Team:UC Chile/Cyanolux/Results
From 2012.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| (51 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | This plasmid backbone was constructed by standard assembly techniques. Recombination sites ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K743000 BBa_K743000] and [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K743001 Part:BBa_K743001]) were Biobricked by | + | This plasmid backbone was constructed by standard assembly techniques. Recombination sites ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K743000 BBa_K743000] and [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K743001 Part:BBa_K743001]) were Biobricked by Gibson assembly and were consenquently ligated to neighboring parts and KanRB0015 in parallel assembly. Afterwards, we ligated both composites through a standard assembly reaction. Final construct was validated by digestion (see gel image at right) and corroborated through sequencing. |
| - | After obtaining [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K743006 BBa_K743006], we proceeded assembling our constructs through | + | After obtaining [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K743006 BBa_K743006], we proceeded assembling our constructs through Gibson assemblies. |
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <i>If you wondering | + | <i>If you are wondering why the plasmid was constructed by standard assembly and not by gibson assembly from scratch, please refer to </i> [[Team:UC_Chile/Results/Gibson | Gibson assembly for small parts ]] |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
<h3>Insertion of LuxAB genes</h3> | <h3>Insertion of LuxAB genes</h3> | ||
| - | <br> | + | <br /> |
| - | Starting from [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K743006| K743006] as a plasmid backbone, we were able to build our LuxAB constructs for the bacterial luciferase using | + | |
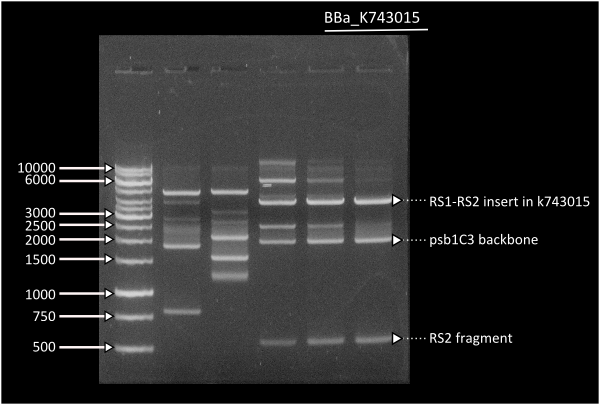
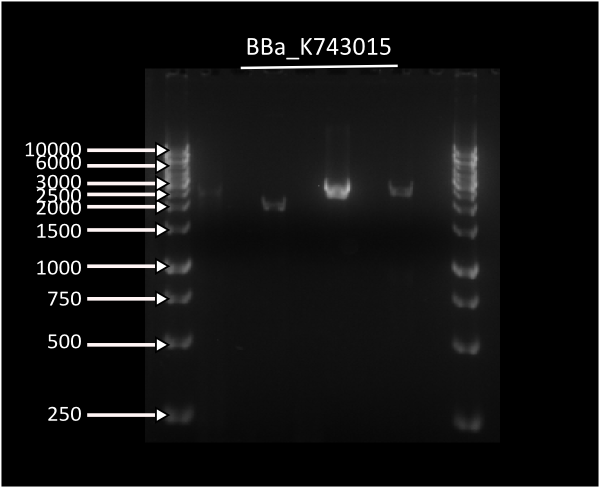
| + | Starting from [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K743006| K743006] as a plasmid backbone, we were able to build our LuxAB constructs for the bacterial luciferase using two different versions available at the registry (from [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K743014 Photorhabdus luminiscent, BBa_K743014] and [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K743015 Vibrio fisherii, BBa_K743015]) under an endogenous Synechocystis's promoter (transaldolase Reference???). Resulting constructs were verified by digestion (see gel images below) and corroborated by sequencing. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 40: | ||
<div id="boxright"> | <div id="boxright"> | ||
[[File: LuxABxl_digestion.jpg| 400px| right]] | [[File: LuxABxl_digestion.jpg| 400px| right]] | ||
| - | Lane 1 = Ladder 1Kb, Lane | + | Lane 1 = Ladder 1Kb, Lane 6 = K743014. Band at 4000: RS1-Pta-LuxABvf-Kan-RS2partial, band at 2000: pSB1C3, band at 500: RS2partial. |
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | <div id="boxleft"> | + | <div id="boxleft" style="width: 366px;"> |
[[File: LuxABvf_digestion.jpg| 366px| left]] | [[File: LuxABvf_digestion.jpg| 366px| left]] | ||
Lane 1 = Ladder 1Kb, Lane 3 = K743014. Band at 4000: RS1-Pta-LuxABxl-Kan-RS2partial, band at 2000: pSB1C3, band at 500: RS2partial. | Lane 1 = Ladder 1Kb, Lane 3 = K743014. Band at 4000: RS1-Pta-LuxABxl-Kan-RS2partial, band at 2000: pSB1C3, band at 500: RS2partial. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 58: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <br> | + | <br /> |
| - | <br> | + | <br /> |
| - | <br> | + | <br /> |
| - | <br> | + | <br /> |
| - | <br> | + | <br /> |
| - | <br> | + | <br /> |
| - | <br> | + | <br /> |
| - | <br> | + | <br /> |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
<h2>Suceptibility construct</h2> | <h2>Suceptibility construct</h2> | ||
| Line 70: | Line 73: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
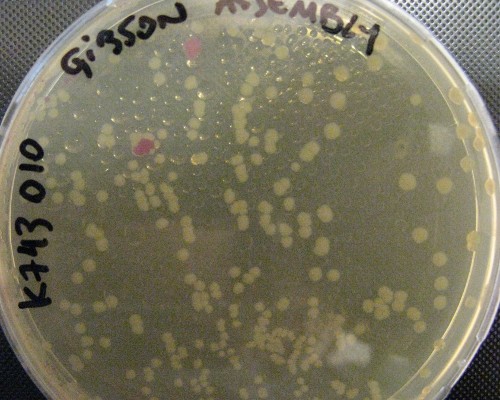
| - | pSB1C3_IntS was constructed in two successive | + | pSB1C3_IntS was constructed in two successive Gibson assemblies. The first assembly inserted the CopS region (the entire RS5 & RS6 recombination locus) to a chopped-down pSB1C3 lacking the whole VF2 to VR region. The second assembly inserted the Spectynomycin resistance selection marker and the whole VF to VR region of plasmid pSB4K5-J04450 right in between of the RS5 & RS6 CopS region. This construct yields red colonies if correctly assembled (see image at left). Red colonies were colony PCRed, verificated by digestion (see image down right) and corroborated by sequencing. |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 76: | Line 79: | ||
<div id="boxleft"> | <div id="boxleft"> | ||
[[File: K743010.jpg| 400px| left]] | [[File: K743010.jpg| 400px| left]] | ||
| + | A couple of picked red colonies are shown in this plate. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div id="C10"> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div id="boxright"> | <div id="boxright"> | ||
[[File: C10 digestion.jpg| 400px| right]] | [[File: C10 digestion.jpg| 400px| right]] | ||
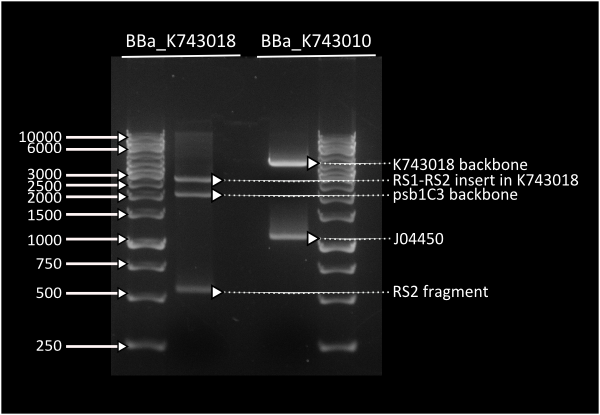
| + | Digestion profile for [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K743018 K743018] & [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K743010 K743010 ] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 114: | Line 122: | ||
<h3>Insertion of Lux substrate biosynthesis genes under twilight promoters</h3> | <h3>Insertion of Lux substrate biosynthesis genes under twilight promoters</h3> | ||
| - | + | <br /> | |
| - | + | We have amplified all the parts of the substrate production pathway ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K325902 LuxCD] and [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K325903 LuxEG]) for the final construct under the Pcaa3 promoter (which has also been Biobricked with code [[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K743002 K743002]]. Also, we are amplifying one remaining part (LuxCD with 5' homology to PsigE) to do Gibson assembly of the LuxCDEG construct under PsigE. Gibson reaction will be done along with the substrate production construct under Pcaa3 in pSB1C3_IntS for both constructs. | |
| - | + | <br /> | |
| + | <h1>Synechocystis PCC 6803</h1> | ||
<h2>Transforming Synechocystis PCC 6803</h2> | <h2>Transforming Synechocystis PCC 6803</h2> | ||
| - | [[ | + | <br /> |
| - | + | ||
| + | Once constructs were corroborated by sequencing, we proceeded to [[Team:UC_Chile/Protocols#Transformation_of_Synechocystis_PCC._6803 | transform synechocystis]]. Prior to transforming, we verified that our Synechocystis cultures were in exponential growth by comparison to our [[Team:UC_Chile/Results/Growthcurve | growth curve characterization]]. | ||
| + | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | + | Transformation in Synechocystis takes about two weeks to reveal transformant colonies, which in turn have to be restreaked again before PCR verification. This makes working in Synechocystis pressing as mistakes [[Team:UC_Chile/Results/Int_C | can take long to unravel]]. | |
| + | |||
| + | <!-- | ||
| + | <div id="boxleft"> | ||
| + | [[File:Vivas.JPG|400px| left]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div id="boxright"> | ||
| + | [[File:Muriendo1Chile.JPG|400px| right]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div id="boxleft"> | ||
| + | [[File:Muriendo_2Chile.JPG|400px| left]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div id="boxright"> | ||
| + | [[File:ColonieChile.JPG|400px| right]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="width: 600px; padding: 10px; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"> | ||
| + | [[File:ColoniasChilenas.jpg | 600px | center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This image shows various time points during a Synechocystis PCC. 6803 transformations. Be advised that it is only to be used as a reference of what to expect during the first week of transformation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | </div> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<h3>LuxABxl under transaldolase promoter transformation</h3> | <h3>LuxABxl under transaldolase promoter transformation</h3> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="width: 600px; padding: 10px; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"> | ||
[[File:Pta_LuxABxl.JPG| 600px| center]] | [[File:Pta_LuxABxl.JPG| 600px| center]] | ||
| + | Transformation of Synechocystis PCC 6803 with [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K743014 K743014] on the 14th day of transformation. The left plate is the control transformation plate (no DNA) on Kanamycin 25ug/mL and on the right, successfully transformed Synechocystis colonies growing throughout the Millipore membrane on the same antibiotic. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| - | + | <h3>LuxABvf under transaldolase promoter transformation</h3> | |
| - | < | + | |
| - | < | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | <div style="width: 600px; padding: 10px; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"> | ||
| + | [[File:Pta_LuxABvf.JPG| 600px| center]] | ||
| + | Transformation of Synechocystis PCC 6803 with [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K743015 K743015] on the 14th day of transformation. The left plate is the control transformation plate (no DNA) on Kanamycin 25ug/mL and on the right, successfully transformed Synechocystis colonies growing throughout the Millipore membrane on the same antibiotic. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | <h2>Corroboration of integration</h2> | |
| - | < | + | |
| - | < | + | To corroborate if the transformant colonies had integrated the actual insert, we did colony PCR for multiple parts contained in the insert. |
| - | < | + | |
| - | < | + | |
| + | <h3>Integration of LuxABxl under transaldolase promoter</h3> | ||
| + | We did a massive colony PCR to corroborate the presence of the parts which composed the original K743014 integration plasmid, with corresponding negative controls to avoid confusing a genomic amplicon with an insert amplicon. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Regretably we had many negative controls which had amplicons and also lots of amplicons of the insert which we could not obtain... We are not certain about the repercussions of this result so we will try the experiment after the wiki freeze. | ||
| + | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h3>Integration of LuxABvf under transaldolase promoter</h3> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="width: 400px; padding: 10px; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"> | ||
| + | [[File:LuxABvf colony PCR.JPG| 400px| center]] | ||
| + | This PCR was done using DNA from transformant LuxABvf colonies to amplify parts contained in the insert in lanes 2,4,6,8 and DNA from wild-type Synechocystis PCC 6803, used as a negative control in lanes 3,5,7,9. Ladder 1Kb is placed in lane 1 and 10. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | + | <p style="font-size:150%">We would like to make notice that to our knowledge we are the first iGEM team to do a succesful direct transformation of Synechocystis PCC. 6803 with naked DNA!</p> | |
| + | |||
| + | <h2>Testing constructions in Synechocystis</h2> | ||
| + | |||
| + | To test our constructions, we managed to get access to a Luminometer which also has dispensing capabilities. To test the activity of the transformed Synechocystis with the luciferases we used decanal and dodecanal exogenously, using incremental concentrations of substrate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="width:965px"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:decanalxp.jpg| 400px | left]] | ||
| + | [[File:dodecanalxp.jpg| 400px | right]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | According to these results we are inclined to think that our the transaldolase promoter that we are using is not driving the expression of the luciferases. Furthermore, we have received recent advice to use much larger (up to 1 Kb) of promoter upstream of the +1 transcription site of the transaldolase gene. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>sfGFP with degradation tag to characterize transaldolase promoter</h2> | ||
| + | |||
| + | To describe the circadian behaviour of the transaldolase promoter without having the dificulties of equipment (luminometer and substrate), we built a fast-degrading reporter consisting of sfGPF(I746916) with a LVA degradation tag in the C-terminal end of the protein, [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K743019 BBa_K743019]. This construct will serve as a real-time reporter of promoter activity. As it is a reporter plasmid with fast-degradation tags, verificating if sfGFP is being expressed circadianly by Synechocystis should be effortless. | ||
| + | |||
| + | You may find more information about the half-life of proteins with the LVA tag [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_M0050 | here]. The construct has been verified by digestion and corroborated by sequencing. Check construct digestion [[Team:UC_Chile/Cyanolux/Results#C10 | here]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <h3>High-sensitive camera</h3> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | During the Latin America Jamboree, we had a chat with a couple of judges and a student from the Universidad de los Andes, David Olarte, on how to induce Synechocystis with n-decanal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | David sent us some work he had done on luminescence assays in cyanobacteria. Following his methods we finally were able to see light emittion, confirming prescence of catalytically active luciferase. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html><center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/1/1e/Results.post.colombia.camera.jpg" align="left" width="700"></center></html> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /><br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h1>Experimental Highlights</h1> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | - Constructed two functional integration plasmids for <i>Synechocystis</i> PCC. 6803 | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | - Transformed <i>Synechocystis</i> PCC. 6803 with an optimized transformation protocol, available [https://2012.igem.org/Team:UC_Chile/Protocols#Transformation_of_Synechocystis_PCC._6803 here] | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | - Verified integration of constructs | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | - Confirmed expression of genes and activity of luciferase through a bioluminescence assay with exogenous substrate. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h1>Conclusions</h1> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>Transformation in Synechocystis PCC. 6803</h2> | ||
| + | We have successfully transformed Synechocystis PCC. 6803. We have been able to standarize growth conditions and transformation protocols. We believe that we are the first iGEM team to transform Synechocystis PCC. 6803 directly with naked DNA. | ||
| + | <h2>Verification of integrations</h2> | ||
| + | We have been able to verify the integration of the construct into Synechocystis's genome. | ||
| + | <h2>Promoters</h2> | ||
| + | We have been able to demonstrate that the transaldolase is driving the expression of the constructs but we have no certainty as if it is behaving circadianly. With our sfGFP construct with degradation tag we will be able to determinate if that is so. | ||
| - | < | + | <h2>Luciferases</h2> |
| - | + | With our new results with the High-sensitivity CCD camera we have been able to observe bioluminescence from our transformed Synechocystis. The luciferase is catalytically active, however we need to see if we can enhance light output by changing the length of the promoter. | |
| - | + | <h2> Susceptibility construct</h2> | |
| + | We have been unable to obtain a correct assembly of the LuxCDEG (substrate production) into our suceptibility construct. Due to repetitive failures, we will try a new strategy of cloning, by ordering new primers with longer overlapping ends. | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:UC_Chile/Cyanolux/Modelling"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/a/ab/UC_Chile-Continue_button.jpg" align="right"> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
{{UC_Chilefooter}} | {{UC_Chilefooter}} | ||
Latest revision as of 10:05, 26 October 2012
 "
"