Team:TMU-Tokyo/Project abstract
From 2012.igem.org
| (8 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
<div class="grid_7"> | <div class="grid_7"> | ||
| - | |||
<p class="description"> | <p class="description"> | ||
| - | + | We planed to create E.coli which removes formaldehyde, named <Strong>Chef Ant E.coli</Strong>. It is appended 3 devices and gets removal ability of formaldehyde.<Br> | |
<Br> | <Br> | ||
| - | <Img Src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/7/7d/TMU-Tokyo_project_fig1.png"><Br> | + | <Center><Img Src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/7/7d/TMU-Tokyo_project_fig1.png"></Center><Br> |
| + | <p class="description"> | ||
| + | The pathway of formaldehyde remove is done through 2 stages. First, formaldehyde dehydrogenase derived from <i>Pseudomonas putida</i> (PFDH) changes formaldehyde to formate. Subsequently, formate dehydrogenase derived from <i>Methylobacterium extorquens</i> (FDH4) changes formate to water and carbon dioxide.<Br> | ||
<Br> | <Br> | ||
| - | + | In parallel with this dehydrohenation, formaldehyde content is measured with GFP. So <b>Chef Ant E. coli</b> enables to visualize formaldehyde decomposing process.<Br> | |
| + | <Br> | ||
| + | <Br> | ||
| + | Following is device details. | ||
| + | <Br> | ||
| + | <Br> | ||
| + | <A Href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:TMU-Tokyo/Project_device1"><b>Device1</b></A>; Visualize formaldehyde with GFP.<Br> | ||
| + | <A Href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:TMU-Tokyo/Project_device2"><b>Device2</b></A>; Dehydrogenize formaldehyde to formate.<Br> | ||
| + | <A Href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:TMU-Tokyo/Project_device3"><b>Device3</b></A>; Dehydrogenize formate to carbon dioxide and water.<Br> | ||
| + | <Br> | ||
| + | Details of our devices is available each device page.<Br> | ||
| + | |||
</p> | </p> | ||
<Br> | <Br> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 56: | ||
<p class="description2"> | <p class="description2"> | ||
| - | + | <B><Br><Br><Br><Br><Br>■fig.1</B><Br> | |
| - | + | This is the pathway of formaldehyde visualization and removal. | |
| - | + | ||
| Line 55: | Line 66: | ||
<div class="clear"></div> | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
| + | <Center> | ||
| + | <p class="description"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <A Href="Project">Project Top</A> Abstract <A Href="Project_device1">Device1 <A Href="Project_device2">Device2</A> <A Href="Project_device3">Device3</A><Br><Br></p></Center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
</html> | </html> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:16, 27 September 2012
Abstract
We planed to create E.coli which removes formaldehyde, named Chef Ant E.coli. It is appended 3 devices and gets removal ability of formaldehyde.
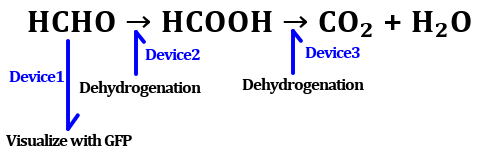
The pathway of formaldehyde remove is done through 2 stages. First, formaldehyde dehydrogenase derived from Pseudomonas putida (PFDH) changes formaldehyde to formate. Subsequently, formate dehydrogenase derived from Methylobacterium extorquens (FDH4) changes formate to water and carbon dioxide.
In parallel with this dehydrohenation, formaldehyde content is measured with GFP. So Chef Ant E. coli enables to visualize formaldehyde decomposing process.
Following is device details.
Device1; Visualize formaldehyde with GFP.
Device2; Dehydrogenize formaldehyde to formate.
Device3; Dehydrogenize formate to carbon dioxide and water.
Details of our devices is available each device page.
■fig.1
This is the pathway of formaldehyde visualization and removal.
Project Top Abstract Device1 Device2 Device3
 "
"