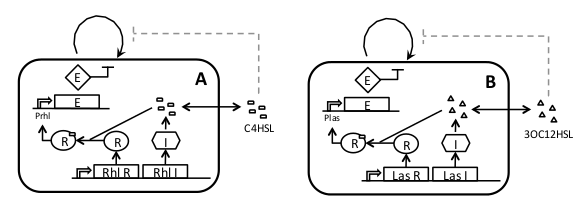
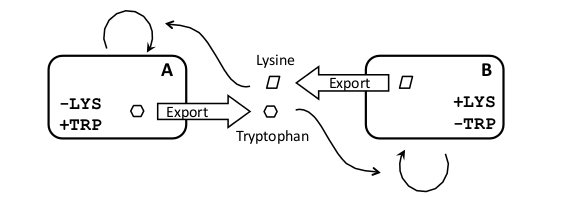
| In the cross-feeding scheme we plan to use strains which are auxotrophic for certain amino acids (e.g. lysine and tryptophan). By starting with a strain with both auxotrophies, A will be created by rescuing the biosynthetic pathway for Trp and forcing its export from the cell. Analogously, we will create strain B by rescuing the Lys pathway and forcing the secretion of Lys from the cell.
Amino-acid export from the cell can be engineered in the form of peptides (enriched for the relevant amino acid) which, in turn, can be easily controlled at the transcriptional and translational level. Export will be done either with secretion tags or as «trojan peptides» (Derossi et. al., 1998), which can diffuse through the plasma membrane. The main tuneability of the system could be changing the export rates for each amino acid.
Because of the availability of auxotrophic mutants in yeast, this chassis is ideally suited for the crossfeeding circuit design.
| 
|

 "
"