Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials
From 2012.igem.org
Devices
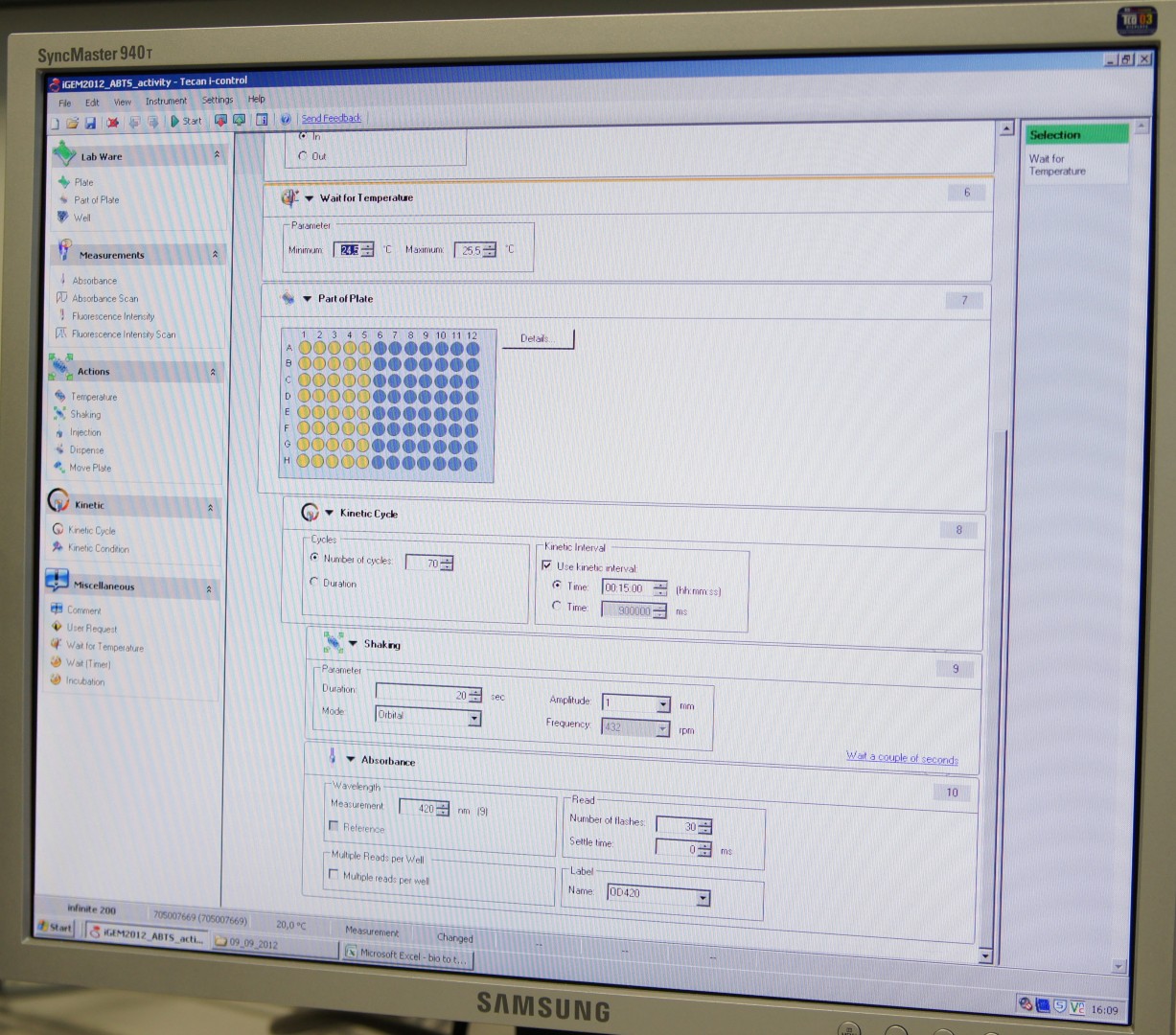
Tecan Infinite Microplate Reader
For measuring the Laccase activity we detected the level of oxidized ABTS via optical density at 420nm. The device we were able to use was a [http://www.tecan.com/platform/apps/product/index.asp?MenuID=1812&ID=1916&Menu=1&Item=21.2.10.1 Tecan Infinite Reader M200]. The program setup was in some parts adapted to the needs of our probes (like duration of the measurement) and in some parts standardized.
Used setup for Laccase activity measurements: Temperature: 25°C; Orbital shaking before each measuring cycle (time depends on duration of each cycle); Number of flashes: 30
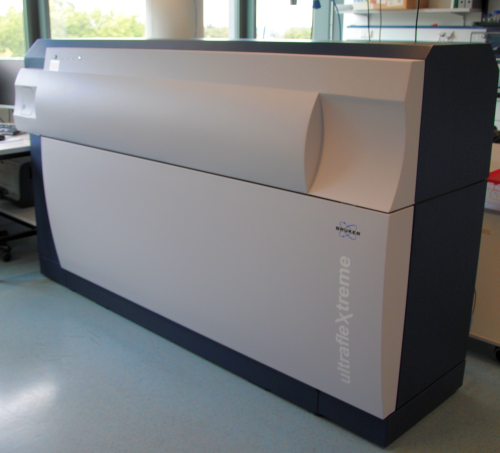
Maldi-TOF
Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization – Time of flight (MALDI-TOF) is a procedure to analyze large biomolecules by their mass.
Before measurement, the analyte is co-crystallized on a metal plate within a solid matrix. 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (sinapinic acid) and 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHB) are most commonly used. Desorption of the analyte is taken by a laser beam, commonly with a wavelength of 337 nm. The matrix absorbs the laser light and the upper layer explosively vaporizes, ejecting both, matrix and analyte molecules. In addition to this vaporization, the laser beam also leads to an ionization of the analytes. The mass analysis is performed by the TOF (time of flight)-analysator. The evaporated ions are accelerated in an electric field. Typical acceleration voltages for this are 10-30 kV. The velocity of an ion depends on its mass and the charge. An ion detector converts the incoming ions into an electrical signal. The advantage of this method is the rapid analysis of a relatively large mass range.
The MALDI-TOF analysis was performed with the [http://www.bdal.com/products/maldi/ultraflextreme-series/overview.html ultrafleXtreme™] by Bruker Daltonics.
We used the MALDI-TOF Analysis to characterize the following BioBricks:
- <partinfo>K863000</partinfo>
- <partinfo>K863005</partinfo>
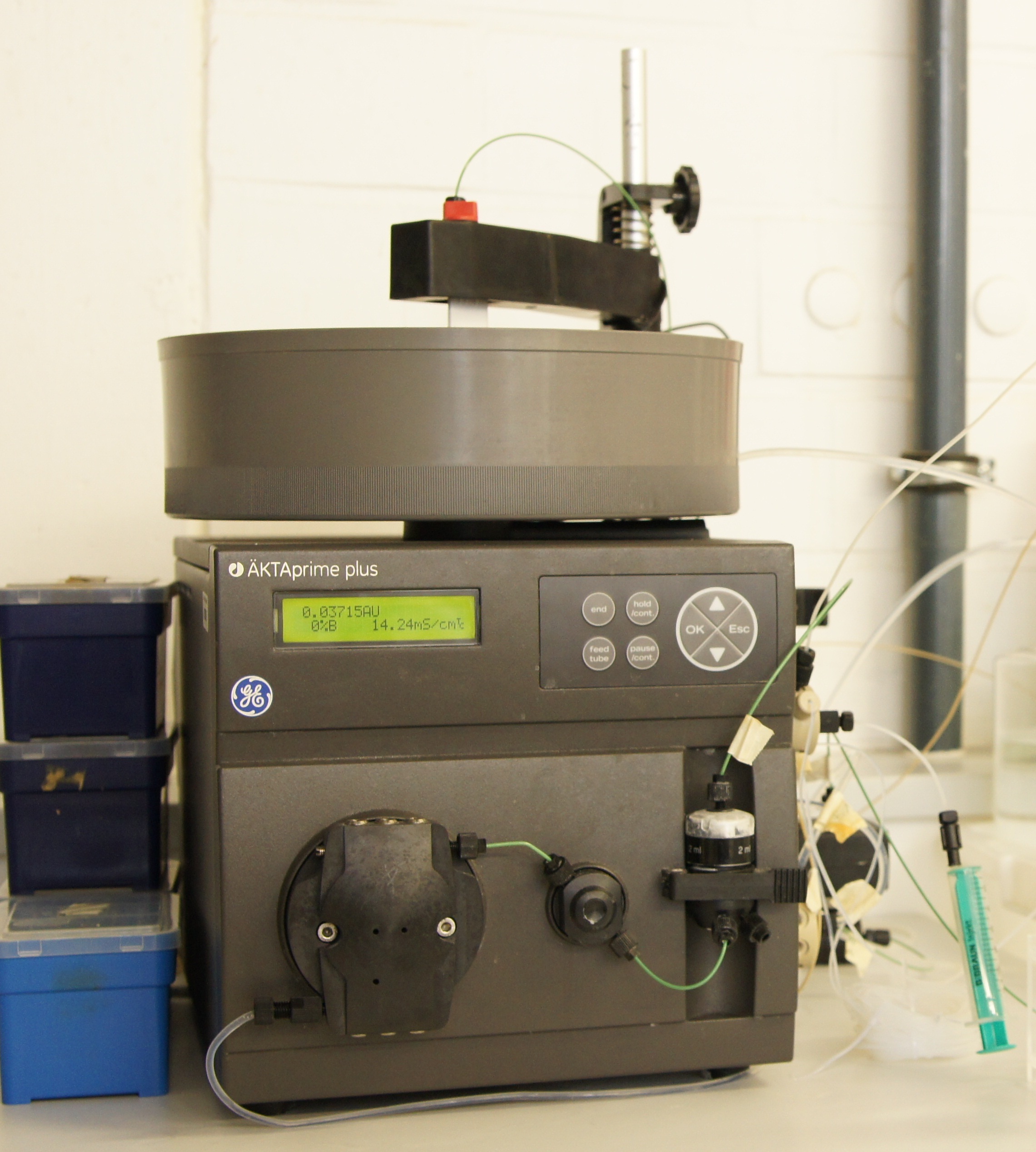
ÄKTAprime plus Chromatographiesystem
ÄKTA is a Swedish word that means true, genuine, or real. ÄKTAprime plus is a compact pumping system which can be used for a range of columns, chromatography media, and filters. This device is ease-of-use and present a high flexibility of liquid handling and minimizing the problem of sample loss.This system can record pH-value, pressure, conductivity, UV-absorption and the flowrate. Different programms are available like PrimeView™ software to evaluate the recorded data.
We used this system to purify our produced laccases with a Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography strategy.
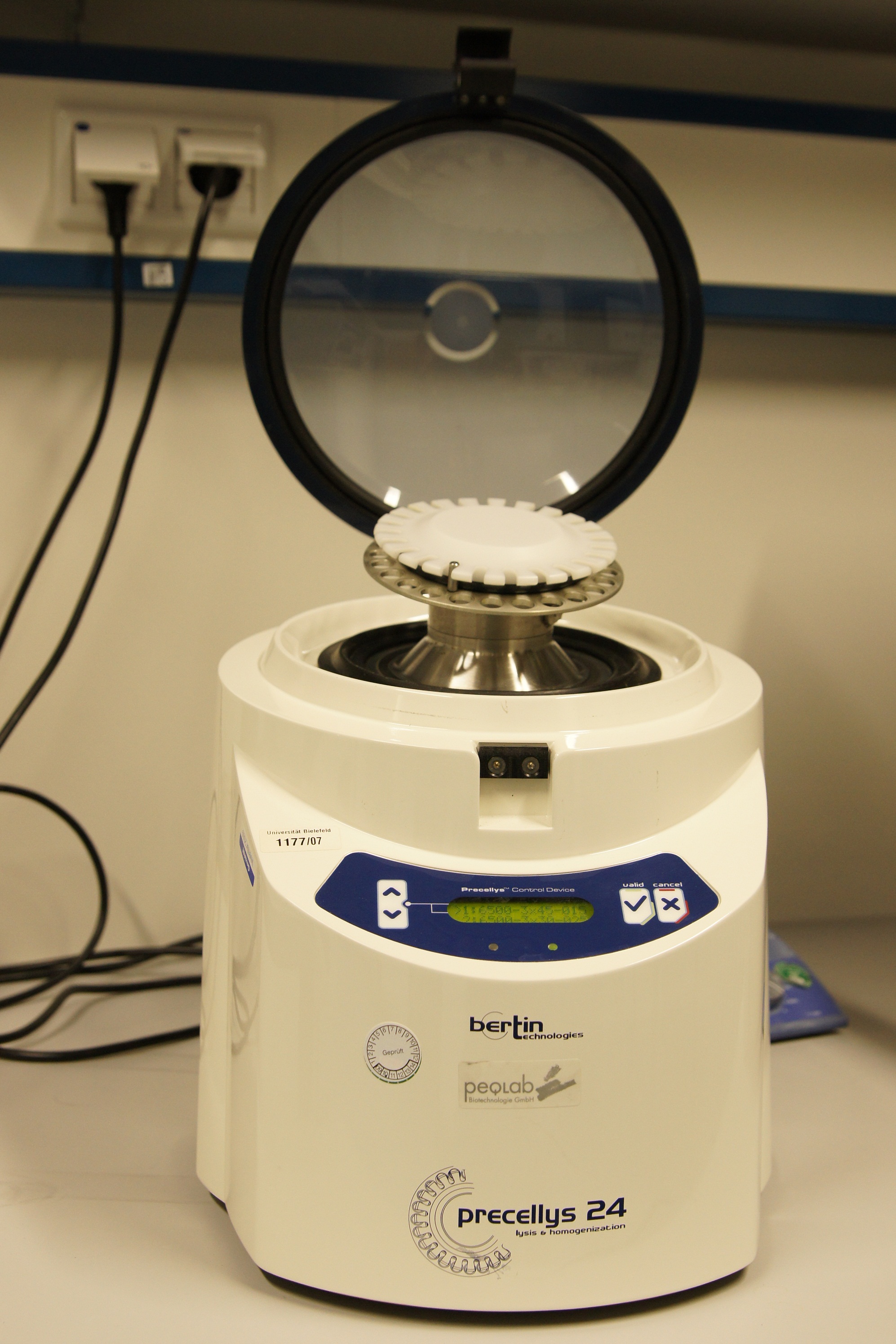
The Precellys® 24 homogenizer
[http://www.peqlab.de/wcms/en/pdf/91-PCS24.pdf The Precellys® 24] is an effective and efficient sample homogenisation to enable effective DNA, RNA or protein extraction. To disrup tumor tissues, hair, cartilages, bones, plant materials, yeasts, bacterium and fungi the samples are loaded in beads containing 2 ml tubes. The tubes can be supplied with steel, ceramic or glass beads. The homogenization effect takes place during a 3-dimensional figure of eight motion. This lead to strong acceleration of the used beads. The forces between the beads and the collisions induce the disruption of cell or the homogenisation of samples.
The first cell disruptions ot the iGEM-team Bielefeld were made by this system.
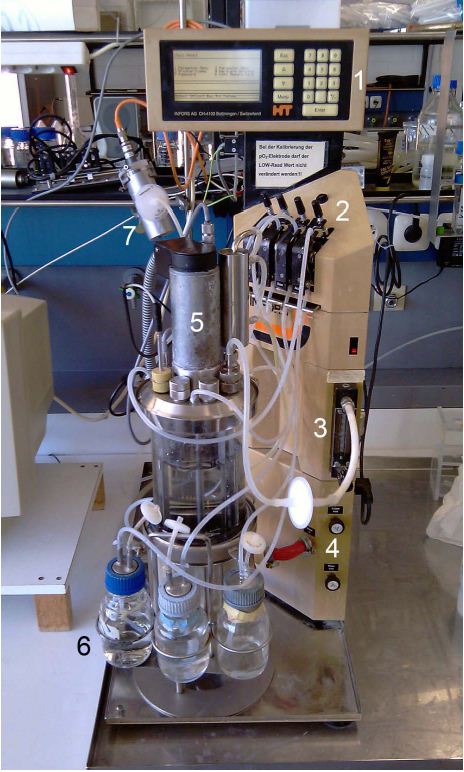
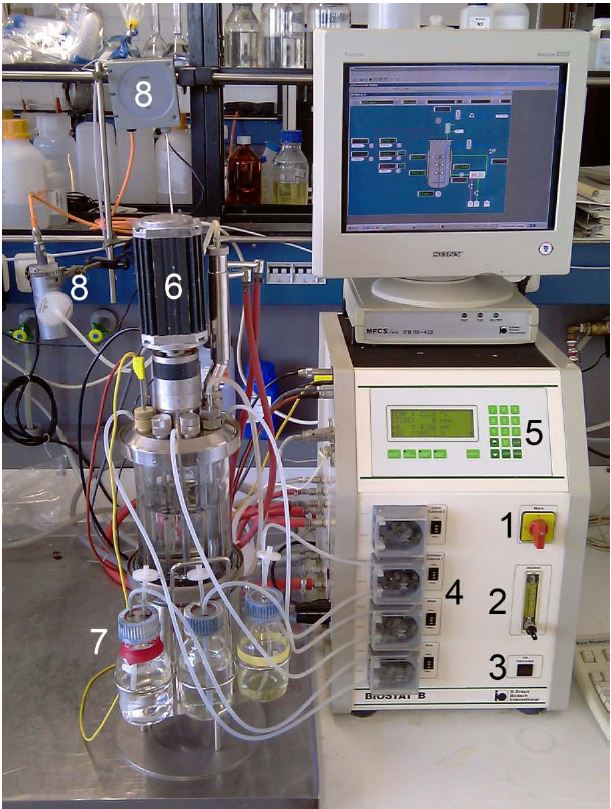
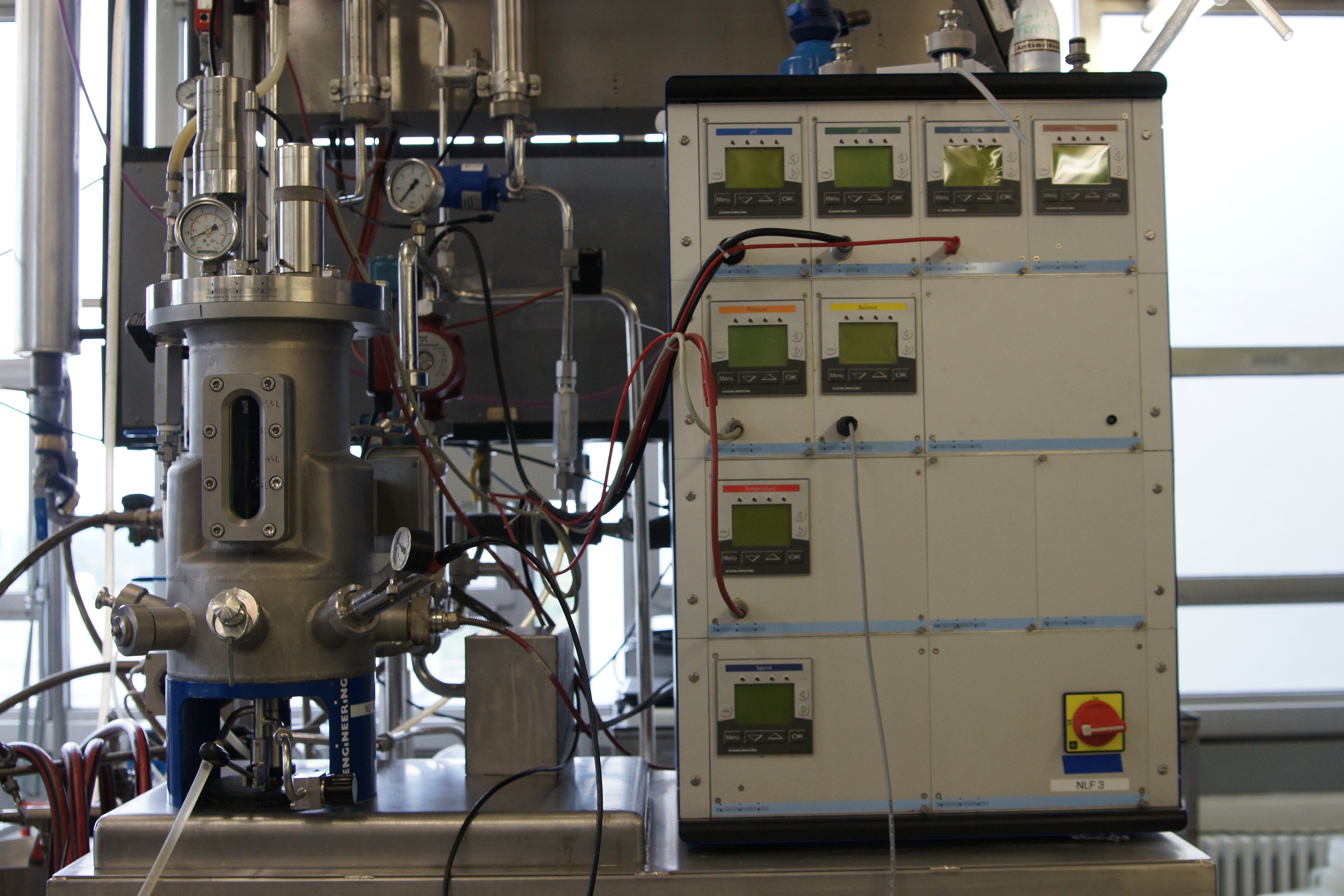
Bioreactors
For the production of the different laccases we used three different variations of bioreactors. These Bioreactors includes different kinds of sonsors:
- pO2
- pCO2
- pH
- airflow
- agitation
- temperatur
- antifoam/level
The process could be monitored and controlled by a bioreactor specific programm.
Infors labfors fermenter
Device specifications:
- Vessel: 3.6; total volume
- Speed range: 100–1200 rpm magnetic drive
- Temperature range: ~5°C above coolant to 60°C (water jacket)
- Pump flow rate: 0.001–1.4 mL/min (small-size tubing)
- Special features: autoclavable fermenter
- Standard parameters:
- Stirrer speed, temperature, pH, pO2, antifoam/level, feed, gas
mix, gas flow
Biostat B Bioreactor (3 L) by Braun
Device specifications:
- Vessel: 3,5; total volume
- Speed range: 100–1200 rpm magnetic drive
- Temperature range: ~5°C above coolant to 90°C (water jacket)
- Pump flow rate: 0.001–1.4 mL/min
- Special features: autoclavable fermenter
- Standard parameters:
- Stirrer speed, temperature, pH, pO2, antifoam/level, feed, gas mix, gas flow
Bioreactor NLF (7L) by BIOENGINEERING
Device specifications:
- Vessel: 7; total volume
- Speed range: 100–3000 rpm magnetic drive
- Temperature range: up to 150°C
- Pump flow rate: 50 mL/min
- Standard parameters:
- Stirrer speed, temperature, pH, pO2, antifoam/level, feed, gas
mix, gas flow
Media, buffer and other solutions
Ampicillin stock solution
- Solubilize 100 mg mL-1 Ampicillin
- Store at -20 °C
Chloramphenicol stock solution
- Solubilize 20 mg mL-1 Chloramphenicol in 100 % Ethanol
- Store at -20 °C
TAE buffer
For 1 L of 50 x TAE buffer you need:
- 242.48 g Tris
- 41.02 g Sodiumacetate
- 18.612 g EDTA
- Adjust pH to 7.8 with acetic acid
- Solve in dH2O
10 mL of the stock is diluted in 1 L dH2O for the gel electrophoresis (0.5 x TAE buffer).
Britton-Robinson Buffer
- 0,1 mM acetic acid
- 0,1 mM boric acid
- 0,1 mM phosphoric acid
- adjust to pH 5 with sodium hydroxide
DNA loading buffer
- 50 % (v/v) glycerol
- 1 mM EDTA
- 0.1 % (w/v) bromphenol blue
- Solve in ddH2O
LB medium
For 1 L of LB medum:
- 10 g Trypton
- 5 g Yeast extract
- 10 g NaCl
- 12 g Agar-Agar (for plates)
- Adjust pH to 7.4
HSG medium
- 14.9 g L-1 glycerine
- 13.5 g L-1 soy peptone
- 7 g L-1 yeast extract
- 2.5 g L-1 NaCl
- 2.3 g L-1 K2HPO4
- 1.5 g L-1 KH2PO4
- 0.249 g L-1 MgSO4 * 7 H2O
Autoinduction medium
The Autoinduction medium is based on LB-medium. Add the following components after heat sterilization of 900 mL LB medium.
- 5 mL of a 200 g L-1 steril L-rhamnose stock solution -> final concentration 2 g L-1
- 2.5 mL of a 200 g L-1 steril glucose stock solution -> final concentration 1 g L-1
- if necessary add antibiotics:
- Cm: 1 mL or 3 mL of a 20 μg mL-1 Cm stock solution -> final concentration 20 or 60 mg L-1
- Amp: 1 mL or 3 mL of a 100 μg mL-1 Amp stock solution -> final concentration 100 or 300 mg L-1
- fill up to 1 L with steril ddH2O
HSG Autoinduction medium
The medium is based on HSG-medium. Add the following components after heat sterilization of 900 mL HSG medium.
- 5 mL of a 200 g L-1 steril L-rhamnose stock solution -> final concentration 2 g L-1
- 2.5 mL of a 200 g L-1 steril glucose stock solution -> final concentration 1 g L-1
- if necessary add antibiotics:
- Cm: 1 mL or 3 mL of a 20 μg mL-1 Cm stock solution -> final concentration 20 or 60 mg L-1
- Amp: 1 mL or 3 mL of a 100 μg mL-1 Amp stock solution -> final concentration 100 or 300 mg L-1
- fill up to 1 L with steril ddH2O
SOC medium
- Add the following components to 900 ml of distilled H2O
- 20 g Bacto Tryptone
- 5 g Bacto Yeast Extract
- 2 ml of 5 M NaCl
- 2.5 ml of 1 M KCl
- 10 ml of 1 M MgCl2
- 10 ml of 1 M MgSO4
- 20 ml of 1 M glucose
- Adjust to 1L with distilled H2O
- Sterilize by autoclaving
YPD medium
For 1 L of YPD medium:
- 20 g Peptone
- 10 g Yeast extract
- 20 g Dextrose (add 50 mL sterile stock solution (40% dextrose))
- Adjust pH to 6.5
- For plates: add 17 g/L agar.
Yeast Nitrogen Base (YNB) 10x stock solution
- Dissolve 69 g Yeast Nitrogen Base (without aminoacids; with ammonium sulfat) in 500 mL bidest water and filter sterilize.
- Store at 4 °C.
- Durable for one year.
Biotin 500x stock solution
- Dissolve 20 mg biotin in 100 mL of 0.05 M NaOH solution and filter sterilize.
- Store at 4 °C.
- Durable for one year.
Minimal dextrose medium (MD)
Medium for selection of recombinant His+ clones For 1 L MD agar plates you need:
- Autoclave 2 g dextrose and 15 g agar
- add 100 mL sterile 10x YNB stock solution and
- 2 mL sterile 500x biotin stock solution.
Minimal methanol media (MM)
Medium for protein induction. For 1 L MM medium you need:
- 5 mL 100% methanol
- 100 mL sterile 10x YNB stock solution and
- 2 mL sterile 500x biotin stock solution.
- 893 mL sterile bidest. water
BEDS buffer
For 1 L of BEDS buffer:
- 1,85 g bicine-sodium salt,
- 30 mL ethylene glycol (final concentration 3%(v/v))
- 50 mL (v/v) dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)(final concentration 5%(v/v))
- 182.17 g sorbitol
- Adjust pH at 8,3
Dithiothreitol-Solution (DTT)
For 50mL of DTT-Solution:
- 7.71 g Dithiothreitol
special buffers for resuspending the cell pellet
for KRX and KRX with [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K863015 BBa_K863015] and [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K863005 BBa_K863005]:
- sodium acetate 100 mM
- adjust to pH 5
for KRX with [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K863010 BBa_K863010]:
- sodium acetate 20 mM
- adjust to pH 5
for KRX with [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K863000 BBa_K863000]: [http://www.aeisner.de/rezepte/puffer1.html Mc Ilvaine buffer]
- solution A: 21,01 g/L citric acid
- solution B: 35,60 g/L disodium phosphate dihydrate
- mix 38,6 mL of solution B and 61,4 mL of solution A
- adjust to pH 4
for KRX with [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K863020 BBa_K863020]:
- 1 mM CuSO4
- 15 mM PBS mit K2HPO4
- 100 mM NaCl
- adjust to pH 7 and shake before use
Buffers for His-Tag affinity chromatography
- Adjust pH to 7.4 - 7.6
Buffer for Ni-NTA-HisTag affinity chromatography
| Buffer | Sodium phosphate [mM] | Imidazole [mM] |
|---|---|---|
| Binding buffer | 50 | 20 |
| Elution buffer | 50 | 500 |
Buffer for Talon-HisTag affinity chromatography
| Buffer | Sodium phosphate [mM] | NaCl [mM] | Imidazole [mM] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binding buffer | 50 | 300 | 0 |
| Elution buffer | 50 | 300 | 150 |
SDS-PAGE gel
The following amouts are for one gel. Stacking gel 5 %:
- 775 μL H2O
- 1.25 mL 0,25 M Tris (pH 6,8)
- 425 μL Bis/Acrylamide (0,8 %, 30 %)
- 50 μL 5 % SDS
- 25 μL 10 % Ammonium persulfate
- 3 μL TEMED
Separating gel 12 %:
- 1.5 mL H2O
- 2.8 mL 1 M Tris (pH 8,8)
- 3.0 mL Bis/ Acrylamide (0,8%, 30%)
- 150 μL 5% SDS
- 37.5 μL 10% Ammonium persulfate
- 5 μL TEMED
SDS running buffer
- 25 mM Tris [pH 8,3]
- 192 mM Glycerol
- 0.1 % SDS
4x Laemmli-buffer
- 250 mM Tris-HCl
- 40 % [v/v] Glycerol
- 20 % [v/v] 2-Mercapthoethanol
- 80 g L-1 SDS
- 0.04 g L-1 BPB
Colloidal Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 staining solution
for 1 L staining solution
- dissolve 50 g L-1 (NH4)2SO4 in ddH2O
- add 10 % (v/v) ethanol
- dissolve 0.2 g L-1 Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250
- add 2 % (v/v) phosphoric acid
- fill up to 1 L with ddH2O
Fairbanks Coomassie staining solutions
Solution A:
- 25 % (v/v) ispropanol
- 10 % (v/v) acetic acid
- 0,5 g L-1 Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250
Solution B:
- 10 % (v/v) ispropanol
- 10 % (v/v) acetic acid
- 0,05 g L-1 Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250
Solution C:
- 10 % (v/v) acetic acid
- 0,025 g L-1 Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250
Solution D:
- 10 % (v/v) acetic acid
Solutions for Gibson assembly
5x isothermal reaction buffer for Gibson assembly
- 3 mL of 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.5)
- 150 µL of 2 M MgCl2
- 60 µL of 100 mM dGTP
- 60 µL of 100 mM dATP
- 60 µL of 100 mM dTTP
- 60 µL of 100 mM dCTP
- 300 µL of 1 M DTT
- 1.5 g PEG-8000
- 300 µL of 100 mM NAD
storage -20˚C
Hanks Buffered Saline Solution (HBSS)
- 0.137 M NaCl
- 5.4 mM KCl
- 0.25 mM Na2HPO4
- 0.44 mM KH2PO4
- 1.3 mM CaCl2
- 1.0 mM MgSO4
- 4.2 mM NaHCO3
Primers
This is a list of primers we have used.
| primer name | length | sequence |
|---|---|---|
| F | 28 | GTTTCTTCGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAG |
| R | 29 | GTTTCTTCCTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTA |
| pSB1C3-5aox1-f | 60 | CGCTAAGGATGATTTCTGGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAGAGATCTAACATCCAAAGACG |
| pSB1C3-5aox1-r | 30 | GGTGGCGGCGGGCGTTTCGAATAATTAGTT |
| 5aox1-mfalpha1-f | 68 | AGAAGATCAAAAAACAACTAATTATTCGAAACGCCCGCCGCCACCATGAGATTTCCTTCAATTTTTAC |
| 5aox1-mfalpha1-r | 20 | AGCTTCAGCCTCTCTTTTCT |
| mfalpha1-aarI-taox1-f | 80 | GTATCTCTCGAGAAAAGAGAGGCTGAAGCTACACGCAGGTGGTATGTATCACCTGCGTGTCT TGCTAGATTCTAATCAAG |
| mfalpha1-aarI-taox1-r | 20 | TAAGCTTGCACAAACGAACT |
| taox1-phis4-f | 60 | GTACAGAAGATTAAGTGAGAAGTTCGTTTGTGCAAGCTTATCATGCCATGGACAAGATTC |
| taox1-phis4-r | 20 | GGCCGCTCGAGTATTCAGAA |
| phis4-kozak-his4-f | 72 | AATAGTTTACAAAATTTTTTTTCTGAATACTCGAGCGGCCCCCGCCGCCACCATGACATTTCCCTTGCTACC |
| phis4-kozak-his4-r | 30 | TTATTATTTCTCCATACGAACCTTAACAGC |
| his4-3aox1-f | 60 | TCACCGCAATGCTGTTAAGGTTCGTATGGAGAAATAATAACGAGTATCTATGATTGGAAG |
| his4-3aox1-r | 20 | AAAACAAGATAGTGCCCCTC |
| 3aox1-pSB1C3-f | 60 | AGTCTGATCCTCATCAACTTGAGGGGCACTATCTTGTTTTTACTAGTAGCGGCCGCTGCA |
| 3aox1-pSB1C3-r | 20 | CTCTAGAAGCGGCCGCGAAT |
| taox-his4-f | 61 | GTACAGAAGATTAAGTGAGAAGTTCGTTTGTGCAAGCTTAAGATCTCCTGATGACTGACTC |
| taox-his4-r | 27 | CTCGGATCTATCGAATCTAAATGTAAG |
| his4-3aox1-f02 | 60 | TTATTTAGAGATTTTAACTTACATTTAGATTCGATAGATCCGAGTATCTATGATTGGAAG |
| his4_gi537483_f | 46 | ACGTgaattcgcggccgcttctagagAGATCTCCTGATGACTGACT |
| his4_gi537483_r | 41 | ctgcagcggccgctactagtaGATCTATCGAATCTAAATGT |
| 5'AOX_FW | 45 | ACGTgaattcgcggccgcttctagagAGATCTAACATCCAAAGACG |
| 5'AOX_RV | 41 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTACGTTTCGAATAATTAGTTGT |
| 3'AOX_FW | 45 | ACGTgaattcgcggccgcttctagagCGAGTATCTATGATTGGAA |
| 3'AOX_RV | 41 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTAAAAACAAGATAGTGCCCCTC |
| pAOX1_FW | 44 | ACGTgaattcgcggccgcttctagagcatccgacatccacaggtc |
| pAOX1_RV | 45 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTCTCAAGTTGTCGTTAAAAGTCG |
| tAOX1_FW | 45 | ACGTGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAGCTTGCTAGATTCTAATCAA |
| tAOX1_RV | 41 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATAAGCTTGCACAAACGAACT |
| Ko_alpha_FW | 58 | ACGTgaattcgcggccgcttctagagcccgccgccaccATGAGATTTCCTTCAATTTT |
| Ko_alpha_RV | 41 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTAAGCTTCAGCCTCTCTTTTCT |
| B.pumi_LAC_FW | 44 | ACGTGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGATGAACCTAGAAAAATTTGT |
| B.pumi_LAC_RV | 41 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTACTGGATGATATCCATCG |
| B.halo_FW | 44 | ACGTGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGATGAAAAAATCATATGGAGT |
| B.halo_RV | 41 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTACTCAGGCATATTTGGAA |
| T.thermo_LAC_FW | 44 | ACGTGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGATGCTGGCGCGCAGGAGCTT |
| T.thermo_LAC_RV | 41 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTACTAACCCACCTCGAGGACTC |
| E.coli_LAC_FW_T7 | 79 | ACGTGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAGtaatacgactcactatagggagagaggagaaaaATGCAACGTCGTGATTTCTT |
| E.coli_LAC_RV_HIS | 62 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTATTAGTGATGGTGATGGTGATGTACCGTAAACCCTAACA |
| Xcc_LAC_FW_T7 | 79 | ACGTGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAGtaatacgactcactatagggagagaggagaaaaATGTCATTCGATCCCTTGTC |
| Xcc_LAC_RV_HIS | 62 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTATTAGTGATGGTGATGGTGATGTGCCTCCACCCGCACTT |
| B.pumi_LAC_FW_T7 | 79 | ACGTGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAGtaatacgactcactatagggagagaggagaaaaATGAACCTAGAAAAATTTGT |
| B. pumi_LAC_RV_HIS | 62 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTATTAGTGATGGTGATGGTGATGCTGGATGATATCCATCG |
| E.coli_LAC_FW_T7 | 79 | ACGTGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAGtaatacgactcactatagggagagaggagaaaaATGCAACGTCGTGATTTCTT |
| E.coli_LAC_RV_HIS | 62 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTATTAGTGATGGTGATGGTGATGTACCGTAAACCCTAACA |
| T.thermo_LAC_FW_T7 | 79 | ACGTGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAGtaatacgactcactatagggagagaggagaaaaATGCTGGCGCGCAGGAGCTT |
| T.thermo_LAC_RV_HIS | 62 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTATTAGTGATGGTGATGGTGATGACCCACCTCGAGGACTC |
| Tv_lac5_FW_oS | 38 | acgtcacctgcgtgtagctggtatcggtcctgtcgccg |
| Tv_lac5_RV | 39 | acgtcacctgcgtgtcaagTTACTGGTCGCTCGGGTCGC |
| Tv_lac5.P.FW | 43 | gaattcgcggccgcttctagATGTCGAGGTTTCACTCTCTTCT |
| Tv_lac5.S.RV | 41 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTACTGGTCGCTCGGGTCGC |
| Pc_lac35.P.FW | 43 | gaattcgcggccgcttctagATGTCGAGGTTCCAGTCCCTCTT |
| Pc_lac35.S.RV | 41 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATCAGAGGTCGCTGGGGTCAA |
| Pc_lac35_FW_oS | 38 | acgtcacctgcgtgtagctgccatagggcctgtggcgg |
| Pc_lac35_RV | 39 | acgtcacctgcgtgtcaagTCAGAGGTCGCTGGGGTCAA |
| GFP_FW_SV | 39 | acgtcacctgcgtgtagctCGTAAAGGAGAAGAACTTTT |
| GFP_RV_SV | 41 | acgtcacctgcgtgtcaagTTATTTGTATAGTTCATCCATG |
| J23117_RBS_FW | 70 | aattcgcggccgcttctagagttgacagctagctcagtcctagggattgtgctagcaaagaggagaaata |
| J23117_RBS_RV | 70 | ctagtatttctcctctttgctagcacaatccctaggactgagctagctgtcaactctagaagcggccgcg |
| J23103_RBS_FW | 70 | aattcgcggccgcttctagagctgatagctagctcagtcctagggattatgctagcaaagaggagaaata |
| J23103_RBS_RV | 70 | ctagtatttctcctctttGCTAGCATAATCCCTAGGACTGAGCTAGCTATCAGctctagaagcggccgcg |
| J23110_RBS_FW | 70 | aattcgcggccgcttctagagtttacggctagctcagtcctaggtacaatgctagcaaagaggagaaata |
| J23110_RBS_RV | 70 | ctagtatttctcctctttgctagcattgtacctaggactgagctagccgtaaactctagaagcggccgcg |
| J23103_K_FW | 25 | CTGACAGCTAGCTCAGTCCTAGGTA |
| J23110/117_K_FW | 25 | TTTACGGCTAGCTCAGTCCTAGGTA |
| T7_K_FW | 26 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAAAGAG |
| CBDcex_2AS-Link_Frei | 56 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTAACCGGTGCTGCCGCCGACCGTGCAGGGCGTGC |
| CBDcex_Freiburg-Prefix | 54 | GCTAGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGATGGCCGGCGGTCCGGCCGGGTGCCAGGTG |
| CBDcex_T7RBS | 80 | TGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAAAGAGGAGAAATAATGGGT CCGGCCGGGTGCCAGGT |
| CBDclos_2ASlink_compl | 63 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTAACCGGTGCTGCCTGCAAATCCAAATTCAACATATGTATC |
| CBDclos_Freiburg-Prefix | 57 | GCTAGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGATGGCCGGCTCATCAATGTCAGTTGAATTTTAC |
| CBDclos_T7RBS | 73 | CCGCTTCTAGAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAAAGAGGAGAAATAATGTCAGTTGAATTTTACAACTCTAAC |
| Cex_Freiburg_compl | 54 | ACGTCTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTAACCGGTGCCGACCGTGCAGGGCGTGC |
| Clos_Freiburg_compl | 56 | ACGTCTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTAACCGGTTGCAAATCCAAATTCAACATAT |
| Eco_Freiburg | 53 | ACGTGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGATGGCCGGCCAACGTCGTGATTTCTTAAA |
| Eco_Freiburg_compl | 53 | ACGTCTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTAACCGGTTACCGTAAACCCTAACATC |
| GFP_Frei | 54 | TACGGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGATGGCCGGCATGCGTAAAGGAGAAGAACTT |
| GFP_Freiburg | 54 | ACGTGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGATGGCCGGCCGTAAAGGAGAAGAACTTTTC |
| GFP_Freiburg_compl | 61 | ACGTCTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTAACCGGTTTTGTATAGTTCATCCATGCCATGTGT |
| GFP_His6_compl | 74 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTAACCGGTGTGATGGTGATGGTGATGTTTGTATAGTTCATCCATGCCATGTG |
| GFP_FW | 48 | ATGCGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAGTCCCTATCAGTGATAGAGATTG |
| S3N10_Cex_compl | 40 | TTGTTGTTGTTCGAGCTCGAGCCGACCGTGCAGGGCGTGC |
| S3N10_Clos_compl | 40 | TTGTTGTTGTTCGAGCTCGAGCTGCCGCCGACCGTGCAGG |
| S3N10_GFP | 40 | CAATAACAATAACAACAACCGTAAAGGAGAAGAACTTTTC |
| 5AOX-Phenotype-FW | 21 | GACTGGTTCCAATTGACAAGC |
| TT-Phenotype-RV | 21 | GCAAATGGCATTCTGACATCC |
| A.th_cDNA_FW_T7 | 79 | ACGTgaattcgcggccgcttctagagtaatacgactcactatagggaaagaggagaaaaATGTCACATTCCTTCTTCAA |
| A.th_cDNA_HIS_RV | 62 | CTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTATTAGTGATGGTGATGGTGATGTTCATAGCAAGGCGGCA |
Used enzymes
| Enzyme | Producer |
|---|---|
| AarI | [http://www.fermentas.de/product_info.php?info=p166&language=de Fermentas] |
| AgeI | [http://www.fermentas.de/product_info.php?info=p247 Fermentas] |
| DpnI | [http://www.fermentas.de/product_info.php?info=p296 Fermentas] |
| EcoRI | [http://www.fermentas.de/product_info.php?info=p336 Fermentas] |
| GoTaq DNA-polymerase | [http://www.promega.com/products/pcr/routine-pcr/gotaq-pcr-core-systems/ Promega] |
| NgoMIV | [http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/productR0564.asp NEB] |
| lysozym | [http://www.carlroth.com/catalogue/catalogue.do;jsessionid=488EF42170F5810F6A64C9ED26264DD7?favOid=000000010000a36800020023&act=showBookmark&lang=de-de&market=AT Carl Roth] |
| Pfu DNA-polymerase | [http://www.promega.com/products/pcr/routine-pcr/pfu-dna-polymerase/ Promega] |
| PstI | [http://www.fermentas.de/product_info.php?info=p458 Fermentas] |
| Phusion HF DNA-polymerase | [http://www.finnzymes.com/pcr/phusion_high_fidelity_dna_polymerase.html Finnzymes] |
| Shrimp alkaline phosphatase | [http://www.fermentas.de/product_info.php?info=p592 Fermentas] |
| SpeI | [http://www.fermentas.de/product_info.php?info=p202 Fermentas] |
| T4-DNA-Ligase | [http://www.fermentas.de/product_info.php?info=p580 Fermentas] |
| BIOTAQ DNA-polymerase | [http://www.bioline.com/h_prod_detail.asp?itemid=219 Bioline] |
| XbaI | [http://www.fermentas.de/product_info.php?info=p247 Fermentas] |
| T5 exonuclease | [http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/productM0363.asp NEB] |
| taq DNA Ligase | [http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/productM0208.asp NEB] |
| PvuII | [http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/productr0151.asp NEB] |
| HindIII | [http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/productr0104.asp NEB] |
| KOD Hot Start DNA Polymerase | [http://www.merckmillipore.com/germany/life-science-research/kod-hot-start-dna-polymerase/EMD_BIO-71086/p_iFCb.s1O874AAAEj2Bl9.zLX Merck Millipore] |
| NotI | [http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/productr0189.asp NEB] |
Used Kits
| Function | Name |
|---|---|
| Plasmid purification | [http://www.fermentas.de/product_info.php?info=p874 Fermentas GeneJET™ Plasmid Miniprep Kit] |
| Plasmid purification | [http://www.promega.com/b/de/minis/default.aspx?utm_source=Promega&utm_medium=Online&utm_campaign=Online_DEPureYield100Preps_Promega_HP_Banner Promega PureYield™ Plasmid Preps] |
| PCR Cleanup | [http://www.promega.com/products/dna-and-rna-purification/dna-fragment-purification/wizard-sv-gel-and-pcr-clean_up-system/ Promega Wizard® SV Gel and PCR Clean-Up] |
| PCR core system | [http://www.promega.com/products/pcr/routine-pcr/gotaq-pcr-core-systems/ Promega GoTaq® PCR Core System I] |
| Protein quantitation | [http://www.carlroth.com/media/_nl-nl/usage/K880.pdf Roti®-Nanoquant] |
| gDNA Isolation | [http://www.promega.com/resources/protocols/technical-manuals/0/wizard-genomic-dna-purification-kit-protocol/ Promega Wizard genomic DNA purification system kit] |
Substrates
Hormones
Analgesics
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- [http://www.merckmillipore.com/chemicals/naphthalene/MDA_CHEM-820846/p_Kreb.s1LaPgAAAEWeOEfVhTl Naphthalin]
- Acenaphthen
- Phenanthren
- Anthracen
Used chemicals
| 55px | | | | | | | | | | |
 "
"