Team:TU-Delft/HP/Study
From 2012.igem.org

For our Human Practice we did a study in to what extent our proof of principle, if it would be translated into a product, could make a difference. To answer this we evaluate the most important parts of this question below.
What is Tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection. TB usually attacks the lungs, but can also attack other parts of the body, such as the brain, spine, or kidneys. TB bacteria can live in the body without making a person sick. This is called latent TB infection. People with latent TB infection do not feel sick, do not have TB symptoms, and cannot spread TB bacteria to others. Some people with latent TB infection go on to develop TB disease.
TB becomes even a larger problem because of HIV, 60.1% of TB patients tested for HIV were HIV-positive. HIV-patients with TB have to be cured even faster because of their immune system is weakened.
In 2010, 8.8 million people were infected with TB and 1.4 million died from it. Over 95% of TB deaths occur in low -and middle- income countries.

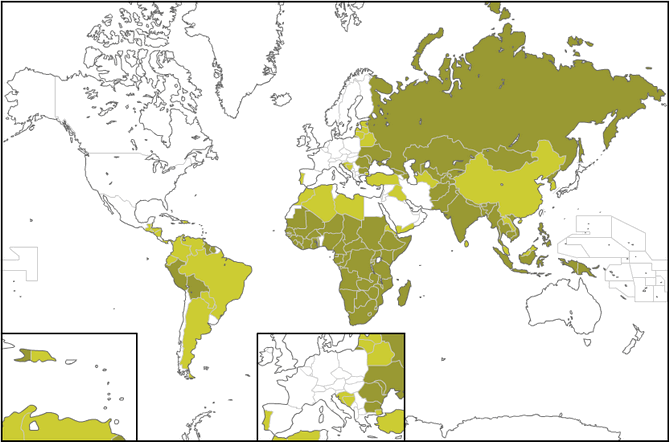
At the map below you can see the countries suffering from Tuberculosis. According to www.vaccinatiesopreis.nl the dark green refers to many cases of TB, the light green to less and the white to a few cases.
The problem
The problem of tuberculosis lies mainly in the less developed countries. The frontline are the remote areas where the people have no or limited access to hospitals with sufficient facilities. Standard TB diagnostic tools are either expensive and need to be used in a lab setting or are not very reliable, all these reasons are posing major barriers for diagnosing.
Six Ways to Diagnose Tuberculosis
These are six main diagnosis tools for TB. The problem is that there is not one of them that is very reliable and also suitable for the frontline. Not suitable for the frontline because it needs facilities, doesn't give a quick result and/or is expensive.
- Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)
- Sputum Smear Microscopy (SSM)
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- Blood Test for TB detection
- Chest X-ray
- Culture
Our ideal Solution
A cheap test that quickly gives an reliable result, that can be taken by a 4x4 car to the people.
What would a test based on our principle contribute?
Reach
Yeast cells can be kept in dried form, which makes them very well transportable and easy to store. Remote areas can be easily reached.Evaluating of test result
Now we did the tests with GFP but if would use a visible output, it would be very easy to see a result. Which also mean that there are not many facilities needed.Cheap
The producing of a large amount of yeast cells is in general not this expensive.Reliability
This is something that should still be evaluated.Waiting time
The waiting time for the result will be approximately 3 hours.Conclusion
We strongly believe that our project is well worth to be further developed. We believe it can make a change in how diagnostics in remote areas take place. But also for areas with facilities, it can be a cheap alternative for the diagnosing of other diseases that can be detected by specific compounds.
Example Mozambique; lack of facilities
Mozambique ranks the 19th among the 22 Tuberculosis High Burden Countries 2011 according to the WHO.One of our team members, Isabelle, traveled to Mozambique in july 2011. The lack of the diagnostic capacity is very clear at the hospital of Ilha de Mocambique. Ilha de Mocambique inhabits 14.000 people and they are relying on the hospital there. This picture of the Hospital is taken in july 2011. In contrary to what Wikipedia states, part of this building is still being used as a hospital.


 "
"