Contents |
Western Blot check for LovTAP-VP16 expression
Protocol: Western Blot
Gel Ingredients (choose percentage according to the size of the protein)
| 4-40 kDA | 20% |
| 12-45 kDA | 15% |
| 10-70 kDA | 12.5% |
| 15-100 kDA | 10% |
| 25-200 kDA | 8% |
| Separating gel | |
| Gel percentage | 7.5 % |
| 30% Polyacrylamide | 10 mL |
| 1.5M Tris (pH 8.8) | 10 mL |
| 10% Ammonium persulfate | 0.4 mL |
| 10% SDS | 0.4 mL |
| TEMED | 0.038 mL |
| H2O | 19.2 mL |
| Total volume | 40 mL |
| Stacking gel | |
| Gel percentage | 5 % |
| 30% Polyacrylamide | 1.36 mL |
| 1M Tris (pH 6.8) | 1 mL |
| 10% Ammonium persulfate | 0.08 mL |
| 10% SDS | 0.08 mL |
| TEMED | 0.008 mL |
| H2O | 5.44 mL |
| Total volume | 8 mL |
Preparing Protein Samples
1. Centrifuge around 5 million cells (of any volume) at 2,500 rpm for 10 min.
2. Discard the supernatant with a vacuum pump.
3. Resuspend the cell pellet with 1x PBS and centrifuge it at 2,500 rpm for 10 min.
4. Discard the supernatant with a vacuum pump.
5. Add appropriate amount of lysis buffer depending on the pellet size (for a 20 mg pellet, 150 µl of IP lysis buffer).
6. Keep the lysed sample on ice for 10 min - flick every 3 minutes.
7. Add 3x SDS lysis buffer (for a 20 mg pellet, 75 µl).
8. Incubate the sample for 5 minutes at 95 degrees, to denature proteins.
Preparing loading samples
1. Load the ladder (7 µl is the recommended volume).
2. Complete sample volume to 50 µl.
3. Load the samples.
I. SDS Gel electrophoresis
1. Prepare the separating and stacking gel solutions without APS and TEMED.
2. Add APS and TEMED to the separating gel solution only when the SDS kit is ready to be used, they are time-sensitive. Move the solution inside of the setup. Add some distilled water on top of it.
3. After 20-30 mins, remove the water and check whether the gel has solidified. Don't move to the next step until it does.
4. Add TEMED to the stacking gel solution, pour it on top of the solidified separating gel.
5. Insert a stack carefully and leave it for 20-30 mins.
6. Take the stack out and fill the kit with SDS loading buffer.
7. Load the samples.
8. Add more loading buffer, set the voltage to 80 Volts. Leave for 1.5 hours.
II. Membrane transfer
1. Prepare a membrane transfer kit.
2. Take the gel out of the SDS kit and put it on the membrane paper.
3. From bottom to top, assemble the components in the following order: 1) Sponge - 2) Blot paper - 3) Membrane - 4) Gel (Pour some M-transfer buffer on the gel) - 5) Blot paper again - 6) Sponge again.
4. Close the sandwich, set the voltage to 20 V. Leave for 30 mins - 1 hour.
5. Discard the gel. Leave the membrane in 5% skim milk with 30ml of TBST buffer (blocking buffer, to achieve the 5%, add 1.5 g of skim milk powder to the buffer) for one hour.
III. Antibody tagging
1. Discard the blocking buffer, leave only 5ml of it. Add primary antibody with a ratio of 1:1000 or 1:2000 (5 µl of antibody in 5 ml of buffer gives 1:1000)
2. Leave the mix overnight at 4 °C.
3. Wash 3 times with 1x TBST (5 minutes on shaker for every wash).
4. Dilute the secondary antibody (for example, goat anti-rabbit antibody) to 1:2000 in 5% skim milk buffer. Add it. Leave at room temperature for 2 hours.
5. Wash 3 times with 1x TBST (5 minutes on shaker for every wash).
6. Reveal the protein bands in the dark room.
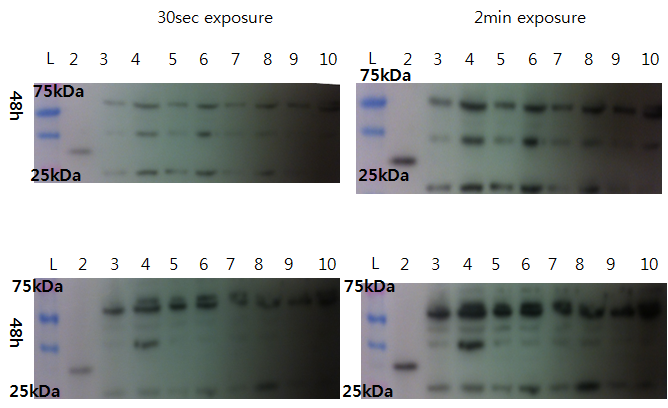
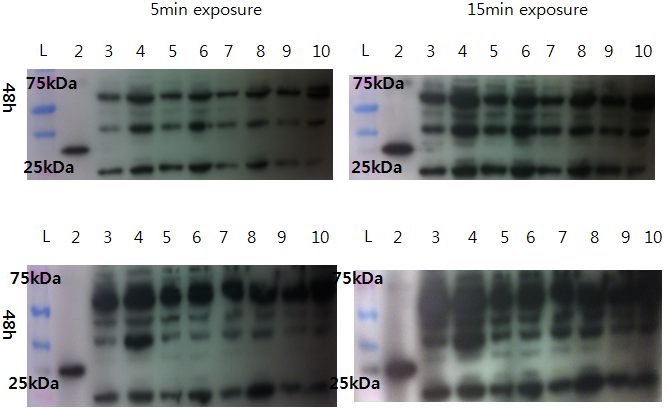
We compare 48h-transfected CHO cells and non-transfected CHO cells.
- Loading plan
Top gel:
- Lane 1: Ladder
- Lane 2: VP16 only
- Lane 3: 5 µL non-transfected CHO
- Lane 4: 15 µL non-transfected CHO
- Lane 5: 5 µL Sample 1 (100% LovTAP)
- Lane 6: 15 µL Sample 1 (100% LovTAP)
- Lane 7: 5 µL LovTAP Sample 2 (95% LovTAP + 5% GFP)
- Lane 8: 15 µL LovTAP Sample 2 (95% LovTAP + 5% GFP)
- Lane 9: 5 µL Sample 3 (100% LovTAP)
- Lane 10: 15 µL Sample 3 (100% LovTAP)
Bottom gel:
- Lane 1: Ladder
- Lane 2: VP16 only
- Lane 3: 10 µL non-transfected CHO
- Lane 4: 20 µL non-transfected CHO
- Lane 5: 10 µL Sample 1 (100% LovTAP)
- Lane 6: 20 µL Sample 1 (100% LovTAP)
- Lane 7: 10 µL LovTAP Sample 2 (95% LovTAP + 5% GFP)
- Lane 8: 20 µL LovTAP Sample 2 (95% LovTAP + 5% GFP)
- Lane 9: 10 µL Sample 3 (100% LovTAP)
- Lane 10: 20 µL Sample 3 (100% LovTAP)
No difference was observed.
FACS
Protocol: FACS
We've used flow cytometry to check the measure the expression of LovTAP.
As we had no machines in our lab, we used the FCCF's (Flow Cytometry
Core Facility) machines to perform the measurements. The cells normally
need to be fixed before being
brought to the lab but, as our project has a biosafety level 1, we could
bring in the cells alive.
The sample preparation required only a single washing step with PBS:
- Centrifuge the cells at 1500rpm for 3 minutes in a centrifuge (or at 3000rpm for 3 minutes in a microcentrifuge).
- Aspirate away the medium (be very careful not to disturb the pellet).
- Resuspend in PBS (we used ~400µl for 400'000 cells, but the required density is different for every machine).
FACS at EPFL facility.
CHO transfection with LovTAP
Protocol: Transfection of CHO cells
This is the transfection protocol used at the LBTC lab for CHO DG44 cells. The transfection reagent is PEI (polyethylenimine).
Please use the provided Excel sheet to calculate the volume of plasmid you should add to the cells. Replace every value in red by your own, then print the sheet out and follow the provided protocol.
1. Passage seed 1 day prior to transfection.
2. Prepare tubes (yellow caps with holes) by addition of the calculated amount of DNA.
3. Centrifuge the necessary volume of seed (after a PCV measurement), remove conditioned medium with the pump (use a 2 ml serological pipet with a broken neck) and resuspend (first in 10 ml) in necessary volume of fresh medium to achieve the required cell density (3 mio/ml).
4. Add 5 mL of the cell suspension to the tube with DNA and mix orbitally.
5. Add the PEI (45 µl) to the Cell+DNA mixture as soon as possible, flick 3 times.
6. Place in the incubator at 37°C.
Transfection of LovTAP for microscopy at BIOP. 6 tubes (LovTAP 100%, LovTAP 50% and dsRed 50%, dsRed 50% and filler 50%, all in duplicates).
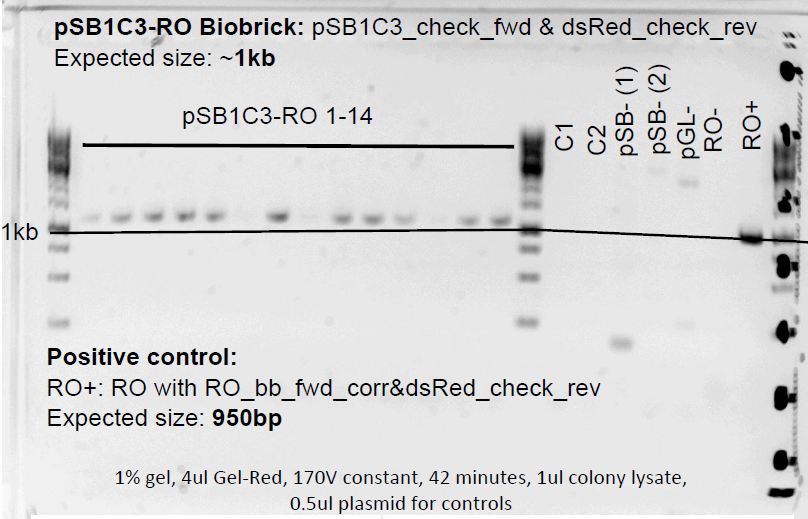
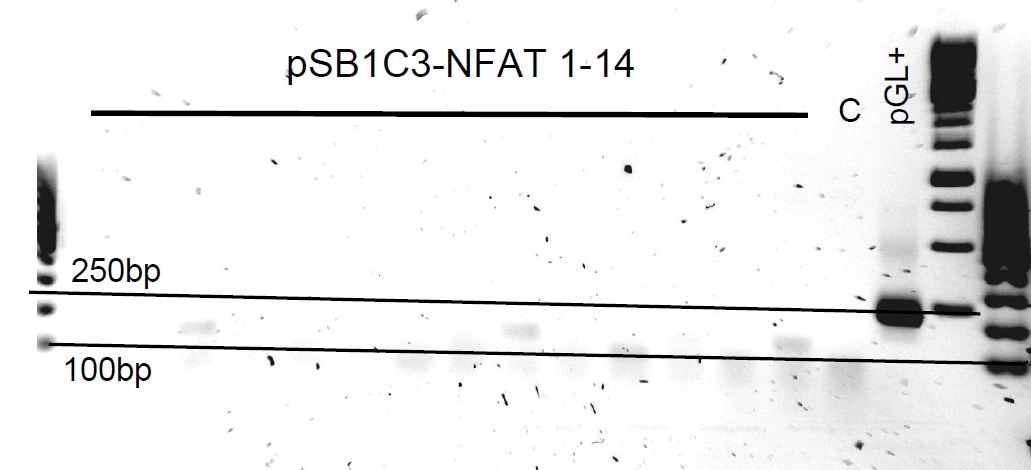
pSB1C3-NFAT and pSB1C3-RO colony PCR
Protocol: PCR
PCR is a reaction that makes it possible (and relatively easy) to amplify
a certain region of DNA. The first step is the selection of that region
(and the design of the relevant primers). Primer design can be done by hand, or by
using our Primer Design Helper. Once
done, order the primers (in our case, we ordered from them IDT).
When you've received the primers, prepare them and make sure you've got your PCR kit (we used the "Phusion® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase"). Start preparing your master mix, the composition for one tube is:
1X Mastermix 20μl reaction, add in this order
| Reagent | Volume [μl] |
|---|---|
| Water | Complete to total volume of 20μl |
| HF-Buffer (5x) | 4 |
| DMSO (optional) | 0.6 |
| dNTPs | 0.4 |
| Forward primer (50μM) | 0.2 |
| Reverse primer (50μM) | 0.2 |
| Template (10ng/μl) | 0.5 |
| Phusion HF polymerase | 0.2 |
Prepare one or two extra tubes-worth of reagent (you'll use some liquid on the walls of your tips).
Once you've finished, you should run the resulting products on a gel to check if everything went as planned.
Tips
- Thaw the HF-Buffer, DMSO and dNTPs before making the mastermix.
- Avoid taking the Phusion-HF polymerase out of the freezer (only take it out briefly when you need to add it).
- If the reactions have different primers and/or template, add the polymerase right after the dNTPs, split the mastermix and add the rest.
- Don't forget positive and negative controls
- Primers should have similar Tms (less than 5°C).
- Primer Tm calculation is a less exact science than it should be (just test several tools and compare their results). If you're not sure what the correct Tm is, consider using a gradient PCR.
- Avoid primers with strong secondary structures.
- PCR can introduce mutations. Don't forget to sequence your final product (this could be your final plasmid): you really don't want to lose a few weeks because of a "corrupt" plasmid.
Colonies grew on both ligation plates. So 14 colonies were picked in each pSB1C3-RO and pSB1C3-NFAT plate and also on the control plates.
Negative controls:
RO:
- RO-: RO with pSB1C3_check_fwd & dsRed_check_rev
- pSB-(2): pSB1C3 with pSB1C3_check_fwd & dsRed_check_rev
NFAT:
- pGL-: pGL4.30 with pSB1C3_check_fwd & NFAT_bb_rev_v3
- pSB-(1): pSB1C3 with pSB1C3_check_fwd & NFAT_bb_rev_v3
- pGL+: pGL4.30 with NFAT_bb_fwd & NFAT_bb_rev_v3 (positive control)
pSB1C3-NFAT failed. We also observed red culture tubes in the evening which confirms that the colonies that grew contain the original pSB1C3-RFP plasmid and not the ligation we want.
 "
"