|
|
| Line 42: |
Line 42: |
| | | | |
| | <h1>Characterization in Synechocystis</h1> | | <h1>Characterization in Synechocystis</h1> |
| | + | |
| | + | <br /> |
| | | | |
| | <h2>Transformation</h2> | | <h2>Transformation</h2> |
| | | | |
| - | We used our plasmid backbones to transform Synechocystis PCC. 6803, to verify that our initial design could indeed integrate into <i>Synechocystis's</i> genome. | + | |
| | + | We used our plasmid backbones to transform Synechocystis PCC. 6803 to verify that our initial design could indeed integrate into <i>Synechocystis's</i> genome. |
| | + | |
| | | | |
| | Transformation with pSB1C3_IntK (BBa_K743015): | | Transformation with pSB1C3_IntK (BBa_K743015): |
| | + | |
| | | | |
| | [[File:Pta_LuxABvf.JPG| 600px| center]] | | [[File:Pta_LuxABvf.JPG| 600px| center]] |
| | + | |
| | | | |
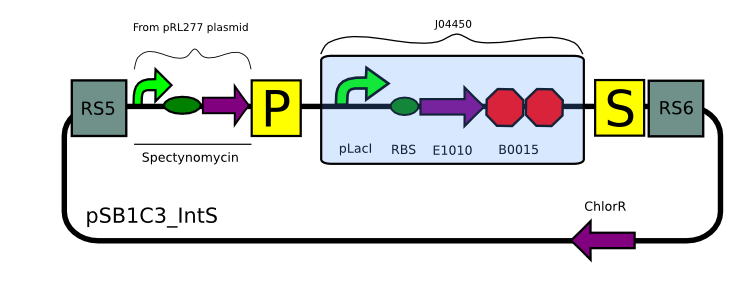
| | Transformation with pSB1C3_IntS (BBa_K743010): | | Transformation with pSB1C3_IntS (BBa_K743010): |
| | + | |
| | | | |
| | [[File:Trans_IntS.JPG| 600px| center]] | | [[File:Trans_IntS.JPG| 600px| center]] |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | After two weeks, colonies became apparent in the transformation plates for both plasmid backbones while in negative controls (transformations with no DNA) there was complete absence of surviving colonies. |
| | + | |
| | | | |
| | <h2>Verification of constructs</h2> | | <h2>Verification of constructs</h2> |
| | + | |
| | | | |
| | We proceeded to verify the integration of the constructs in <i>Synechocystis</i> by doing multiple PCRs to amplify various parts. | | We proceeded to verify the integration of the constructs in <i>Synechocystis</i> by doing multiple PCRs to amplify various parts. |

Construction
Plasmids backbones
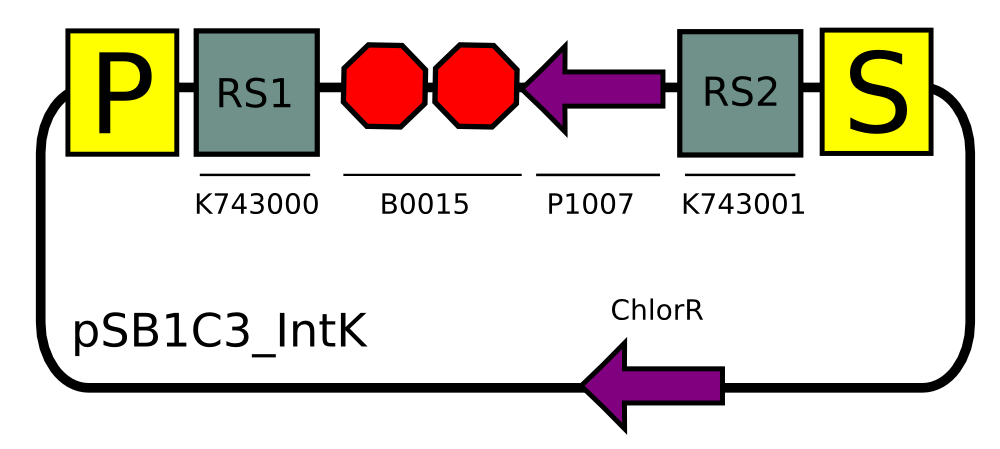
We built two integrative plasmid backbones for Synechocystis PCC. 6803 (see design here)
Plasmids were verified by digestion and then corroborated by sequencing.
Constructs for Synechocystis
Using our plasmid backbones as a starting point, we proceeded to build our constructs for Synechocystis:
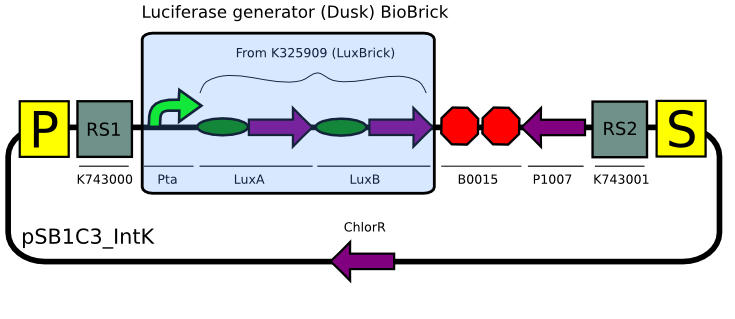
Even though we tried many times (>6) to assemble the substrate production (LuxCDEG) plasmid,we were unable to obtain a correct product. We are currently designing another strategy to build the construct...
Characterization in Synechocystis
Transformation
We used our plasmid backbones to transform Synechocystis PCC. 6803 to verify that our initial design could indeed integrate into Synechocystis's genome.
Transformation with pSB1C3_IntK (BBa_K743015):
Transformation with pSB1C3_IntS (BBa_K743010):
After two weeks, colonies became apparent in the transformation plates for both plasmid backbones while in negative controls (transformations with no DNA) there was complete absence of surviving colonies.
Verification of constructs
We proceeded to verify the integration of the constructs in Synechocystis by doing multiple PCRs to amplify various parts.
(New image with illustration of verification from outer RS1 and RS2 - October 1X something)
Bioluminescence Assays
We proceeded to check if our Synechocystis strain with the Luciferase genes did indeed produce light in the prescence of exogenous substrate.
Bioluminometer
We measured bioluminescence by adding directly the substrate to the cells and measuring light-output in a Luminometer. While we could measure bioluminescence of the positive LuxBrick E.coli controls, no apparent bioluminescence was seen in our Synechocystis cells. This let us to think that the problem might be the size of the promoter, which if not long enough, would not be able to recruit necessary transcription factors for expression.
High-sensitive camera
During the Latin America Jamboree, we had a chat with a couple of judges and a student from the Universidad de los Andes, David Olarte, on how to induce Synechocystis with n-decanal.
David sent us some work he had done on luminescence assays in cyanobacteria. Following his methods we finally were able to see light emittion, confirming prescence of catalytically active luciferase.

Experimental Highlights
 "
"