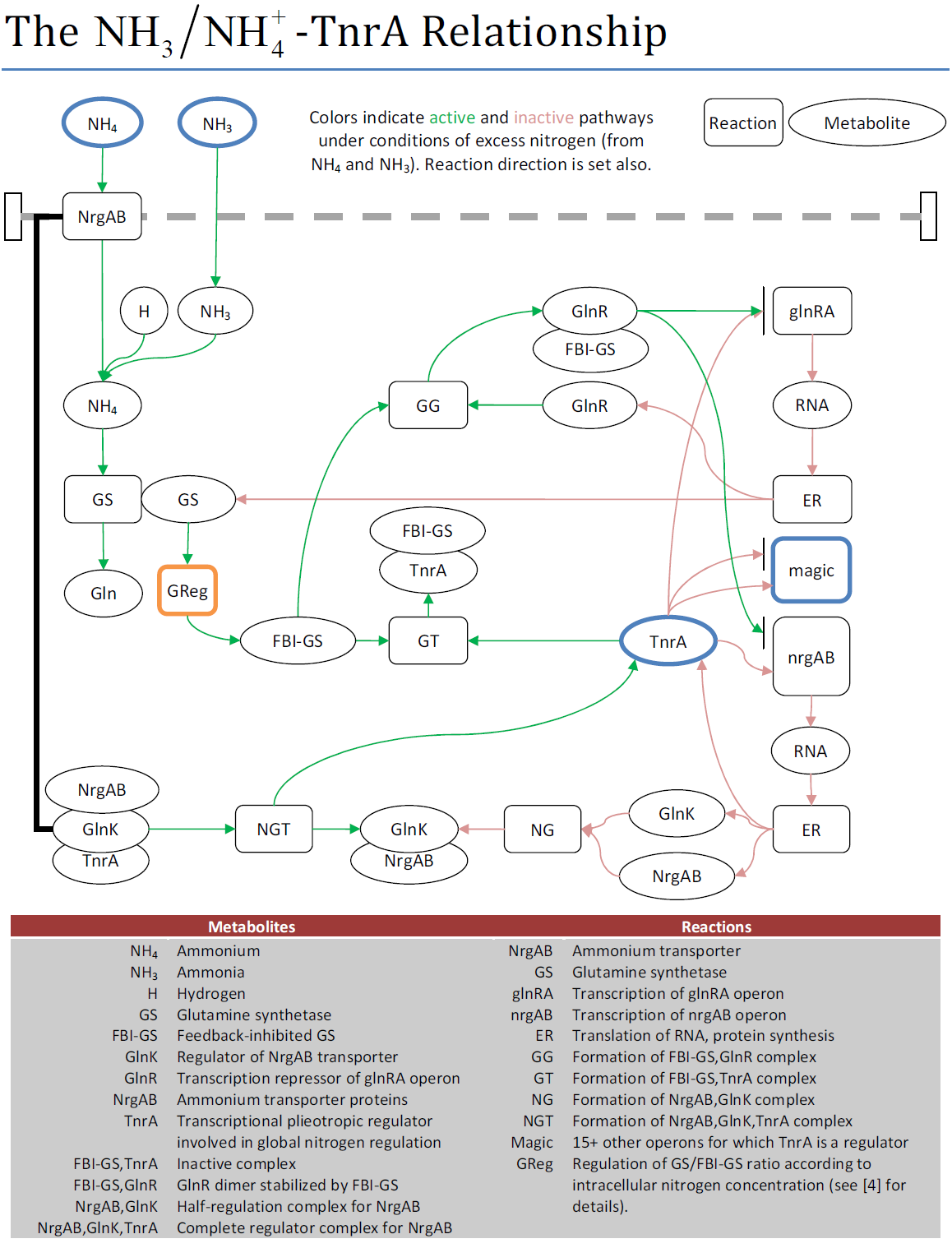
| - | {|align="center" | + | |Fig. m2. Reactions involved between ammonium uptake and TnrA. |
| - | |Fig. | + | |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | References | ||
| + | # SubtiWiki, http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/wiki/index.php | ||
| + | # K. Gunka, F.M. Commichau, “Control of glutamate homeostasis in Bacillus subtilis: a complex interplay between ammonium assimilation, glutamate biosynthesis and degradation,” Molecular Biology, under review (2012). | ||
| + | # N.A. Doroshchuk, M.S. Gelfand, D.A. Rodlanov, “Regulation of Nitrogen Metabolism in Gram-Positive Bacteria,” Molecular Biology, vol. 40(5), pp. 829-836, (2006). | ||
| + | # Study Guide, Chem153C, University of California, Los Angeles. http://vohweb.chem.ucla.edu/voh/classes%5Cspring10%5C153CID28%5C11AminoAcidBiosynthesisSQA.pdf | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| - | |'''Modeling Targets''' | + | |'''Possible Modeling Targets''' |
<br> | <br> | ||
'''''Germination''''' | '''''Germination''''' | ||
Revision as of 18:56, 12 June 2012








| Fig. m2. Reactions involved between ammonium uptake and TnrA. |
References
- SubtiWiki, http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/wiki/index.php
- K. Gunka, F.M. Commichau, “Control of glutamate homeostasis in Bacillus subtilis: a complex interplay between ammonium assimilation, glutamate biosynthesis and degradation,” Molecular Biology, under review (2012).
- N.A. Doroshchuk, M.S. Gelfand, D.A. Rodlanov, “Regulation of Nitrogen Metabolism in Gram-Positive Bacteria,” Molecular Biology, vol. 40(5), pp. 829-836, (2006).
- Study Guide, Chem153C, University of California, Los Angeles. http://vohweb.chem.ucla.edu/voh/classes%5Cspring10%5C153CID28%5C11AminoAcidBiosynthesisSQA.pdf
Germination
- Effects of h2o and L-alanine concentrations on germination rate.
Volatile production
- Concentration and production rates as a function of temperature, volume, type of meat, geometry. (EX_amine, EX_nh4, EX_h)
Normal operation
- Receptor sensitivities
- Binding rate as a function of volatile concentration (TAAR5)
- Diffusion rates
- Through the membrane (nh4_diffusion, h_diffusion)
- Through ion channels (nh4_ion)
- Reaction rates through the signaling pathways as a function of metabolite concentrations (path1,path2,path3)
- Carotenoid pathway precursor concentrations as a function of the signaling pathways. (IPP,DMAPP)
- Reaction rates of the carotenoid pathway metabolites (crtE, crtB, crtI, crtY)
- Opacity as a function of lycopene concentration
OMIX visualization through reaction pathways
 "
"