Team:Goettingen/Focus Groups
From 2012.igem.org
 | |
Deutsch  / English / English  |
 |
Contents |
Focus Group #1 - Selection / Swimming
In this group it is all about creating a selection system that enables selecting the E. coli clones that are able to swim the fastest. In an extensive literature search we have collected different swimming media and swimming assays and have evaluated them with regard to our goal. The media can differ in various ways from each other and in our case the most important ones are the agar concentration and the nutrient content. The agar concentration has to be low enough to make swimming possible but high enough to form a semisolid structure. The nutrient content hast to be as low as possible without significantly inhibiting growth because the E. coli cells will only start to swim when there are no more nutrients in their current place. The low nutrient content is also necessary to observe whether a directed taxis in dependence on our tested molecule occurs. Through all these different experiments we will be able to set up a selection system that is quick, easy to handle and delivers reproducible results.
Focus Group #2 - Speed Improvement
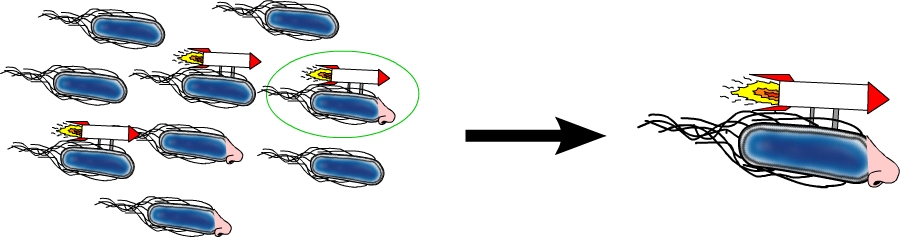
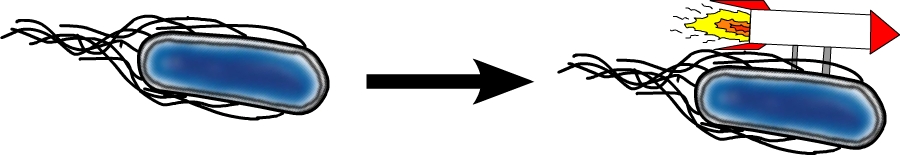
In this group we focus on the improvement of E. coli swimming abilities. To achieve this, we chose a set of different genes that might be able to improve the swimming speed of E. coli. The expression levels of these genes are then controlled by using different promoters and the modified bacteria are tested on swimming agar plates. Such genes include the master regulator of motility and chemotaxis flhDC but also genes coding for parts of the bacterial flagellum such as motB. Furthermore, we use different E. coli strains for our experiments to identify differences in motility.
Focus Group #3 - Chemoreceptor Library
In this group, the main focus is to first clone the aspartate receptor Tar from E. coli under different strong constitutive promoters
into vectors. After examination of effects overexpressing this chemotaxis receptor, the next challenge is to mutagenize this protein to receive
a chemoreceptor library. Ideally, the specificity of the receptor becomes altered due to mutation of the ligand binding sites important for chemical binding.
| ↑ Back to top! |

|
 "
"