Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Modell
From 2012.igem.org
Contents |
Model of a fluidized bed reactor
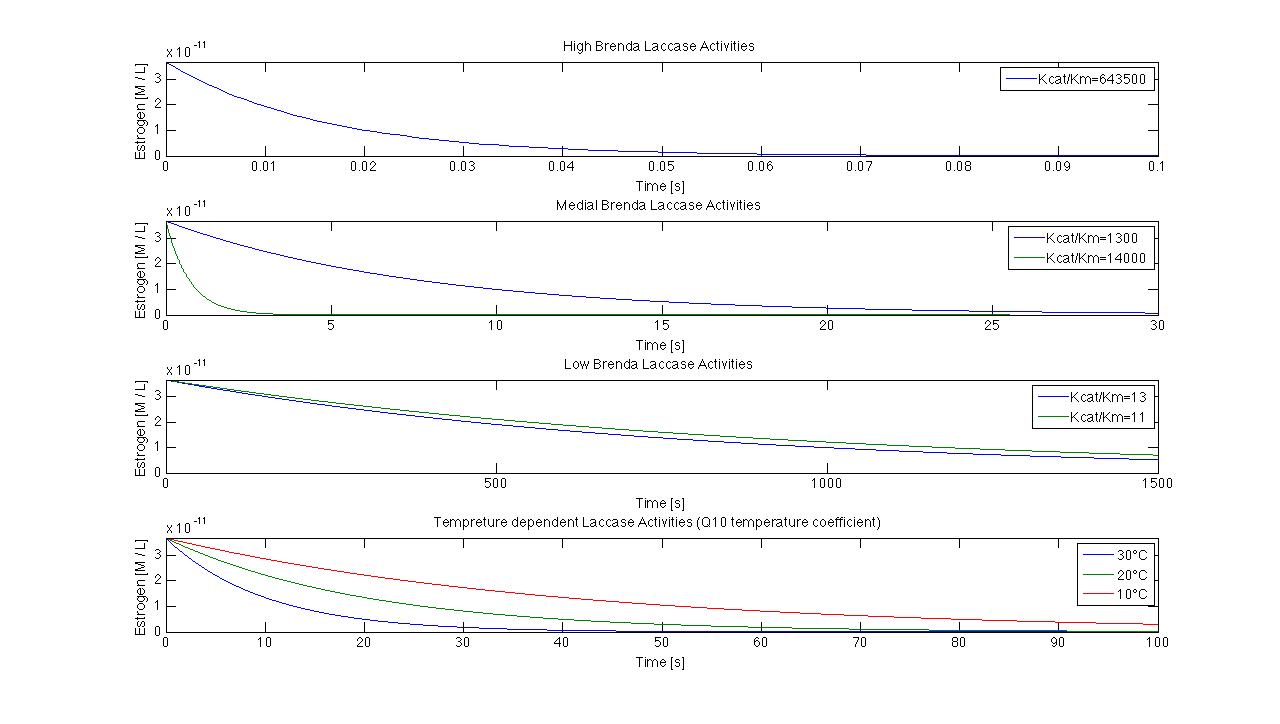
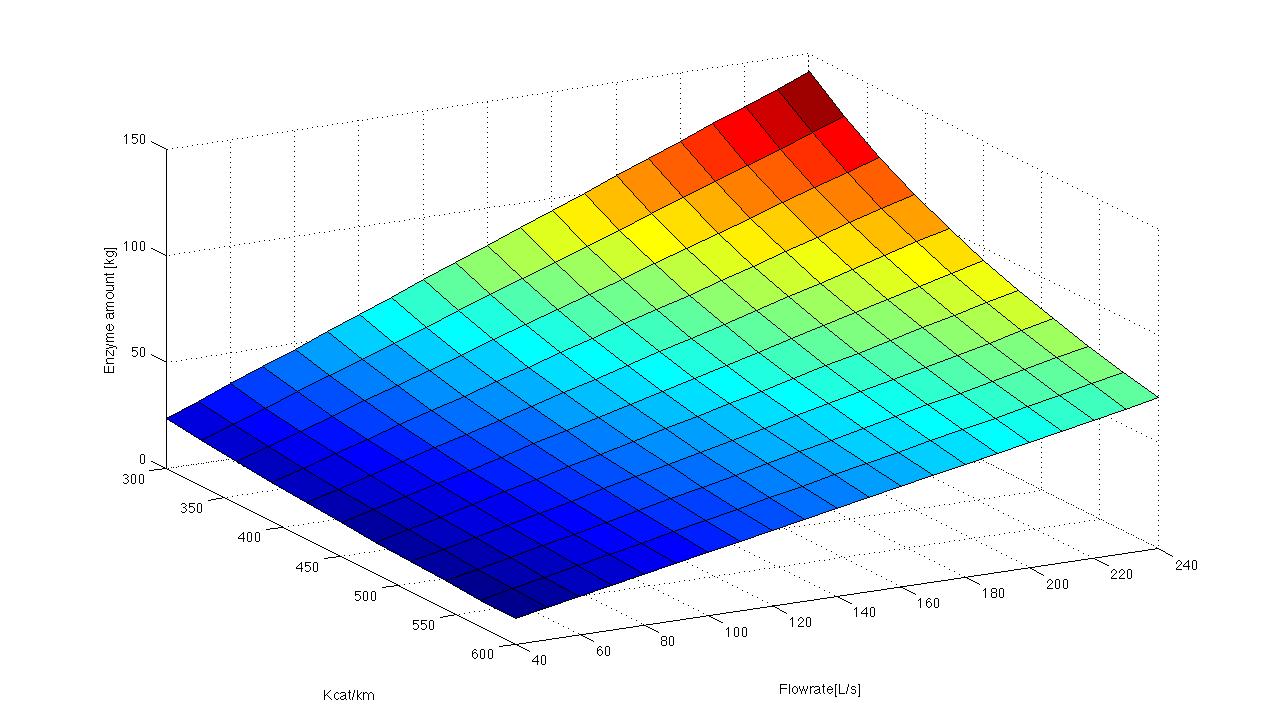
In our project we plan to construct a fluidized bed reactor, where immobilized laccases degrade synthetic estrogen and other harmful substances. As a small selection we plan to caracterize our different laccases for three estrogens, three analgesics, four PAH´s, one insecticide and three possible redox mediators. If we could model the degradation of one substrate by one Laccase, we could easily replace the specific Kcat/Km quotient for another Laccase andand the amounts oft he other substrates.
We ignore the possible cofactors ABTS, syringaldazine and viuloric acid, because on the one hand thy would cause increase the costs, and one the other hand they are harmful substances too. As shown by Team Substrate Analytic TVEL0 degrades ethinyl estradiol without reox mediator. So the reaction should follow the michaelis menten kinetics.
The reaction
File:Bielefeld2012 MM.png This transformation can be found in "Stryer biochemie". This formula is suitable for very low substrate concentrations. In this case we can estimate the substrate concentrations to [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3345074/table/T5| 1.89 ng L-1].
Extend the model with sewageplant data
Testing the model
Laborkläranlage
| 55px | | | | | | | | | | |
 "
"