Team:UNAM Genomics Mexico/Modeling/Heavy Metal AND
From 2012.igem.org

AND's Results
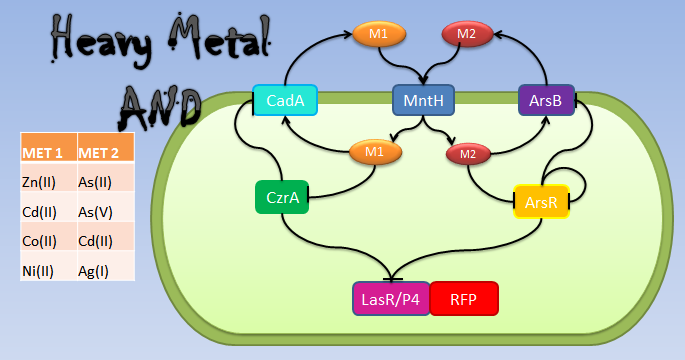
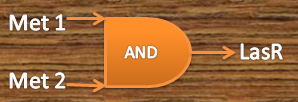
Metal AND
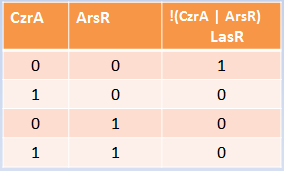
Our system consists of a hybrid promoter which contains binding sites for two transcription factors that act as repressors, CzrA and ArsR. In the presence of Met1, CzrA losses affinity for its binding site.
Similarly, if there is Met2 in the cell, ArsR also dissociates itself from its binding site. Taking into account these facts, unless Met1 and Met2 are present in the culture, we can say that the genes under this hybrid promoter will be repressed, just like a AND gate should function!
|
Repressors
|
|
Inputs
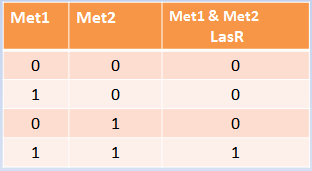
|
|
Kappa
There is no metal catabolism, so as long as metal concentrations are non-lethal, their concentrations reach an equilibrium within the cell through cytosolic influx-efflux. This makes the behavior of a single burst or a continuous dose qualitatively similar, because the metal levels in just one dose will be constant since metals won’t be degraded. Kappa AND metal File

|
|
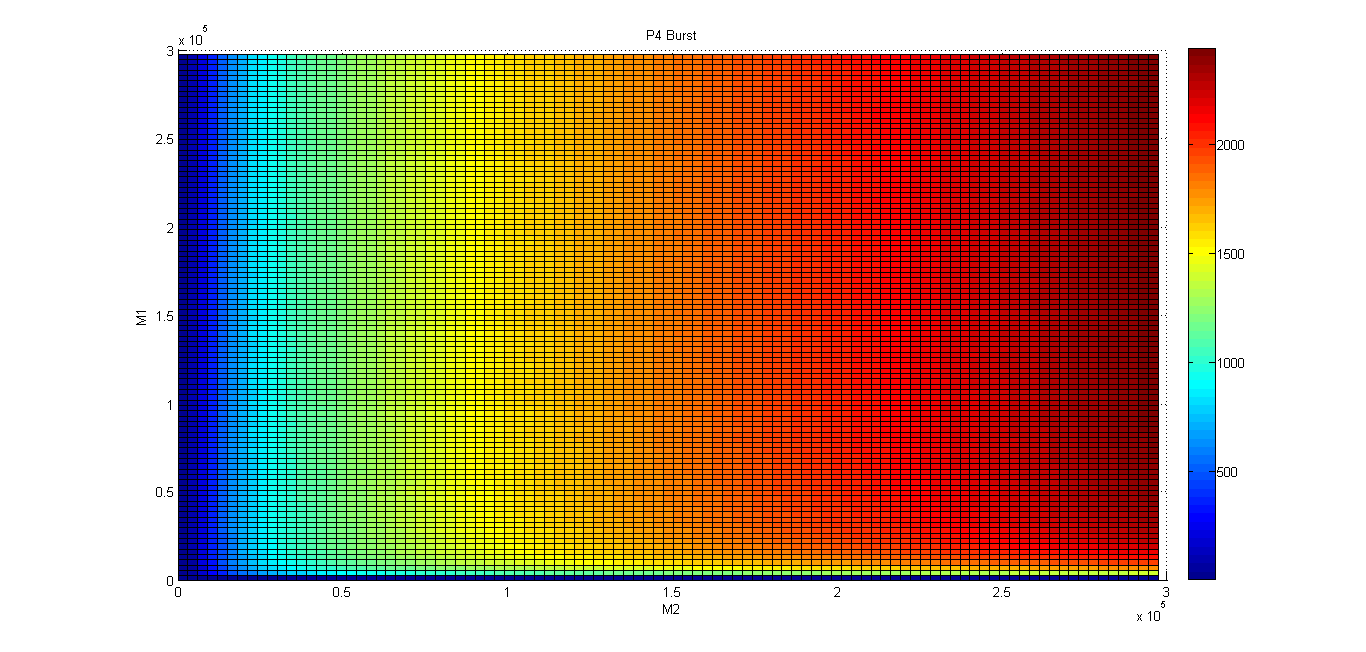
Transfer Function
We were interested in modelling the output of our logic gates based on the input. This is called the "Transfer function". Imagine this process like a black box that will give you the dynamic concentration through time of whatever is downstream of the "AND" when you feed it with input data. In this case, it doesn't matter if it’s a single input burst or a continuous input.
Our logic AND gate is fully dependent on the intracellular concentrations of the inducers (meaning metal ions), and therefore we had to take into account any endogenous regulation already present in our chassis.
So, our first task was to reconstruct the regulatory network of B. subtilis for the influx-efflux systems. The regulation data was retrieved from several papers and databases like [http://bsubcyc.org/ http://bsubcyc.org/]
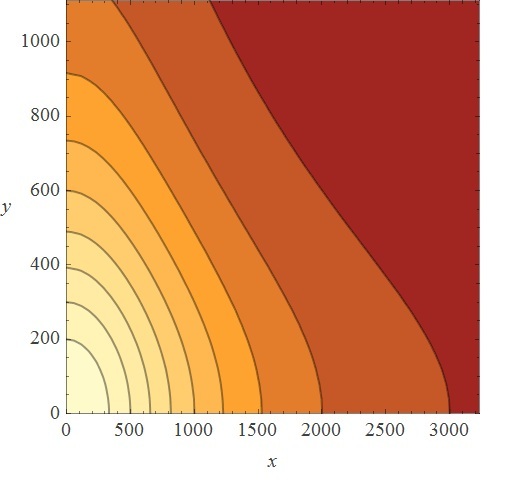
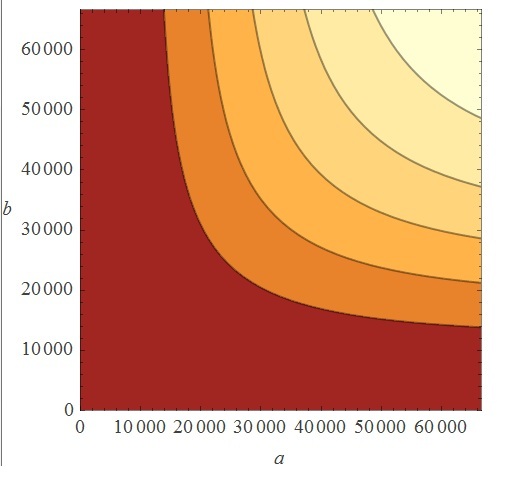
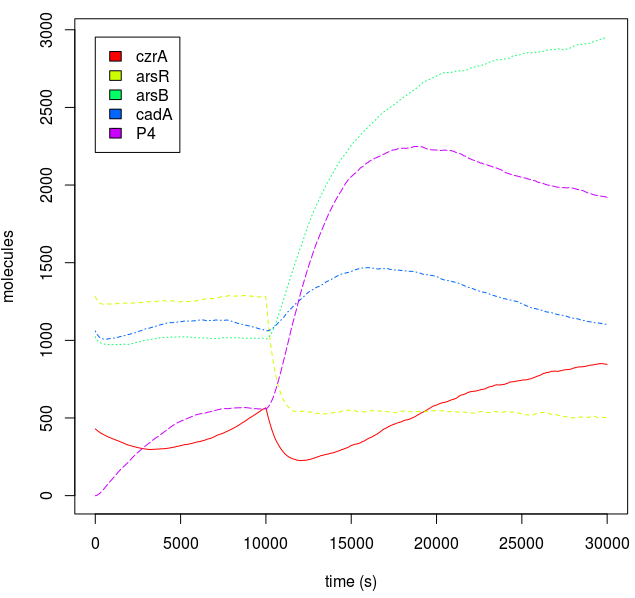
Metal homeostasis in the cell involves an effective response in order to withstand possible stress conditions in which high concentrations of heavy metals are involved. Both approaches, ODEs with Matlab and the stochastic one with kappa, give us similar results. First, we were able to see that the AND response is not as sensitive to higher concentrations. For the AND to have a good performance, low concentrations of Met 1 and 2 are required. We infer that metal response is a fast process. The accumulation of the output protein shows a sudden increase in production resulting from a very small change in metal concentrations. Another remarkable fact is the role each TF (CzrA and ArsR) plays. Since ArsR represses itself, its production has a succession of spikes. Nevertheless, CzrA increases its production if the metal concentration within the cell also increases, but it doesn’t have a drop in production because their decay depends only on the dilution and degradation of the protein. That way, the effects of CzrA are more notable than ArsR. This is reflected in a greater contribution of Met1 in the regulation of the AND promoter than that of Met2.
|
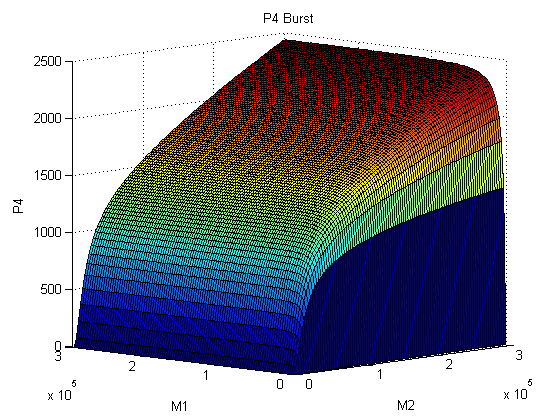 |
The suggested amount of each input that activates the gate according to our model is:
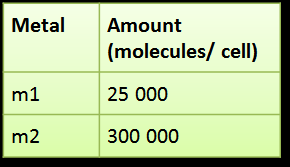
|
Deterministic model
In Bacillus subtilis, many metal ions, both essential, and others like arsenic, are introduced in the cell by the ion pump MntH. We make two assumptions, first, that the used metals were imported by MntH and second, that all the metals introduced by MntH (especially those that we use for our AND gate) have the same intake rate. Met1 is pumped out of the cell by a transporter of the CadA operon (most of them require ATP hydrolysis), and Met2 by ArsB [1]. In that way, each metal’s concentration in the cell was defined by Michaelis-Menten equations as the amount of introduced metal by each MntH molecule in the cell, minus the amount of exported metal by its respective transporter, assuming that all the metals imported or exported by the same transporter had the same affinity to this transporter and had the same chance to pass into the cell.
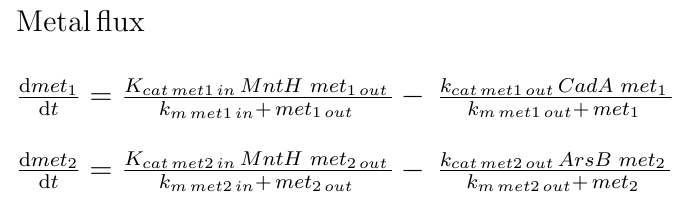
|
The transcription factors which are involved in the AND processing are CzrA and ArsR. ArsR is repressed by itself when there are no Met2 ions. We use a Hill function to express the mRNA production. The function shows the effect of the binding of ArsR in its promoter. This way, the repression effect will be affected by the affinity of ArsR to the binding site and the concentration of ArsR. About CzrA, there are studies that suggest that the total amount of the protein in the cell is correlated with the levels of the metals that it tends to expel [1]. To describe this phenomenon, we defined the production of the mRNA of CzrA as a function of intracellular Met1 through a Michaelis-Menten relationship.
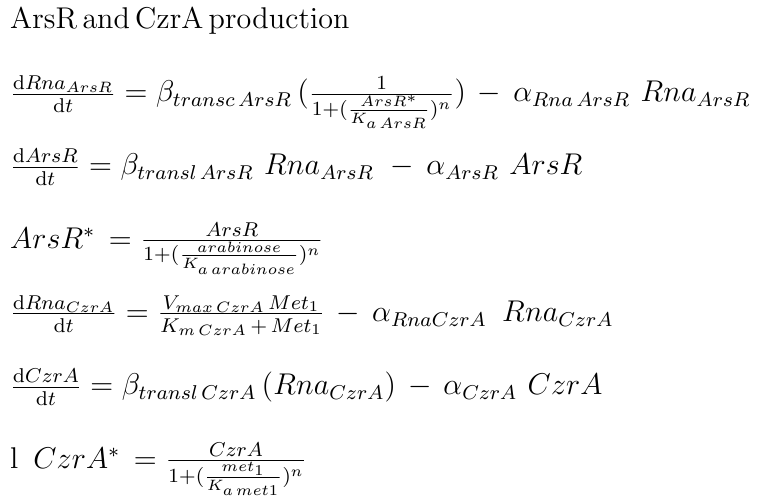
|
Finally, the proportion of active transcription factors (unbound to their respective metals)
are defined with a hill function as the fraction of the total protein plus the relationship between the affinity constant of the binding and the amount of metal. The higher amount of metal or the affinity of it to the binding with TF corresponds with the lower amounts of active TF. The transporters for Met1 and Met2 are also under the regulation of ArsR and CzrA; the CadA operon is repressed by CzrA, and ArsB is repressed by ArsR.
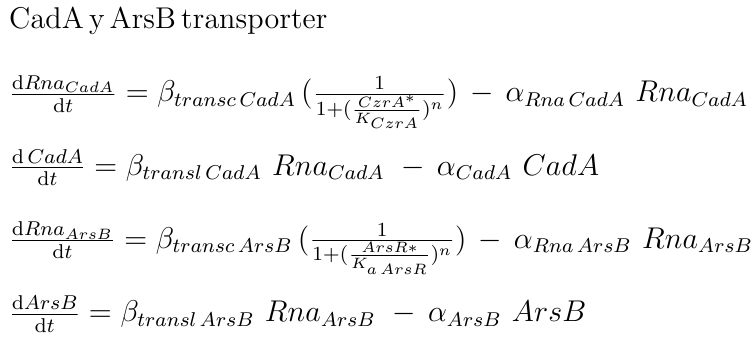
|
The output of the AND operation is the production of one of two reporters, P4 or LasR
respectively. The production of the reporter mRNA depends on the status of its promoter, which has a state space of being bound to ArsR, to CzrA, to both, or none. This approach was made supposing that the binding-mediated repression of each TF is independent, and therefore the cumulative intensity of repression by ArsR and CzrA is the product of their independent repressions.
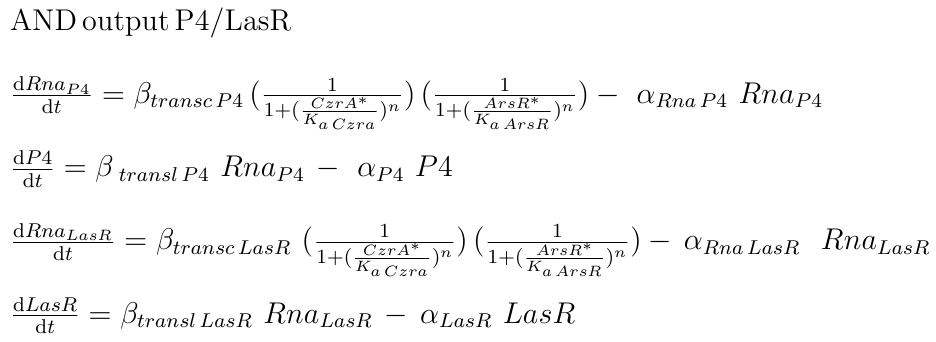
|
Conclusions
After making the model just for our AND, we coupled the endogenous Bacillus subtilis system to our predictions. After this, we found that the predictions given by both assumptions were not the same, proving that the endogenous system was, in fact, an important matter to consider, so we considered it.
Obviously, as the model that did not take into account the endogenous system was farther away from the actual system, we opted for using the model that did take it into account, making our transfer function a more realistic representation of the system, in spite of the fact that we could not find all the parameters.
Some of these parameters, unfortunately, were the diffusion within the nanotubes, and the amount, size, form, frequency of creation, or any other useful data of nanotubes you could think of (luckily for us, we could not think of that many). Even though we had to face all these problems, with the little light shone by people before us onto the spectral essence of the nanotubes, it was possible for us to say that our system can, in theory, simulate Boolean operations.
References
[1]Moore C, Helmann J D. Metal ion homeostasis in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology. April 2005. 8(2):188-195 DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2005.02.007
 "
"