Team:Groningen/Project
From 2012.igem.org
m (→Standard Operating Protocols) |
m (→Modeling-Labwork Cooperation) |
||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
The modeling team of one will provide to the lab: | The modeling team of one will provide to the lab: | ||
# Creation, and critical analysis, of the reaction pathway from literature. | # Creation, and critical analysis, of the reaction pathway from literature. | ||
| - | # Identification of the nutrients necessary to support growth. | + | # Identification of the nutrients necessary to support growth. (Done: D-Glucose, Water, Glutamine, Potassium) |
# Rates of nutrient consumption versus temperature and biomass. | # Rates of nutrient consumption versus temperature and biomass. | ||
# Growth rate as a function of temperature. | # Growth rate as a function of temperature. | ||
Revision as of 21:05, 19 June 2012








Contents |
Goal
To provide a method of monitoring the edibility of packaged meat and fish after the store-bought package has been opened.
More detailed abstract to come once the theory has been proven experimentally. For now, the homepage provides a broad overview.
Construct
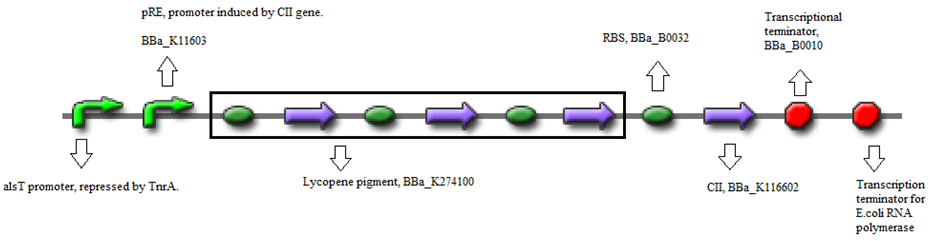
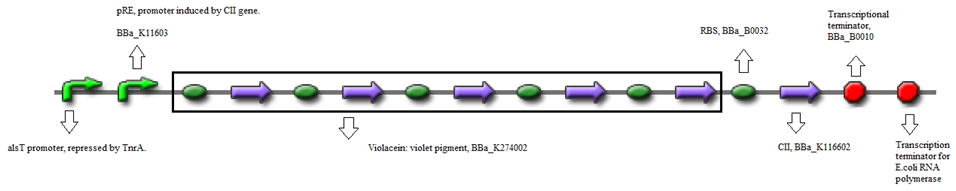
The standard construct is a combination of biobricks.
- BBa_K090403 (Backbone) - Single copy shuttle vector
- BBa_K116632 (Positive feedback loop) - Uses the pRe promoter regulated by C11 and terminated by B0010.
- BBa_K274100 (Reporter) - Modified carotenoid pathway to produce red pigment.
- Or, using BBa_K274002 (Reporter) - Violet pigment producer
States
Sporulation
Magic
Germination
Magic involving tennis rackets, D-alanine, and water.
Pre-Activation
- The growth medium contains a low concentration of glutamine (gln), but no ammonia or ammonium (NH4).
- Glutamine synthetase (GS) is activated due to the inadequate level of glutamine, however, it cannot synthesize more gln as it is lacking NH4.
- The low intracellular gln level shifts the ratio of GS to feedback-inhibited GS (FBI-GS) towards a higher level of GS.
- This higher level of GS allows a higher level of TnrA.
- The TnrA represses the alsT promoter.
Activation
- Rotting meat produces NH4.
- NH4 is enters the cell through the NrgAB ammonium transporter.
- GS converts NH4 into gln.
- Gln reaches the concentration required for steady cell growth.
- The ratio of GS to FBI-GS shifts towards a higher level of FBI-GS.
- The newly created FBI-GS binds to TnrA, creating an inactive complex.
- TnrA is unable to repress the alsT promoter.
- TnrA triggers the plasmid, and its positive feedback loop containing the color reporter.
Post-Activation
- The pRe promoter continually expresses the color and the loop promoter.
- The rate of production is tuned to the spoiling time of the meat.
Death
- The extracellular nutrients are depleted.
- Color reporter builds to toxic levels.
Modeling-Labwork Cooperation
Unlike previous years, there is a direct link between theory and practice.
The modeling team of one will provide to the lab:
- Creation, and critical analysis, of the reaction pathway from literature.
- Identification of the nutrients necessary to support growth. (Done: D-Glucose, Water, Glutamine, Potassium)
- Rates of nutrient consumption versus temperature and biomass.
- Growth rate as a function of temperature.
- Total amount of nutrients required to allow X amount of biomass to grow and survive for Y amount of time.
- Identification of the metabolites required for the reporter.
The lab will provide to the modeling team:
- TnrA concentration as a function of extracellular glutamine concentration.
- Growth rate as a function of extracellular glutamine concentration.
- Rates of volatile production as a function of meat type and volume.
Limitations due to time constraints
- Concept is proven at room temperature, can be extended to less than 7oC using the psychotrophic bacteria bacillus cereus.
- Adaptation of the eukaryotic receptor TAAR5 to bacillus subtilis to sense amines is possible, but not within 3 months.
Standard Operating Protocols
In an effort to apply business concepts to the iGEM project we have agreed to conduct the project according to the following protocols. The specifics of these sections (such as the actual protocols or equipment listing) are contained within the SOP binder in the laboratory. This binder will be digitized for next year’s iGEM teams.
General
- How to set up an experiment.
- Fully describe the experiment in a document before it is scheduled to be performed (document is described in point 2).
- After the experiment is documented, it should be reviewed by at least one other iGEM member.
- Upon completion of the experiment there should be a short discussion/interpretation of the results and a short outlook for subsequent experiments.
- Experiment Template
- Insert outline of the template here
- Acronyms.
- Each iGEM member is assigned an acronym: e.g. Marius Uebel will be MU.
- Data management.
- Each filename should contain the original creator, date, and type of file. E.g. MU_20120412_igem12_sop_proposal.doc
- Ordering of material.
- A single person should be responsible for ordering, this prevents multiple orders of an item and a more controlled inventory.
Lab Equipment and Materials
- Equipment.
- Every piece of lab equipment should be accompanied by the manufacturer’s manual and a short how-to manual.
- Overview and location of all our equipment should be written down in this part
- Protocols
- All lab protocols should be consolidated into a central location in the lab in print form.
Methodology
- Culture
- Contains general information and cultivation requirements of the chassis
- Assay
- Short overview of any assay kits changes undertaken to suit the actual experiment.
- All information on original assays
 "
"