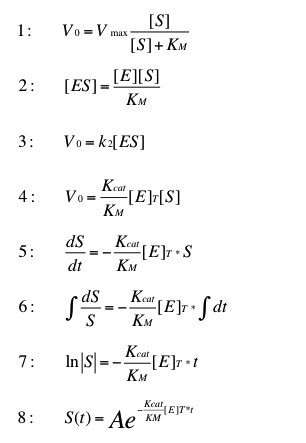Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Modell
From 2012.igem.org
(→The reaction) |
(→Extend the model with sewageplant data) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
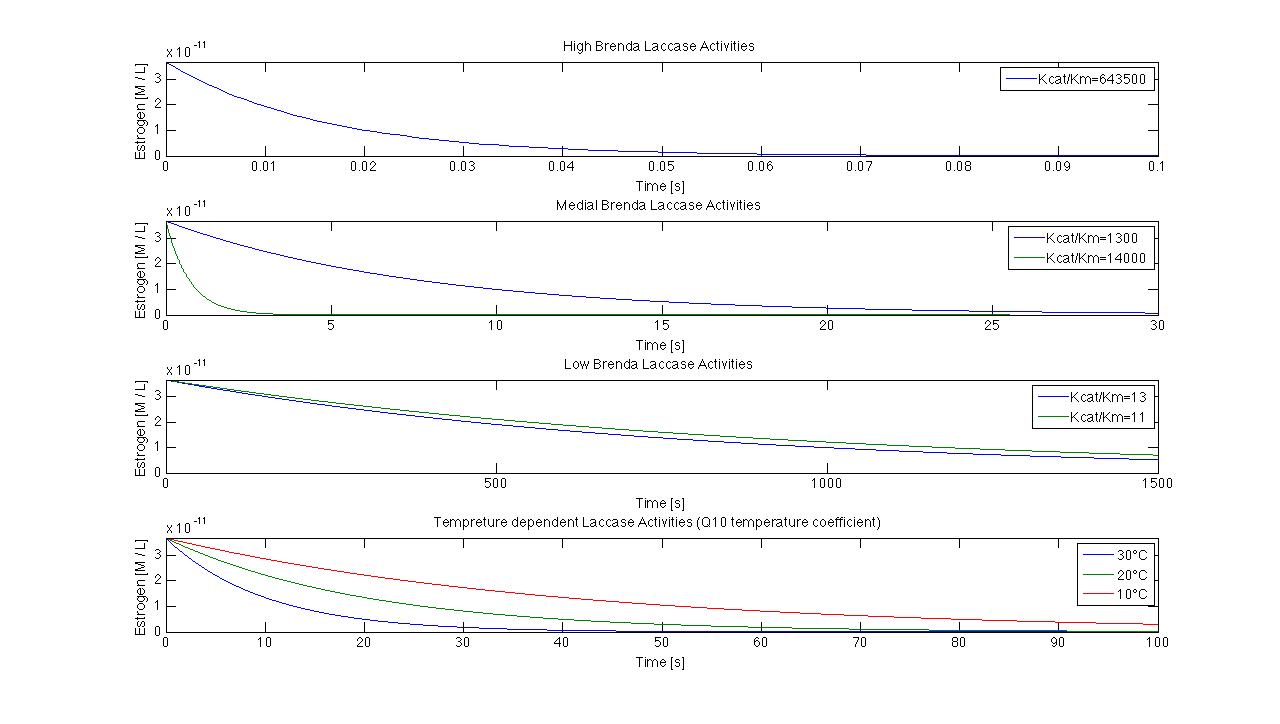
[[File:Bielefeld2012_Schlossholte_Daten.jpg|600px|thumb|left|Sewageplant data from Schlossholte. Temperature minimum: 8.1 °C, maximum: 20,8 °C and average temperature 14.4 °C; pH minimum: 6.6, maximum: 7.2 and average 6.9; flow minimum: 39.2 L s<sup>-1</sup>, maximum 232.8 L s<sup>-1</sup> and avarage 76.8 L s<sup>-1</sup>]] | [[File:Bielefeld2012_Schlossholte_Daten.jpg|600px|thumb|left|Sewageplant data from Schlossholte. Temperature minimum: 8.1 °C, maximum: 20,8 °C and average temperature 14.4 °C; pH minimum: 6.6, maximum: 7.2 and average 6.9; flow minimum: 39.2 L s<sup>-1</sup>, maximum 232.8 L s<sup>-1</sup> and avarage 76.8 L s<sup>-1</sup>]] | ||
| + | We got discharge water data from Schlossholte about the water tempreture, pH value and flowrate. The temperature and pH value have a direct influence of enzymatic activity. Dependent on the enzymatic activity we want to calculate the time our fixed-bed reactor will need to degrdate 80 % of the substrates. This will be the dewll time. Combined with the actual flowrate we can determine the reactorsize. With a previously set enzyme concentration we could now | ||
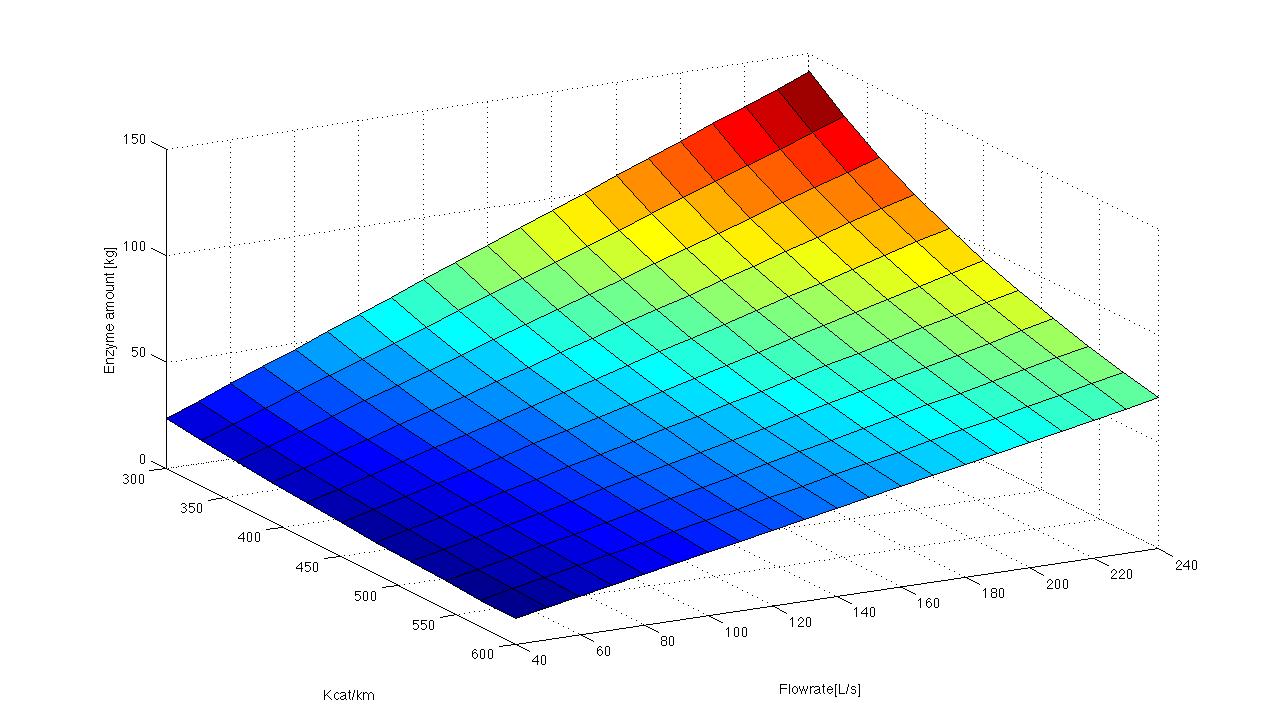
[[File:Bielefeld2012_3d.jpg|600px|thumb|left|The required enzyme amount for a sewageplant is dependent on K<sub>cat</sub> K<sub>M</sub><sup>-1</sup> and the flow rate]] | [[File:Bielefeld2012_3d.jpg|600px|thumb|left|The required enzyme amount for a sewageplant is dependent on K<sub>cat</sub> K<sub>M</sub><sup>-1</sup> and the flow rate]] | ||
Revision as of 19:13, 26 September 2012
Contents |
Model of a fixed-bed reactor
In our project we plan to construct a fixed-bed reactor, where immobilized laccases degrade synthetic estrogen and other harmful substances. As a small selection we plan to caracterize our different laccases for three estrogens, three analgesics, four PAH´s, one insecticide and three possible redox mediators. If we could model the degradation of one substrate by one Laccase, we could easily replace the specific Kcat KM-1 quotient for another Laccase and the amounts of the other substrates.
We ignore the possible cofactors ABTS, syringaldazine and viuloric acid, because on the one hand thy would cause increase the costs, and one the other hand they are harmful substances too. As shown by Team Substrate Analytic TVEL0 degrades ethinyl estradiol without reox mediator. So the reaction should follow the michaelis menten kinetics.
The reaction
This transformation can be found in "Stryer biochemie". This formula is suitable for very low substrate concentrations. In this case we can estimate the substrate concentrations to 1.89 ng L-1.
Extend the model with sewageplant data
We got discharge water data from Schlossholte about the water tempreture, pH value and flowrate. The temperature and pH value have a direct influence of enzymatic activity. Dependent on the enzymatic activity we want to calculate the time our fixed-bed reactor will need to degrdate 80 % of the substrates. This will be the dewll time. Combined with the actual flowrate we can determine the reactorsize. With a previously set enzyme concentration we could now
Outlook
"Team Substrate Analytic" will determine Kcat KM-1. Additionaly we have the opportunity to work with a lab sewageplant. So we´re going to test our model in defined conditions.
| 55px | | | | | | | | | | |
 "
"