Team:TU-Delft/Modeling
From 2012.igem.org
(→Overview) |
|||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
To achieve the stated objectives, three different models were built encompassing the different aspects of the project. | To achieve the stated objectives, three different models were built encompassing the different aspects of the project. | ||
| + | Techniques: ODE, SDE, PDE | ||
| + | Tools: MATLAB, COPASI, Aspen | ||
= Diffusion Model = | = Diffusion Model = | ||
Revision as of 09:38, 25 September 2012


Mathematical models in biology like in every other field, is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. Models have become indispensable tools, aiding researchers express their scientific knowledge.
Contents |
Overview
We decided to use the modeling expertise of the team members to achieve three key objectives for this years project.
- Develop scientific understanding of the yeast pheromone response pathway.
- Test the effects of the changes to the system.
- Aid decision making in the laboratory.
To achieve the stated objectives, three different models were built encompassing the different aspects of the project.
Techniques: ODE, SDE, PDE Tools: MATLAB, COPASI, Aspen
Diffusion Model
Pathway Model
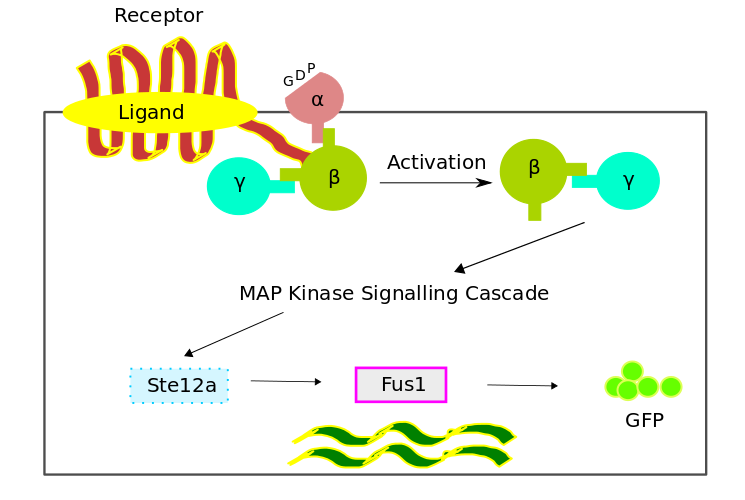
The bio-chemical pathway model was developed based on a scheme favouring the temporal order of the processes, which involved the four fundamental modules,
- Receptor Activation
- G - Protein Cycle
- MAPK Cascade
- Gene Expression
Three different models were used for the analysis of different aspects of the pathway. The dynamics of the system in these models were described using a set of differential equations governing the concentration changes of individual components and of complexes over time.On account of the gene expression module being noisy, a stochastic model of the gene expression module was implemented using stochastic differential equations.
Sensitivity and stability analysis were permformed to determine the sensitivity coefficients which were used to study the parametric dependence of the biological models. The results from the sensitivity analysis were then used in the parameter estimation to fit the model to the data provided by the experimentalists.
Structural Model

 "
"