Team:TU-Delft/Snifferometer
From 2012.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Design of Snifferometer) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Scheme of the Device == | == Scheme of the Device == | ||
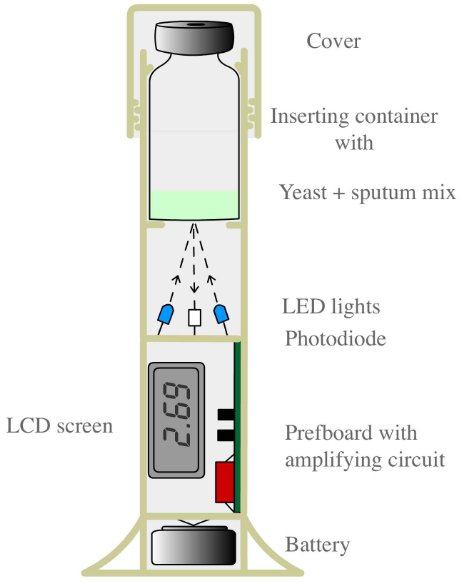
[[File:Scheme of snifferometer.png|270px|left|thumb|'''Figure 1''': Scheme of Snifferometer]] | [[File:Scheme of snifferometer.png|270px|left|thumb|'''Figure 1''': Scheme of Snifferometer]] | ||
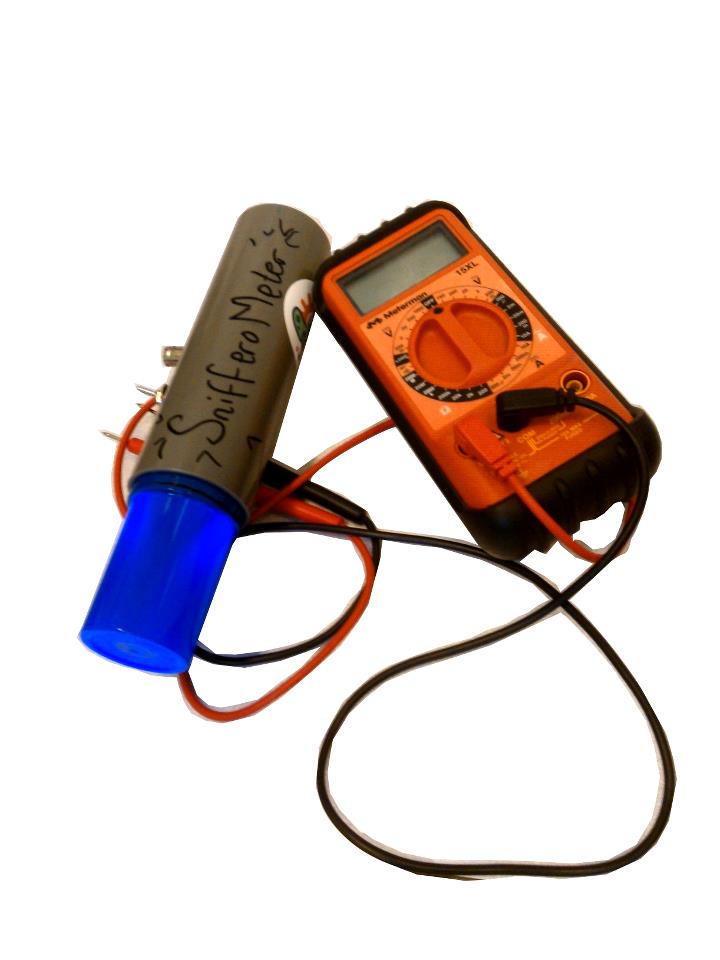
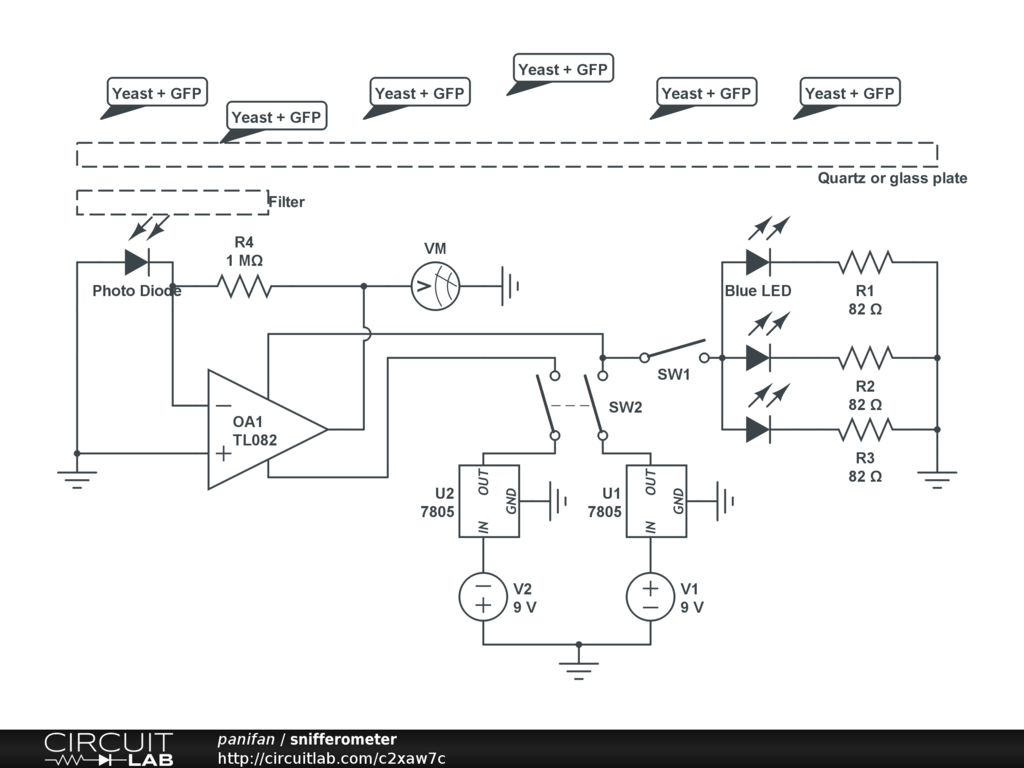
| - | [[File:snifferometer device.png|250px|right|thumb|'''Figure 2''': Snifferometer]] | + | [[File:snifferometer device.png|250px|right|thumb|'''Figure 2''': Real Snifferometer]] |
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 14:15, 26 October 2012

In order to assess the feasibility using our Snifferomyces cells as a diagnosis method, a device called "Snifferometer" was built to measure the status of fluorescence.
Contents |
Design of Snifferometer
Scheme of the Device
Test
Eppendorf tubes are used to contain the liquid.
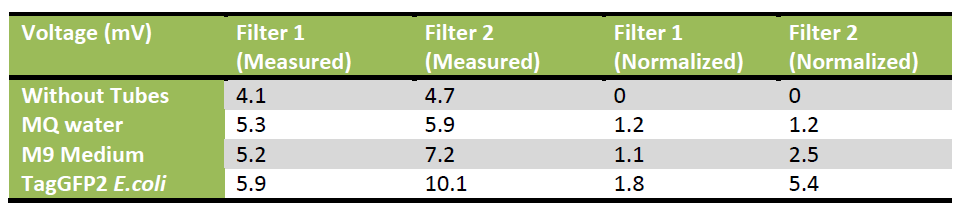
Two filters were tested:
- [http://www.leefilters.com/lighting/colour-details.html#768 LEE Filters 768 Egg yellow].
- [http://www.leefilters.com/lighting/colour-details.html#101 LEE Filters 101 yellow].
Four sets
- Control: M9 medium with E-coli
- Test: M9 medium with E-coli overexpressing TagGFP2
M9 medium is used because it has low autofluorescence.
- reduce background light intensity: right filter
- increase green light intensity
- increase the sensitivity of the circuit
- enlarge the area of fluorescent

 "
"