Team:NTU-Taida/PEPDEX
From 2012.igem.org
(→3. Post-Segregation Killing:srnBC toxin-antitoxin system) |
|||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
:No matter how well partition system and multimer resolution system work, inevitably there still will have some bacteria losing plasmid. We sentence them to death to solve the problem. | :No matter how well partition system and multimer resolution system work, inevitably there still will have some bacteria losing plasmid. We sentence them to death to solve the problem. | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | {{multiple image | |
| - | + | | width = 100 | |
| + | | footer = ...... | ||
| + | | image1 = FIle:NTU-Taida-TAgrenade.png | ||
| + | | alt1 = Yellow cartouche | ||
| + | | caption1 = Caution | ||
| + | | image2 = FIle:NTU-Taida-bacteria-work-hard.png|Work hard or Die hard!!! | ||
| + | | alt2 = Red cartouche | ||
| + | | caption2 = Ejection | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
:Type I toxin-antitoxin srnBC is an ideal executor which belongs to hok/sok homologues, it expresses stable toxin encoded RNA and short lived antitoxin RNA that can neutralize toxin RNA by RNA interaction and RNase III cleavage. It acts as post segregation killing system, which kills bacteria when it loss the DNA(genomic islands, plasmids, mobile gene elements) that contains it. Therefore we use it to reduce plasmid loss rate and make applications without antibiotic selection more feasible. | :Type I toxin-antitoxin srnBC is an ideal executor which belongs to hok/sok homologues, it expresses stable toxin encoded RNA and short lived antitoxin RNA that can neutralize toxin RNA by RNA interaction and RNase III cleavage. It acts as post segregation killing system, which kills bacteria when it loss the DNA(genomic islands, plasmids, mobile gene elements) that contains it. Therefore we use it to reduce plasmid loss rate and make applications without antibiotic selection more feasible. | ||
Revision as of 12:38, 25 September 2012
Circuit
The main circuit is designed to detect the presence of fatty acid in the intestinal environment and produce the peptide drug (GLP-1 in this case) and cell penetrating peptide (CPP) as response. There are two core systems: double repressors and quorum sensing.
Stability and Safety
Every GM system that will function outside lab will face two major problems:system stability and safety! Without selective pressure ,we have to deal with plasmid instability ; to make our coli colonized bowel we have to use recA+ strains which may cause plasmid multimer. Our GM coli will also contact with many kinds of bacteria at the risk of horizontal gene transfer.
The following segment is our struggle against these obstacles.
Contents |
Stability of Delivery System
Briefing
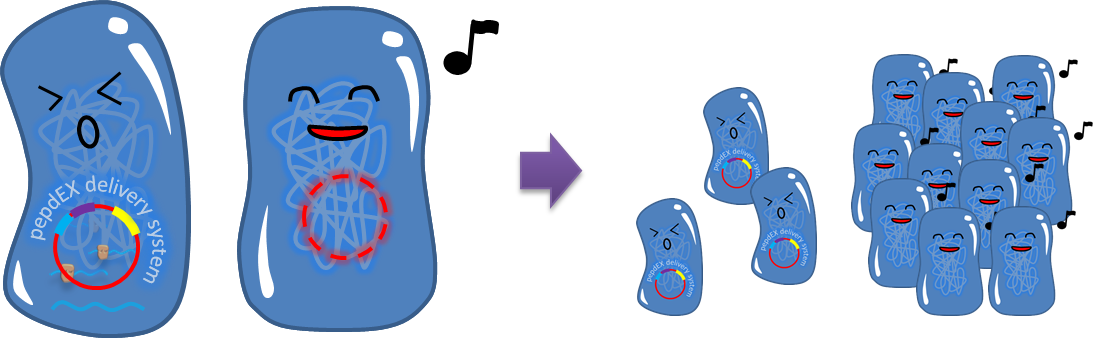
As our system will function outside the labrotory and human gut lack for antibiotic selection pressure, the vector stability is the critical point that determine whether our system is applicable or not. Inspired by natural plasmid & mobile gene element, we cope up with vector instability by incorporating partition system, Multimer resolution system and toxin antitoxin system these modules into our design.
Obstacles
Sources of plasmid instability:
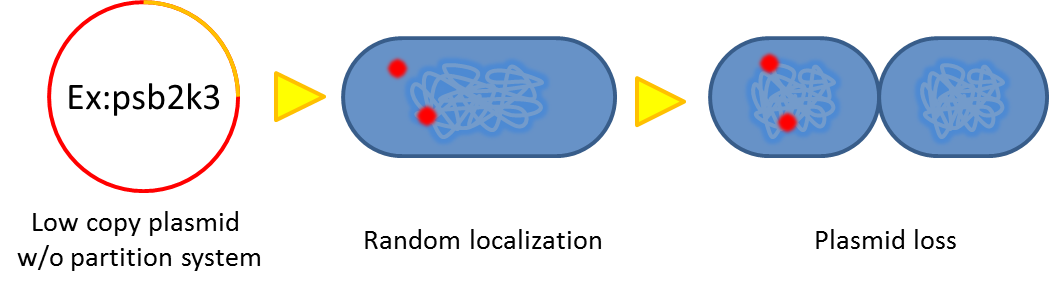
- Segregational instability
Plasmids are unevenly distributed inside bacterium, after cell division, some progeny might loss plasmid.
- Burden Effect
The plasmid free cells sure will grow better than those bearing plasmids because they don't have to spend energy/resources on our pepdEX system, so this growth rate difference will finally eliminate plasmid-bearing bacteria in population
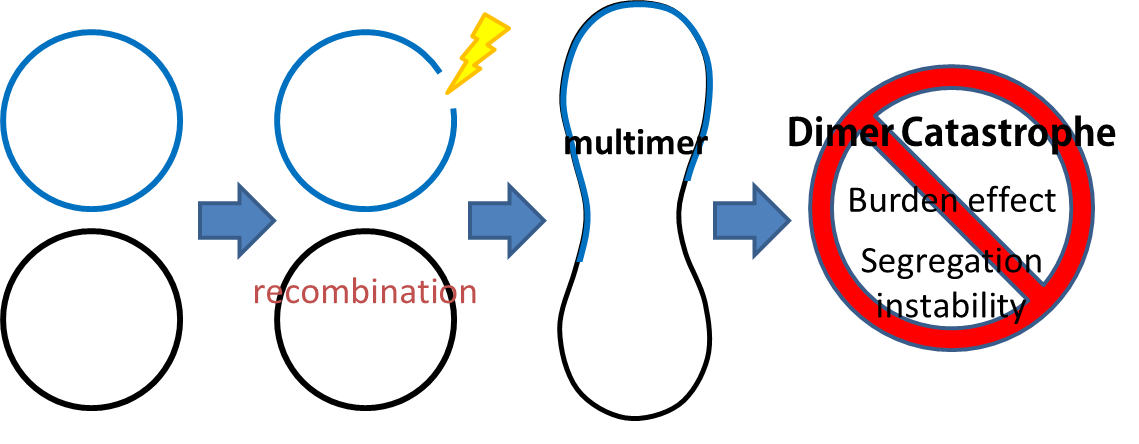
- Dimer Catastrophe
Homologues recombination may cause plasmid multimers which will increases segregational instability and burden, this is the reason why most lab coli are recA1 mutants. But so that our coli must able to colonize gut, it should be recA+ wild type strain. That's the problem!
Stabilization Modules
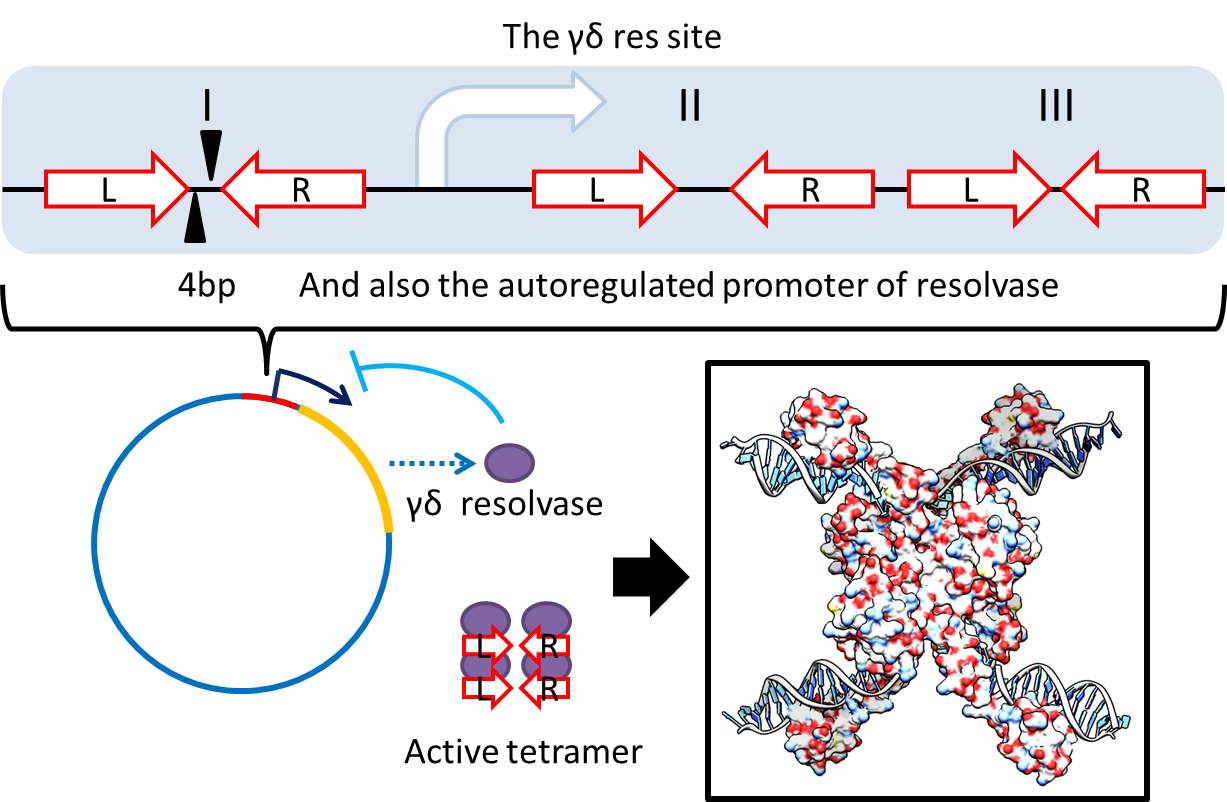
1. Multimer Resolution System:Tn1000(gamma delta) resolution system
- To deal with multimerization, we clone an cassette which encodes an autoregulated resolvase(serine type recombinase)from E.coli F plasmid transposon tn1000(tn3 family). Its promoter region consists of 3 sub-sites(res site) and can process recombination. This cassette can resolve multimer that formed during replicative transposition, so it can also resolve plasmid multimer providing plasmid stability by avoiding dimer catastrophe. For this reason, it is multimer resolution system(MRS) that provide analogous function as E.coli chromosome XerCD/dif but acts independent of cell cycle, DNA localization and may have higher efficiency on plasmids compared with slow XerCD system.
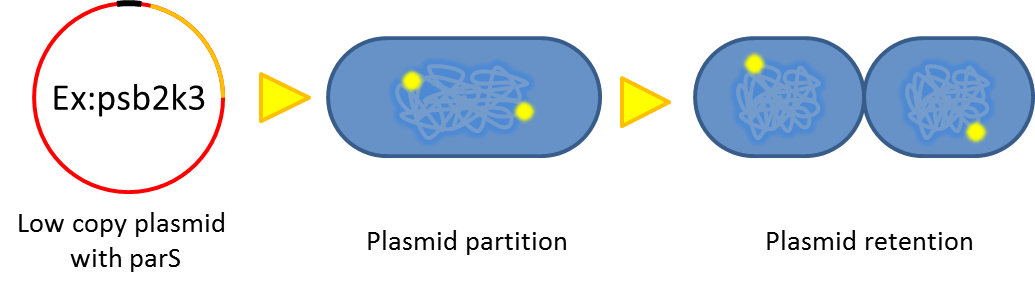
2. Partition System:from Pseudomonas putidaKT2440
- Just like many low copy plasmid, bacterial chromosome distribute chromosome evenly to their progeny by certain dynamic system. These systems include SMC like proteins, type Ia partition system and so on. Type Ia partition system segregate chromosome/plasmid in a process akin to Eukaryotic mitosis,it can be found on most eubacteria but E.coli is not the case.
- Previous study have shown that when provide parAB of P.putida in trans, the low copy plasmid(mini F)carrying conserved parS site can be stabilized in E.coli.(Anne-Marie etl. 2002)pSB2K3 is mini F plasmid thus can be stabilized by this way too, we make a new version of pSB2K3 with parS site. This plasmid that have lower gene dosage(copy number)and can be partitioned is an ideal vector to harbor our pepdEX system.
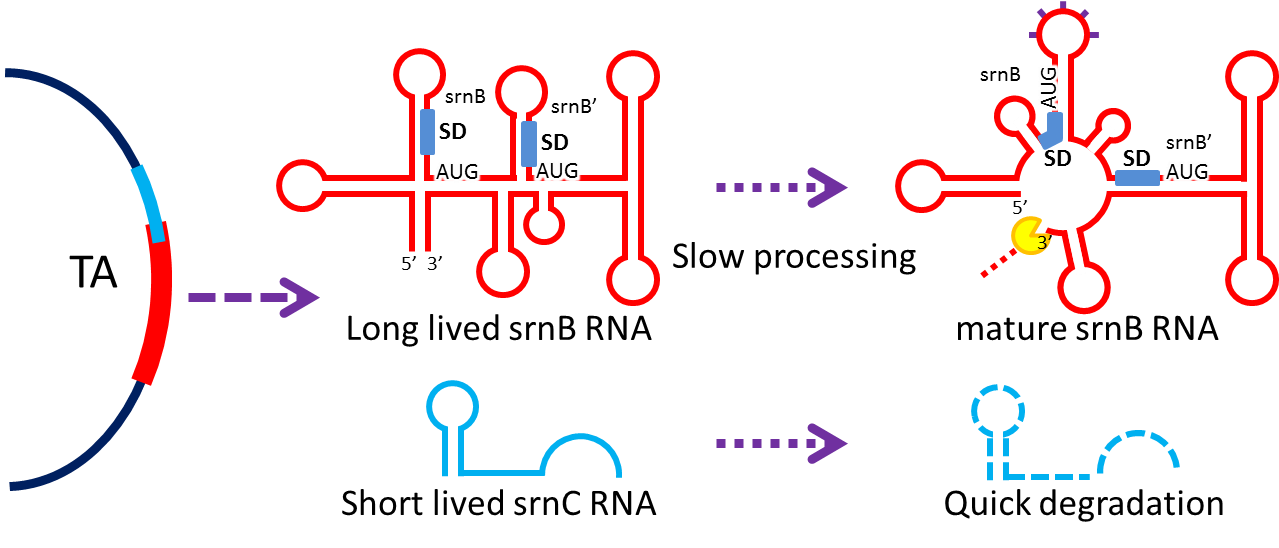
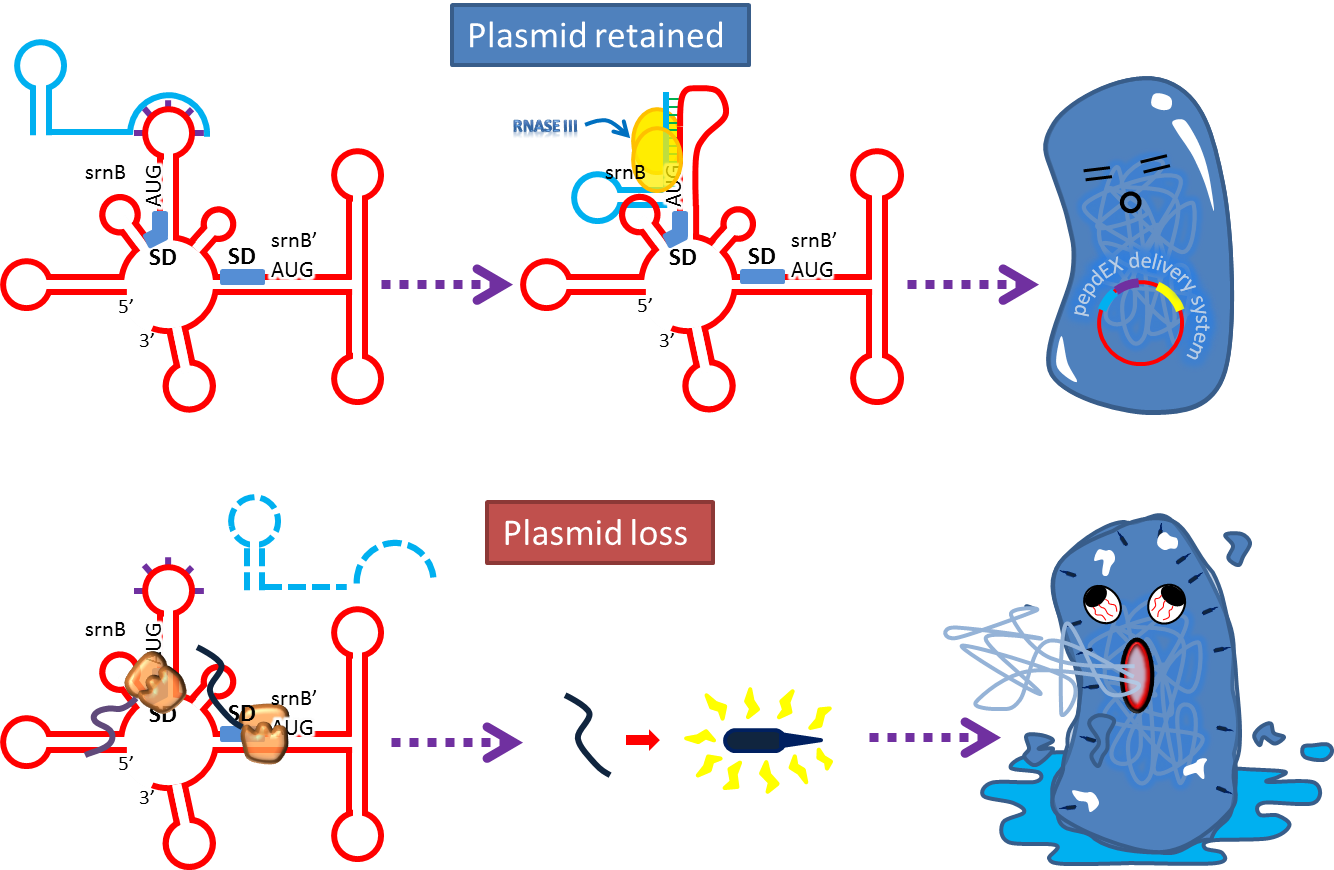
3. Post-Segregation Killing:srnBC toxin-antitoxin system
- No matter how well partition system and multimer resolution system work, inevitably there still will have some bacteria losing plasmid. We sentence them to death to solve the problem.
- Type I toxin-antitoxin srnBC is an ideal executor which belongs to hok/sok homologues, it expresses stable toxin encoded RNA and short lived antitoxin RNA that can neutralize toxin RNA by RNA interaction and RNase III cleavage. It acts as post segregation killing system, which kills bacteria when it loss the DNA(genomic islands, plasmids, mobile gene elements) that contains it. Therefore we use it to reduce plasmid loss rate and make applications without antibiotic selection more feasible.
 "
"