Team:Paris Bettencourt/Encapsulation
From 2012.igem.org
Iversondylan (Talk | contribs) |
Iversondylan (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
'''Experimental system:''' | '''Experimental system:''' | ||
| - | We used a [https://2012.igem.org/Team:Paris_Bettencourt/Encapsulation#Cell_Containment_Assay cell containment assay] based on plating to assess the release of cells from alginate beads. One method for improving the entrapment of cells involves stabilization by polyethyleneimine and covalent cross-linkage by glutaraldehyde. Untreated 2% alginate beads and beads treated by this method were incubated in PBS buffer | + | We used a [https://2012.igem.org/Team:Paris_Bettencourt/Encapsulation#Cell_Containment_Assay cell containment assay] based on plating to assess the release of cells from alginate beads. One method for improving the entrapment of cells involves stabilization by polyethyleneimine and covalent cross-linkage by glutaraldehyde. Untreated 2% alginate beads and beads treated by this method were incubated in PBS buffer for several days, plating each day. Also, to try to discover if more viable cells could be released based on destruction of beads, we assayed another batch of beads cut apart using a razor blade. |
| + | |||
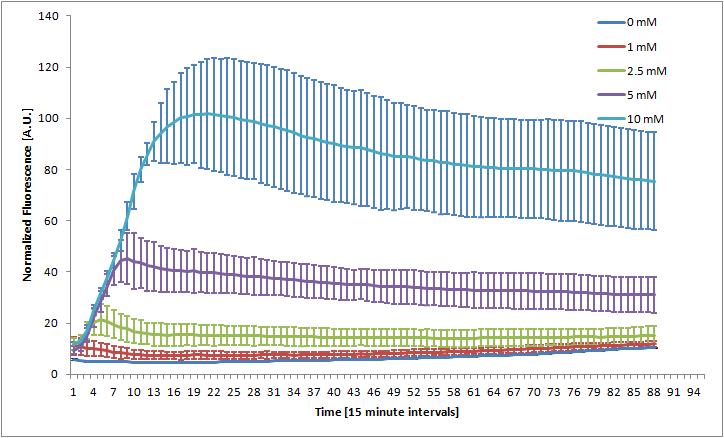
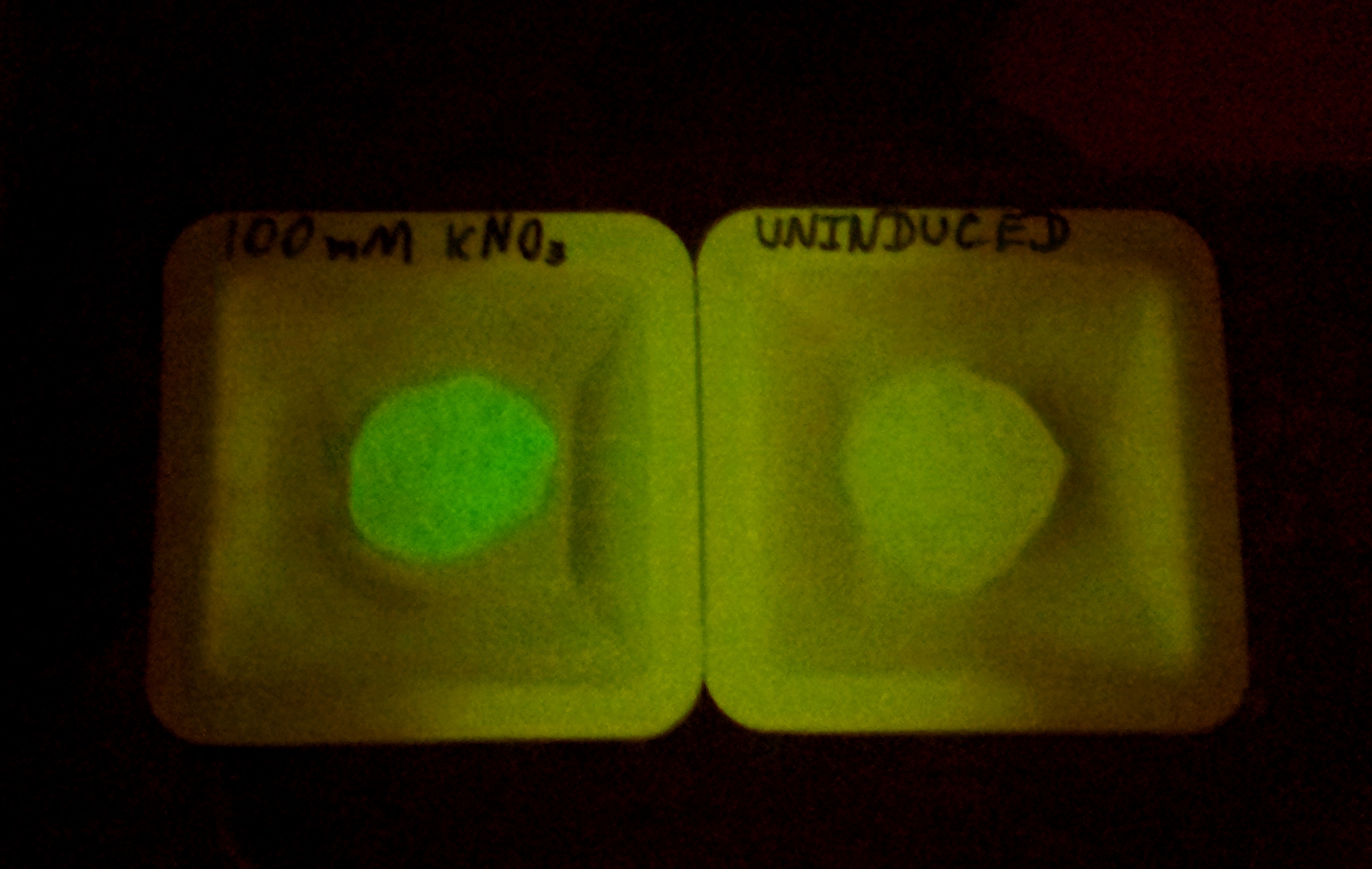
| + | We performed additional characterization of the Bristol 2010 nitrate reporter. Diluted cultures with different KNO3 induction levels were monitored for GFP and OD600 over time. | ||
Revision as of 00:00, 27 September 2012
|
Aim : We want to use bacteria-containing gel beads to enhance cell containment and complement activity of genetic safety systems. Experimental system: We used a cell containment assay based on plating to assess the release of cells from alginate beads. One method for improving the entrapment of cells involves stabilization by polyethyleneimine and covalent cross-linkage by glutaraldehyde. Untreated 2% alginate beads and beads treated by this method were incubated in PBS buffer for several days, plating each day. Also, to try to discover if more viable cells could be released based on destruction of beads, we assayed another batch of beads cut apart using a razor blade. We performed additional characterization of the Bristol 2010 nitrate reporter. Diluted cultures with different KNO3 induction levels were monitored for GFP and OD600 over time.
|
Contents |
Overview
Polymer gels have found a place in microbial biotechnology by providing a means of spatial organization. The micro-environments within gel beads can grant the microbes within protection, nutrients, and selective agents/chemicals. Given this, gel beads are already attractive for environmental applications of genetically modified bacteria. Synthetic bacterial systems may benefit from (or require) nutrients and agents added to gel beads. Many other practical reasons for use of beads exist, such as transportation and analysis.
Our interest is to take the concept of cell encapsulation further by implementing total cell entrapment. While normal gel beads protect the bacteria within from the surroundings, we are here to ensure the surroundings are protected from the bacteria within the beads. A method was found for encapsulation and entrapment of yeast [REF] and was adapted to synthetic bacterial systems.
Objectives
Our goal is to design a live-bacteria entrapment system. More than just encapsulating bacteria, we want to fully prevent their escape from the bead body into the surroundings.
Alginate and other gel-based beads have been used successfully to prolong enzymatic activity in bioreactors[REF], but systems such as these are usually designed to allow steady release of microbes. This is not acceptable when microbes containing potentially dangerous synthetic genes are being used in the environment, so we aim to prevent release of bacteria entirely.
Design
Experiments and results
Cell Containment Assay
Our objective is to entrap cells that are still viable and able to perform metabolism. To asses this, beads were suspended in buffer and allowed to incubate at room temperature over several days. Presuming that treated beads could result in total cell containment, we wished to see if more viable cells would be released by physically destroying the beads.
Experimental setup
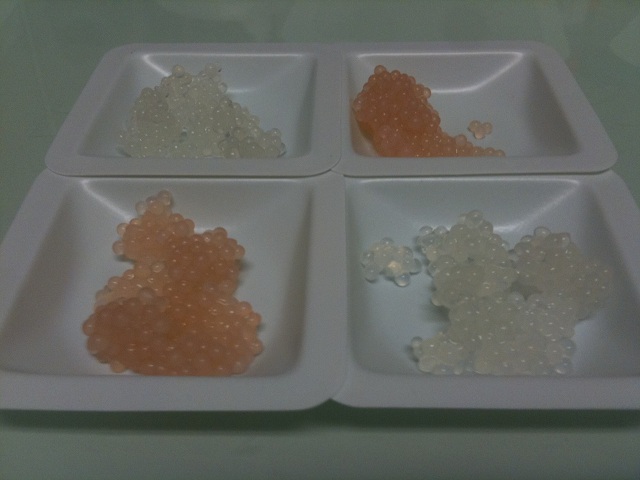
- 2% Alginate beads containing cells were prepared (50mL saturated culture resuspended in 15 mL fresh LB and mixed with 15 mL 4% Alginate).
- 4g beads were set aside in PBS at 4° as a negative control for containment (untreated alginate).
- 8g beads were treated as described above with polyethyleneimine and glutaraldehyde.
- 4g of treated beads were broken by cutting with a razor blade
- 4g of Untreated, Treated, and Treated & Broken beads were suspended in PBS buffer and left at room temperature.
- 100μL of supernatant was plated periodically to quantify release of cells.
Results
| Days | Untreated | Treated | Treated + Cut |
| 0 | 8300 | 3 | 7 |
| 1 | 62300 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | high | 0 | 20 |
Perspectives
This method for stabilization of beads was adapted from a method designed for yeast cells. Although the system appears effective at preventing cell release, we are concerned that the treatment method is lethal for cells. We need to follow up the cell containment assay with cell activity assays to assure that we have living cells capable of performing their intended function. This may include a white-blue screening assay to see if cells are capable of protein production within.
Further Experiments
Since our aim is to provide a safety system that will work with any microbial system, we will continue efforts to characterize functioning SynBio systems within stabilized beads. These experiments could involve biosensors such as Bristol 2010’s nitrate reporter, our own biosafety systems, or other iGEM biobrick systems.
Bristol 2010 Nitrate Reporter
 "
"


 Overview
Overview Delay system
Delay system Semantic containment
Semantic containment Restriction enzyme system
Restriction enzyme system MAGE
MAGE Encapsulation
Encapsulation Synthetic import domain
Synthetic import domain Safety Questions
Safety Questions Safety Assessment
Safety Assessment