|
|
| Line 15: |
Line 15: |
| | | | |
| | In 2010 the Cambridge iGEM team Biobricked the LuxBrick, a collection of genes from the Lux operon that incorporate both the Luciferase and the substrate production enzymes without regulation, allowing endogenous bioluminescence on E. coli. | | In 2010 the Cambridge iGEM team Biobricked the LuxBrick, a collection of genes from the Lux operon that incorporate both the Luciferase and the substrate production enzymes without regulation, allowing endogenous bioluminescence on E. coli. |
| - | <html><center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/f/fc/Biolumilulilu.jpg" align="middle" width="720"></center></html> | + | <html><center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/f/fc/Biolumilulilu.jpg" align="left" width="720"></center></html> |
| | | | |
| | <h3>Chassis</h3> | | <h3>Chassis</h3> |
| Line 22: |
Line 22: |
| | | | |
| | Coupling the endogenous circadian rhythms of this organism to the expression of the Lux genes will enable high-level functionality, through an automatically switching system that turns on bioluminescence only when needed. | | Coupling the endogenous circadian rhythms of this organism to the expression of the Lux genes will enable high-level functionality, through an automatically switching system that turns on bioluminescence only when needed. |
| - | <html><center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/d/da/Synefeatures2.jpg" align="middle" width="690"></center></html> | + | <html><center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/d/da/Synefeatures2.jpg" align="left" width="690"></center></html> |
| | | | |
| | <h2>Strategy</h2> | | <h2>Strategy</h2> |

Main Goal:
Our project consists on achieving bioluminescence controlled under circadian rhythms with long-term functionality. Our aim is to produce a bioluminescent cyanobacteria which lights up during dusk hours and regenerates the substrates during the day.
Rationale:
The importance of Biological context in Synthetic Biology has been largely underestimated. We have addressed this issue by centering our project on enhancing functionality of a previously characterized Biobrick, LuxBrick, by placing it in a context which allows new features.

Bioluminescence
In 2010 the Cambridge iGEM team Biobricked the LuxBrick, a collection of genes from the Lux operon that incorporate both the Luciferase and the substrate production enzymes without regulation, allowing endogenous bioluminescence on E. coli.

Chassis
We have chosen to work with a model cyanobacteria, Synechocystis PCC. 6803 because it exhibits autotrophic metabolism and circadian rhythms.
Coupling the endogenous circadian rhythms of this organism to the expression of the Lux genes will enable high-level functionality, through an automatically switching system that turns on bioluminescence only when needed.

Strategy
The limiting step for the bacterial bioluminescent reaction is the substrate (n-decanal) concentration SHOULD ADD CITATION, therefore, to control light emission over time we decided to control it´s abundance in the cells, which in our model is a function of the substrates generation (by Lux C, D, E and G enzymes) and consumption (by the LuxAB luciferase).

In turn, the production of these enzymes can be specifically set to any desired time of the day by fusing their CDSs to promoters controlled by the circadian rhythm.
Mathematical Modelling
Our model works as a “black box” in which the input takes the form of a specific hour of the day (i.e the hour on which you want your metabolite to reach maximal concentration) and the output is a couple of promoters from Synechocystis genome.
It assumes that the metabolite's production is controlled by enzymes under the control of promoter 1 and it´s degradation by enzymes under promoter 2.
For more details please check [2012.igem.org/Team:UC_Chile/Cyanolux/Modelling here]

Wetlab strategy
Having chosen the right promoters we set out to built our constructs to transform Synechocystis.
As there weren´t straighforward tools to start working with in the registry (i.e characterized plasmids backbones, protocols, etc) we started from scratch.
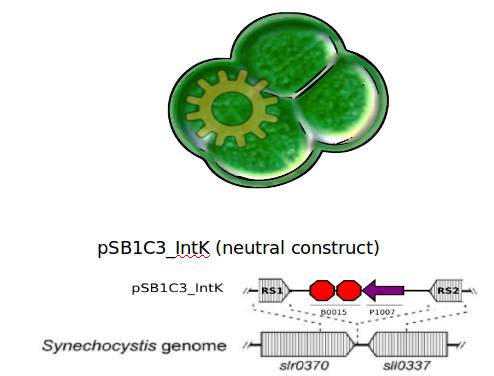
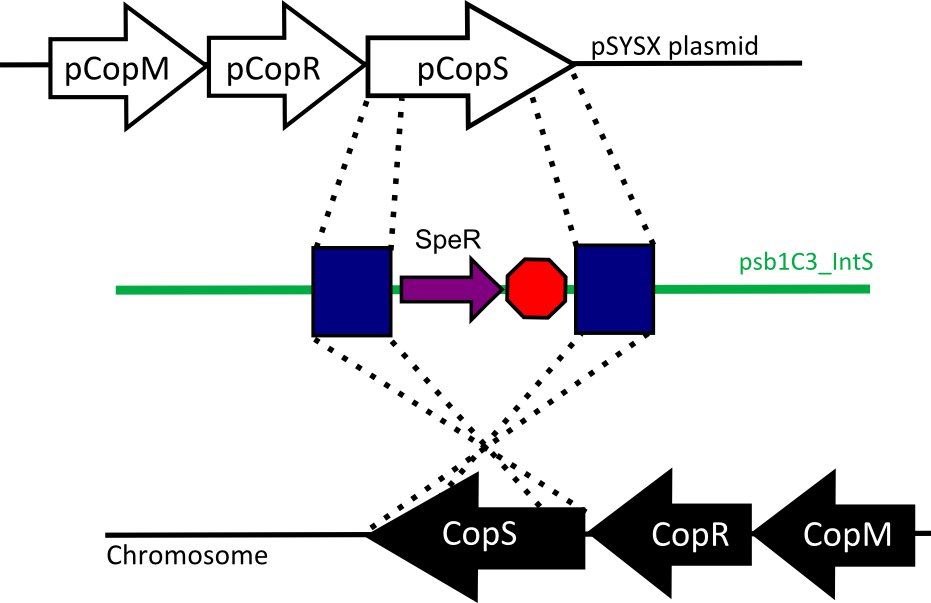
We designed two recombination plasmids backbones. One targets a gene essential for our chassis survival in the environment (link:see biosafety) and the other one a neutral site.
Our strategy was to insert the LuxAB genes (luciferase) under a circadian promoter with an expression peak right after dusk, in the neutral recombination plasmid; and the LuxCDEG genes (substrate production) with the appropriate promoter in the biosafety plasmid.
See plasmids in results section
Implementation
Synthetic biology inspires in nature making abstractions of its principles and mechanisms. We thought this moto could be applied beyond mollecular genetics...
With the relevance of context in mind, a biomimetic biolamp structure was designed that resembles the organ in which Vibrio fischeri -the bacteria from which the lux genes were biobricked- lives.

Full description of the device here
 "
"