|
|
| Line 157: |
Line 157: |
| | | | |
| | A detailed description of this work is in the [https://2012.igem.org/Team:UC_Chile/Bactomithril/notepad notebook section]. After tons of hours of hard work, when finally PCR amplified bands of the correct size, the digestion tests were positive, Colony PCR were succesful, and Gibson Assemblies seemed to work, we sent our final sequence for sequencing, but the results did not match with our designs. Probably this is due to the hihgly repetitive nature of the spider silk monomers. | | A detailed description of this work is in the [https://2012.igem.org/Team:UC_Chile/Bactomithril/notepad notebook section]. After tons of hours of hard work, when finally PCR amplified bands of the correct size, the digestion tests were positive, Colony PCR were succesful, and Gibson Assemblies seemed to work, we sent our final sequence for sequencing, but the results did not match with our designs. Probably this is due to the hihgly repetitive nature of the spider silk monomers. |
| | + | |
| | + | == References == |
| | + | |
| | + | In this section you will find references about production and modelling of recombinant spider silk proteins. |
| | + | |
| | + | <big> Recommended literature </big> |
| | + | |
| | + | Teulé, F., Cooper, A. R., Furin, W. a, Bittencourt, D., Rech, E. L., Brooks, A., & Lewis, R. V. (2009). A protocol for the production of recombinant spider silk-like proteins for artificial fiber spinning. Nature protocols, 4(3), 341-55. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.250 |
| | + | |
| | + | Widhe, M., Johansson, J., Hedhammar, M., & Rising, A. (2012). Invited review current progress and limitations of spider silk for biomedical applications. Biopolymers, 97(6), 468-78. doi:10.1002/bip.21715 |
| | + | |
| | + | Widmaier, D. M., Tullman-Ercek, D., Mirsky, E. a, Hill, R., Govindarajan, S., Minshull, J., & Voigt, C. a. (2009). Engineering the Salmonella type III secretion system to export spider silk monomers. Molecular systems biology, 5(309), 309. doi:10.1038/msb.2009.62 |
| | + | |
| | + | Xia, X.-X., Qian, Z.-G., Ki, C. S., Park, Y. H., Kaplan, D. L., & Lee, S. Y. (2010). Native-sized recombinant spider silk protein produced in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli results in a strong fiber. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(32), 14059-63. doi:10.1073/pnas.1003366107 |
| | + | |
| | + | <big> Complementary literature </big> |
| | + | |
| | + | An, B., Hinman, M. B., Holland, G. P., Yarger, J. L., & Lewis, R. V. (2011). Inducing β-sheets formation in synthetic spider silk fibers by aqueous post-spin stretching. Biomacromolecules, 12(6), 2375-81. doi:10.1021/bm200463e |
| | + | |
| | + | Askarieh, G., Hedhammar, M., Nordling, K., Saenz, A., Casals, C., Rising, A., Johansson, J., et al. (2010). Self-assembly of spider silk proteins is controlled by a pH-sensitive relay. Nature, 465(7295), 236-8. doi:10.1038/nature08962 |
| | + | |
| | + | Ayoub, N. a, Garb, J. E., Tinghitella, R. M., Collin, M. a, & Hayashi, C. Y. (2007). Blueprint for a high-performance biomaterial: full-length spider dragline silk genes. PloS one, 2(6), e514. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000514 |
| | + | |
| | + | Bauer, F., & Scheibel, T. (2012). Artificial egg stalks made of a recombinantly produced lacewing silk protein. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 51(26), 6521-4. doi:10.1002/anie.201200591 |
| | + | |
| | + | Bayley, H. (1998). Puri ® cation and characterization of recombinant spider silk expressed in Escherichia coli. Cell, 1, 31-38. |
| | + | |
| | + | Bogush, V. G., Sokolova, O. S., Davydova, L. I., Klinov, D. V., Sidoruk, K. V., Esipova, N. G., Neretina, T. V., et al. (2009). A novel model system for design of biomaterials based on recombinant analogs of spider silk proteins. Journal of neuroimmune pharmacology : the official journal of the Society on NeuroImmune Pharmacology, 4(1), 17-27. doi:10.1007/s11481-008-9129-z |
| | + | |
| | + | Dams-Kozlowska, H., Majer, A., Tomasiewicz, P., Lozinska, J., Kaplan, D. L., & Mackiewicz, A. (2012). Purification and cytotoxicity of tag-free bioengineered spider silk proteins. Journal of biomedical materials research. Part A, 1-9. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.34353 |
| | + | |
| | + | Das, R., & Baker, D. (2008). Macromolecular modeling with rosetta. Annual review of biochemistry, 77, 363-82. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.062906.171838 |
| | + | |
| | + | Kenney, J. M., Knight, D., Wise, M. J., & Vollrath, F. (2002). Amyloidogenic nature of spider silk. European Journal of Biochemistry, 269(16), 4159-4163. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03112.x |
| | + | |
| | + | Keten, S., & Buehler, M. J. (2010). Nanostructure and molecular mechanics of spider dragline silk protein assemblies. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface / the Royal Society, 7(53), 1709-21. doi:10.1098/rsif.2010.0149 |
| | + | |
| | + | Lazaris, A., Arcidiacono, S., Huang, Y., Zhou, J.-F., Duguay, F., Chretien, N., Welsh, E. a, et al. (2002). Spider silk fibers spun from soluble recombinant silk produced in mammalian cells. Science (New York, N.Y.), 295(5554), 472-6. doi:10.1126/science.1065780 |
| | + | |
| | + | Moisenovich, M. M., Pustovalova, O. L., Arhipova, a Y., Vasiljeva, T. V., Sokolova, O. S., Bogush, V. G., Debabov, V. G., et al. (2011). In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility studies of a recombinant analogue of spidroin 1 scaffolds. Journal of biomedical materials research. Part A, 96(1), 125-31. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.32968 |
| | + | |
| | + | Rising, A., Widhe, M., Johansson, J., & Hedhammar, M. (2011). Spider silk proteins: recent advances in recombinant production, structure-function relationships and biomedical applications. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 68(2), 169-84. doi:10.1007/s00018-010-0462-z |
| | + | |
| | + | Tobar, J. a, Carreño, L. J., Bueno, S. M., González, P. a, Mora, J. E., Quezada, S. a, & Kalergis, A. M. (2006). Virulent Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium evades adaptive immunity by preventing dendritic cells from activating T cells. Infection and immunity, 74(11), 6438-48. doi:10.1128/IAI.00063-06 |
| | + | |
| | + | Vollrath, F. (1999). Biology of spider silk. International journal of biological macromolecules, 24(2-3), 81-8. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10342751 |
| | + | |
| | + | Vollrath, F., & Knight, D. P. (2001). Liquid crystalline spinning of spider silk. Nature, 410(6828), 541-8. doi:10.1038/35069000 |
| | + | |
| | + | Winkler, S., Szela, S., Avtges, P., Valluzzi, R., Kirschner, D. a, & Kaplan, D. (1999). Designing recombinant spider silk proteins to control assembly. International journal of biological macromolecules, 24(2-3), 265-70. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10342773 |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | | | |
| | {{UC_Chilefooter}} | | {{UC_Chilefooter}} |

Overview
Spider dragline silk is an exceptionally strong and elastic fiber and is an ideal material for numerous biomedical and industrial applications. In this secondary project we developed a novel secretion system that allows to export proteins to the extracellular medium and tried to add the first spider-silk biobrick to the Registry. This biobrick would have the synthetic silk gene ADF-3 from the orb weaving spider Araneus diadematus. Nevertheless, due to the repetitive nature of the spider silk monomer we could not finish this biobrick for de Regional Jamboree (despite of several intents and strategies). </p>
Introduction
Spider dragline silk is an exceptionally strong and elastic biomaterial and one of the strongest natural fibers known. It is five times stronger by weight than steel and three times tougher than the top quality man-made fiber Kevlar [1]. That’s why is referred to as “biosteel”. Furthermore, this material is biocompatible, biodegradable and has potential for processing in aqueous solution under ambient conditions.
These properties make the spider silk an ideal material for numerous industrial applications such as bullet-proof vests, parachutes, seat belts and composite materials in aircraft, and a promising substance for biomedical applications such as drug delivery systems and scaffolds for tissue engineering.
The excellent mechanical properties and low immunogenicity of spider webs have fascinated the man for thousands of years, but unfortunately large scale farming of spiders is not convenient because of the highly territorial and aggressive character of these arthropods. Synthetic spider silk production is a promising way to make use of this exceptional biomaterial.
Construct: a novel secretion system
Working Plasmid
This is an intermediate plasmid that we used to build the GFP Reporter Plasmid an the Protease Producer Plasmid.
GFP Reporter Plasmid
The description of the mechanism of this construct is explained in the animation below.
Protease Producer Plasmid
This construct induces the expression of the HIV protease.
Animation describing the first secretion system

Click here to open this animation from the begining in a new tab
Notebook
In this section you will find the complete description of our work in this project.
Results
Experiment 1
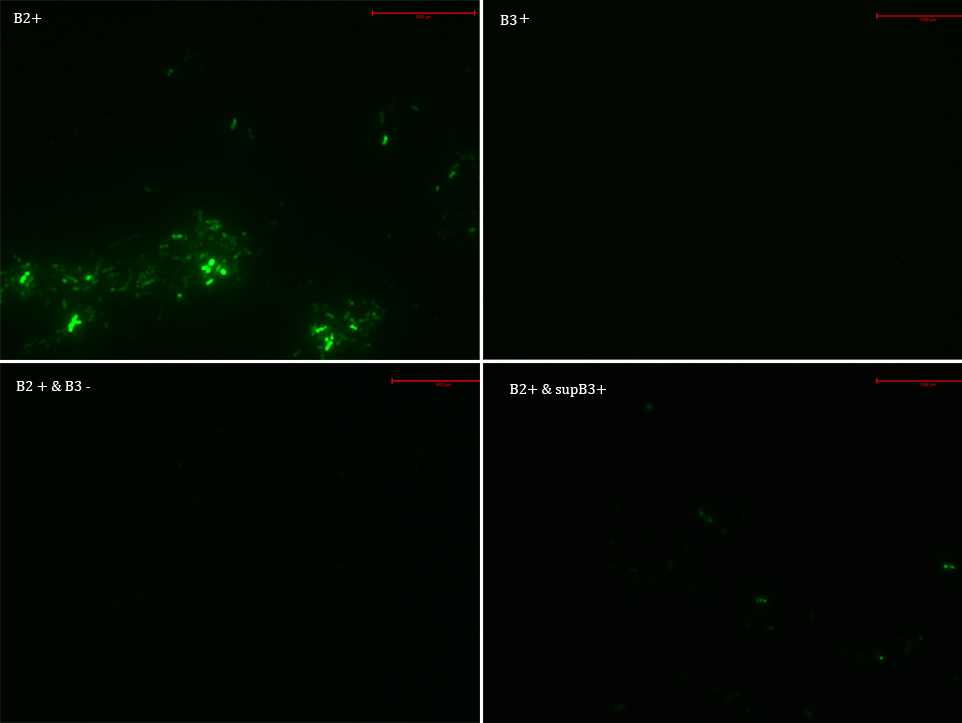
We transformed E. Coli with our GFP Reporter Plasmid (B2) and with the Protease Producer Plasmid (B3). We did a little experiment with those bacteria.
The following samples were prepared:
B2
B2+
B2+ & B3
B2+ & supB3
Nomenclature
B2- (coli transformed with GFP Reporter Plasmid)
B2+ (coli transformed with GFP Reporter Plasmid, induced with Arabinose)
B3+ (coli transformed with Protease Producer Plasmid, induced with Arabinose)
supB3+ (supernatant of coli transformed with Protease Producer Plasmid induced with Arabinose)
Then we observed each sample with an epifluorescence microscope. The results were promising. B2- did not express sfGFP, but B2+ did. Additionally, in both cases (B2+ & B3) and (B2+ & supB3) the fluorescence of sfGFP disappeared almost completely.
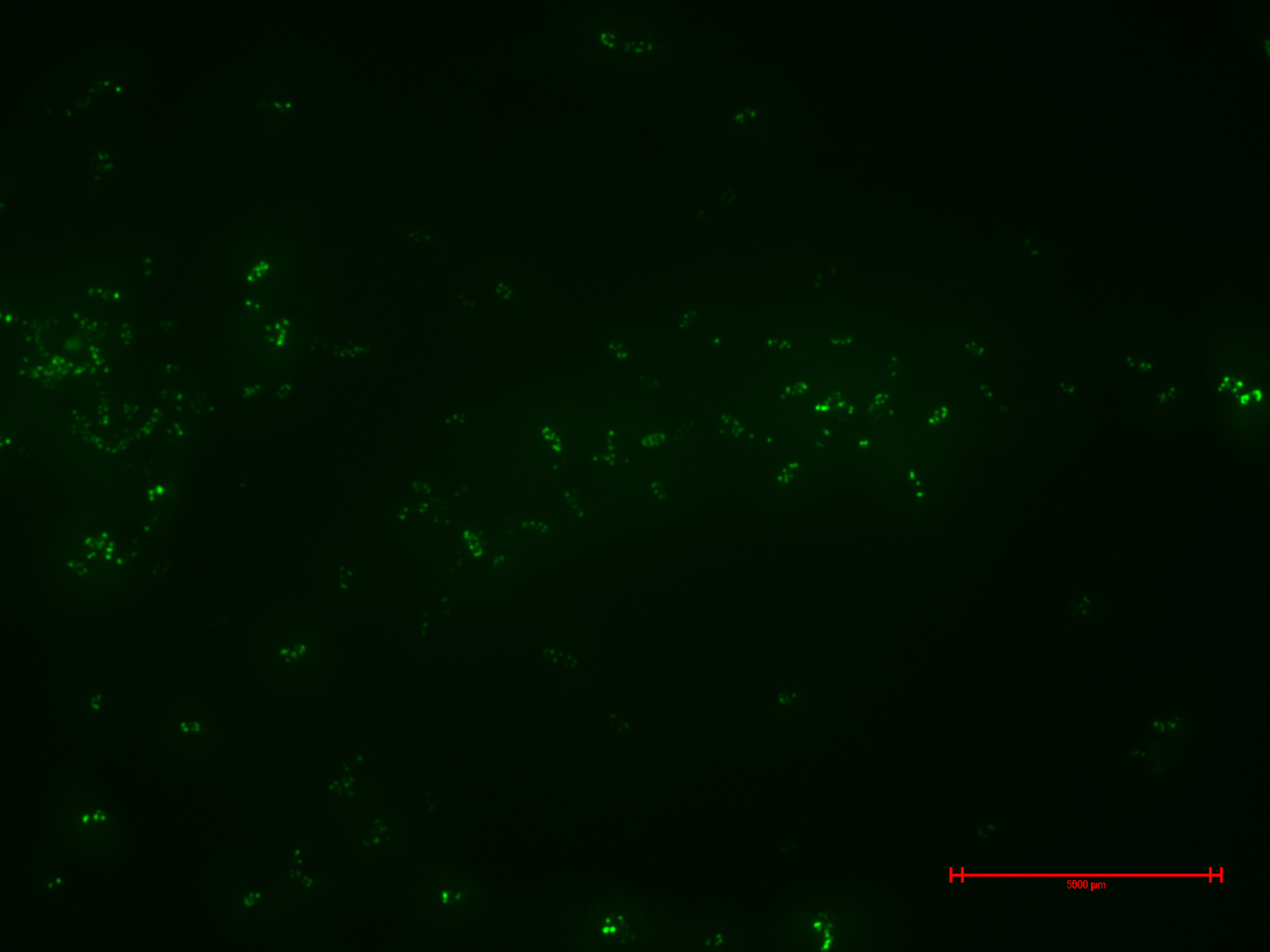
Experiment 2
We prepared for second time samples of B2+ & B3+ to observe in the epifluorescence microscope the effect of time in the samples.
This time B2+ & B3+ presented much more fluorescence, and it persisted over time (at least 1 hour with no significant variation).
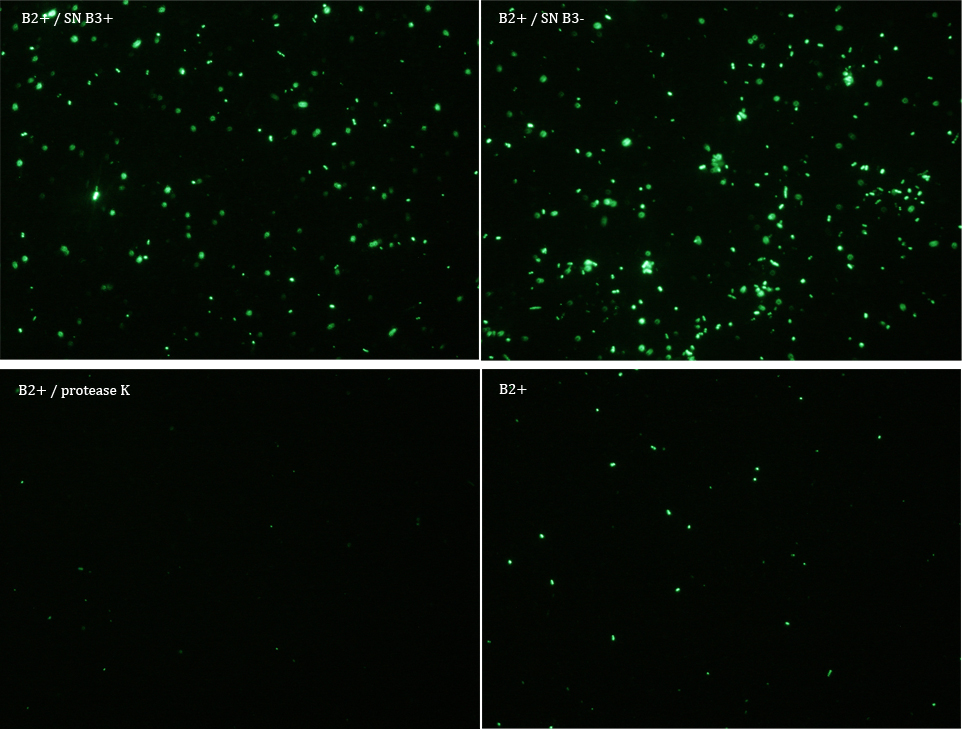
Experiment 3
We did another experiment to investigate the interactions between our bacteria B2+ and B3, but this time with a serious protocol and recording the data for later analysis.
We expected that our results were coherent with our theory. [1]. Both HIV protease and protease K should be able to cut the HIV cleavage site, releasing the sfGFP.
The samples used this time were:
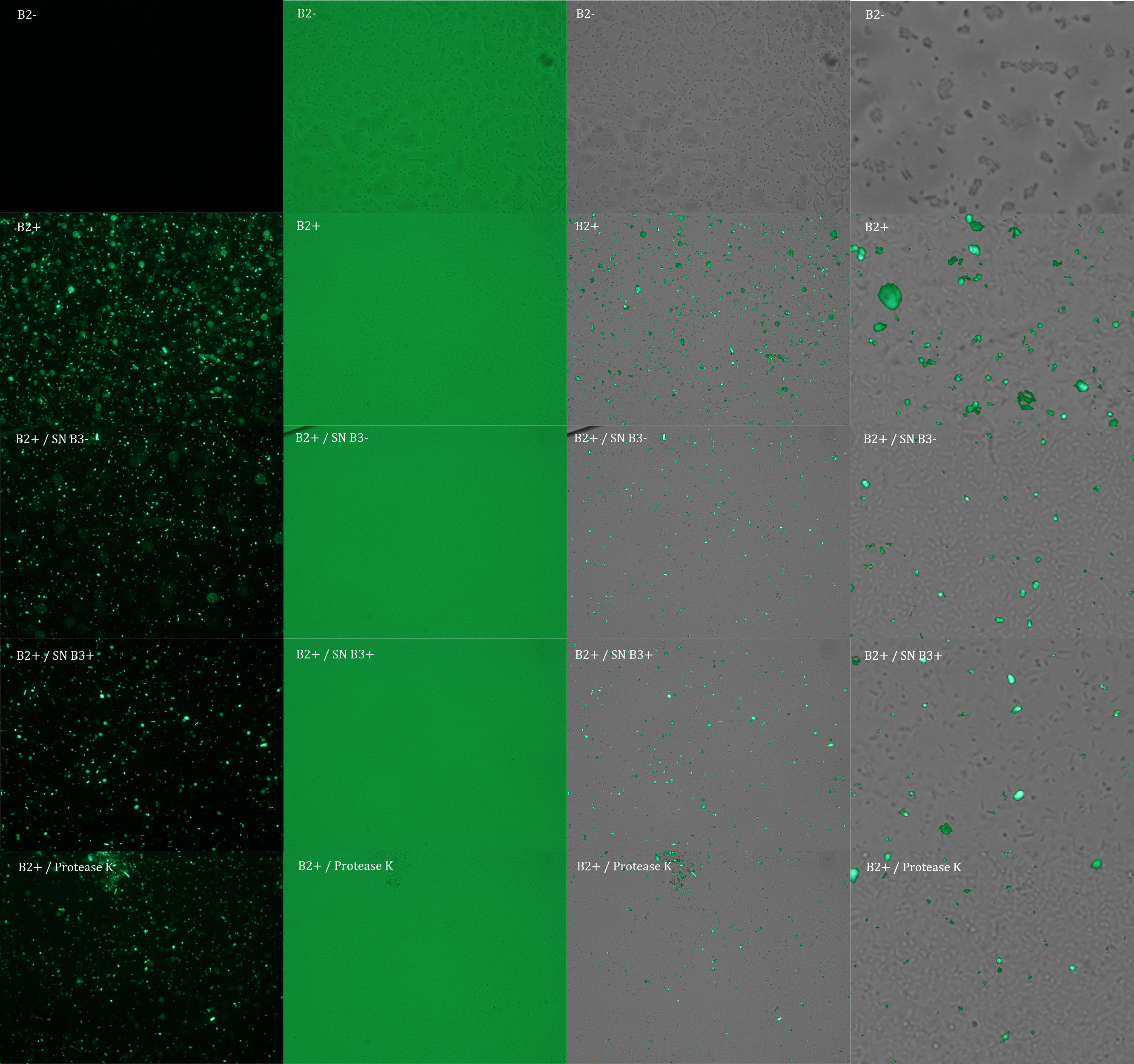
B2+ :
E. coli transformed with GFP Reporter Plasmid and induced with Arabinose
B2+ / SN B3+ :
E. coli transformed with GFP Reporter Plasmid and induced with Arabinose, and Supernatant of coli transformed with Protease Producer Plasmid induced with Arabinose
B2+ / SN B3- :
E. coli transformed with GFP Reporter Plasmid and induced with Arabinose, and Supernatant of coli transformed with Protease Producer Plasmid not induced with Arabinose
B2+ / protease K :
E. coli transformed with GFP Reporter Plasmid and induced with Arabinose, and protease K.
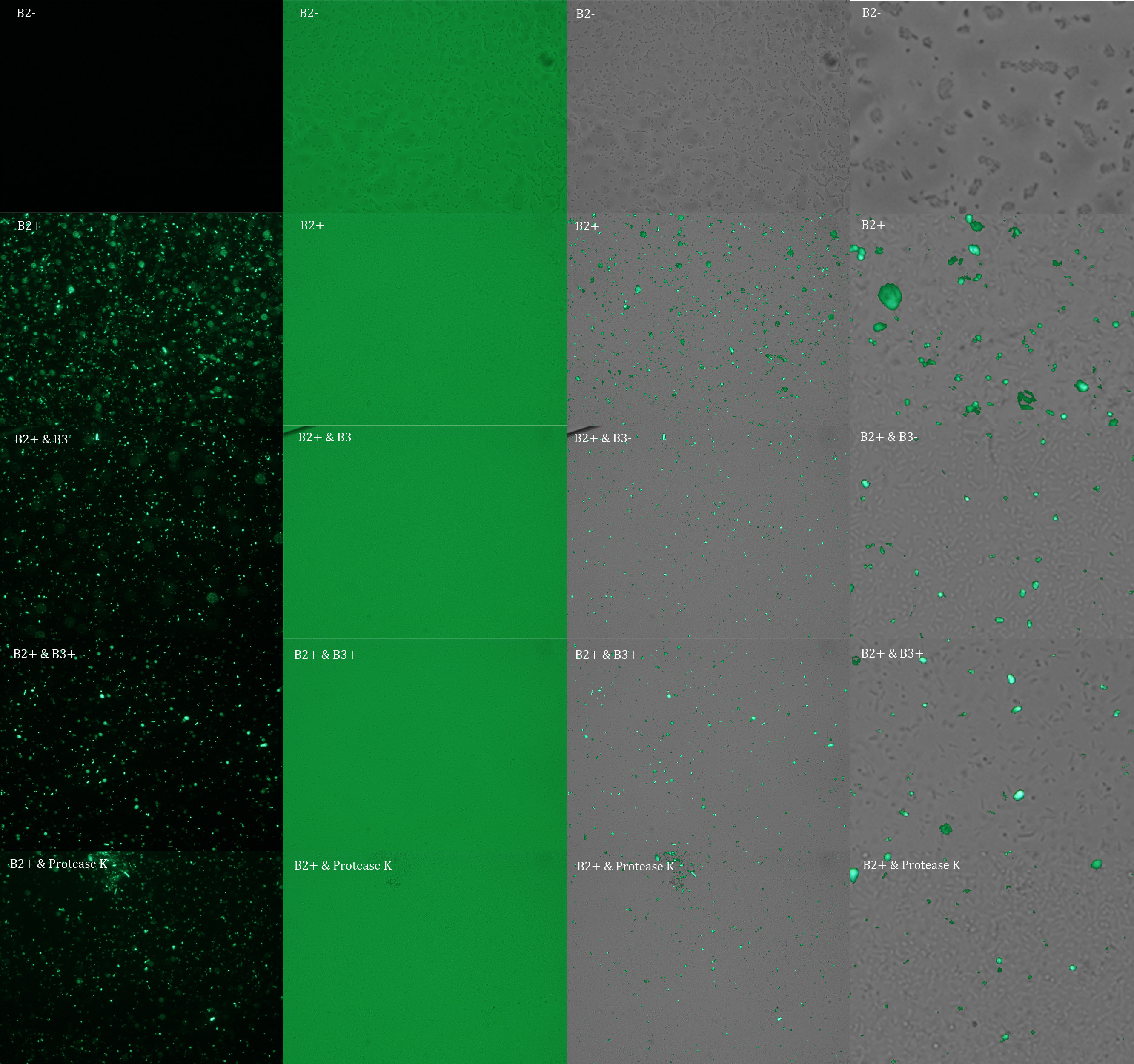
Subsequently we proceeded to observe the samples in an epifluorescence microscope. In the following figure you can see one micrograph of each sample at 100x.
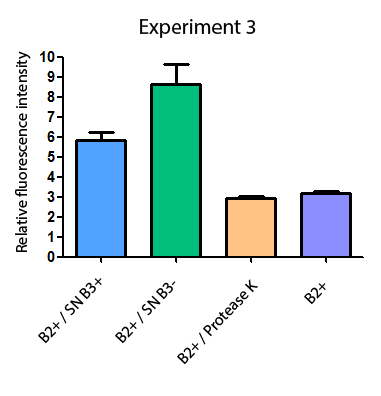
Additionally, we analyzed 4 micrographs of each sample (n=4) with the software ImageJ to compare their fluorescence intensity.
All the different treatments presented significant differences, except (B2+ & protease K) and (B2+). Remarkable is the difference between (B2+ / SN B3+) and (B2+ / NS B3-). Also, the direct application of protease K over the samples decreased even more the fluorescence. However, the low fluorescence of B2+ is very weird. We will have to repeat this experiment, but at least the major part of the results makes is what we expected.
Experiment 4
We repeated the experiment to investigate the interactions between our bacteria B2+ and B3+ with a serious protocol and recording the data for later analysis. This time we added the control B2-.
In the following figure you can see one micrograph of each sample at 100x obtained from a fluorescence microscope.
In the figure each row represents one sample. The first row contains the micragraphs with UV filter. The second row contains the micrographs seen with light. The third row contains the previous micragraphs overlayed (the light image is in grayscale, and the UV image has its black background removed). The forth image is an amplification of the third image (1:4 ratio). Click over the image to open it in a higher resolution.
Additionally, we analyzed 4 UV micrographs of each sample (n=4) with the software ImageJ
The results were quite different compared to the ones of our previous experiment. Remarkable is that, as expected, B2- and B2+ present the lowest and highest fluorescence intensity. Additionally, (B2+ & B3+) and (B2+ & Protease K) present very similar fluorescence. However, for second time we obtained a weird result: (B2+ & B3+) and (B2+ & B3-) present the same amount of fluorescence.
In conclusion, we know that sfGFP expresses in our e. coli. But we don’t know if it is attached to the external side of the membrane, or if the HIV-1 protease works as expected. As this secretion system seems to be failing, we chose to try other alternatives.
The construction of the first spider silk biobrick
We tried with a lot of patience (in SEVERAL intents with many different strategies) to make a biobrick with the spider silk monomer ADF-3 or the sequence of DNA corresponding to ADF-3 and tags necessary to identify and export the protein with the Type 3 Secretion System of Salmonella (SPI 2). The original sequences correspond to the described in
Widmaier, D. M., Tullman-Ercek, D., Mirsky, E. a, Hill, R., Govindarajan, S., Minshull, J., & Voigt, C. a. (2009). Engineering the Salmonella type III secretion system to export spider silk monomers. Molecular systems biology, 5(309), 309. doi:10.1038/msb.2009.62
This sequence was kindly sent by Dr. Christopher Voigt to us.
A detailed description of this work is in the notebook section. After tons of hours of hard work, when finally PCR amplified bands of the correct size, the digestion tests were positive, Colony PCR were succesful, and Gibson Assemblies seemed to work, we sent our final sequence for sequencing, but the results did not match with our designs. Probably this is due to the hihgly repetitive nature of the spider silk monomers.
References
In this section you will find references about production and modelling of recombinant spider silk proteins.
Recommended literature
Teulé, F., Cooper, A. R., Furin, W. a, Bittencourt, D., Rech, E. L., Brooks, A., & Lewis, R. V. (2009). A protocol for the production of recombinant spider silk-like proteins for artificial fiber spinning. Nature protocols, 4(3), 341-55. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.250
Widhe, M., Johansson, J., Hedhammar, M., & Rising, A. (2012). Invited review current progress and limitations of spider silk for biomedical applications. Biopolymers, 97(6), 468-78. doi:10.1002/bip.21715
Widmaier, D. M., Tullman-Ercek, D., Mirsky, E. a, Hill, R., Govindarajan, S., Minshull, J., & Voigt, C. a. (2009). Engineering the Salmonella type III secretion system to export spider silk monomers. Molecular systems biology, 5(309), 309. doi:10.1038/msb.2009.62
Xia, X.-X., Qian, Z.-G., Ki, C. S., Park, Y. H., Kaplan, D. L., & Lee, S. Y. (2010). Native-sized recombinant spider silk protein produced in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli results in a strong fiber. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(32), 14059-63. doi:10.1073/pnas.1003366107
Complementary literature
An, B., Hinman, M. B., Holland, G. P., Yarger, J. L., & Lewis, R. V. (2011). Inducing β-sheets formation in synthetic spider silk fibers by aqueous post-spin stretching. Biomacromolecules, 12(6), 2375-81. doi:10.1021/bm200463e
Askarieh, G., Hedhammar, M., Nordling, K., Saenz, A., Casals, C., Rising, A., Johansson, J., et al. (2010). Self-assembly of spider silk proteins is controlled by a pH-sensitive relay. Nature, 465(7295), 236-8. doi:10.1038/nature08962
Ayoub, N. a, Garb, J. E., Tinghitella, R. M., Collin, M. a, & Hayashi, C. Y. (2007). Blueprint for a high-performance biomaterial: full-length spider dragline silk genes. PloS one, 2(6), e514. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000514
Bauer, F., & Scheibel, T. (2012). Artificial egg stalks made of a recombinantly produced lacewing silk protein. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 51(26), 6521-4. doi:10.1002/anie.201200591
Bayley, H. (1998). Puri ® cation and characterization of recombinant spider silk expressed in Escherichia coli. Cell, 1, 31-38.
Bogush, V. G., Sokolova, O. S., Davydova, L. I., Klinov, D. V., Sidoruk, K. V., Esipova, N. G., Neretina, T. V., et al. (2009). A novel model system for design of biomaterials based on recombinant analogs of spider silk proteins. Journal of neuroimmune pharmacology : the official journal of the Society on NeuroImmune Pharmacology, 4(1), 17-27. doi:10.1007/s11481-008-9129-z
Dams-Kozlowska, H., Majer, A., Tomasiewicz, P., Lozinska, J., Kaplan, D. L., & Mackiewicz, A. (2012). Purification and cytotoxicity of tag-free bioengineered spider silk proteins. Journal of biomedical materials research. Part A, 1-9. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.34353
Das, R., & Baker, D. (2008). Macromolecular modeling with rosetta. Annual review of biochemistry, 77, 363-82. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.062906.171838
Kenney, J. M., Knight, D., Wise, M. J., & Vollrath, F. (2002). Amyloidogenic nature of spider silk. European Journal of Biochemistry, 269(16), 4159-4163. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03112.x
Keten, S., & Buehler, M. J. (2010). Nanostructure and molecular mechanics of spider dragline silk protein assemblies. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface / the Royal Society, 7(53), 1709-21. doi:10.1098/rsif.2010.0149
Lazaris, A., Arcidiacono, S., Huang, Y., Zhou, J.-F., Duguay, F., Chretien, N., Welsh, E. a, et al. (2002). Spider silk fibers spun from soluble recombinant silk produced in mammalian cells. Science (New York, N.Y.), 295(5554), 472-6. doi:10.1126/science.1065780
Moisenovich, M. M., Pustovalova, O. L., Arhipova, a Y., Vasiljeva, T. V., Sokolova, O. S., Bogush, V. G., Debabov, V. G., et al. (2011). In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility studies of a recombinant analogue of spidroin 1 scaffolds. Journal of biomedical materials research. Part A, 96(1), 125-31. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.32968
Rising, A., Widhe, M., Johansson, J., & Hedhammar, M. (2011). Spider silk proteins: recent advances in recombinant production, structure-function relationships and biomedical applications. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 68(2), 169-84. doi:10.1007/s00018-010-0462-z
Tobar, J. a, Carreño, L. J., Bueno, S. M., González, P. a, Mora, J. E., Quezada, S. a, & Kalergis, A. M. (2006). Virulent Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium evades adaptive immunity by preventing dendritic cells from activating T cells. Infection and immunity, 74(11), 6438-48. doi:10.1128/IAI.00063-06
Vollrath, F. (1999). Biology of spider silk. International journal of biological macromolecules, 24(2-3), 81-8. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10342751
Vollrath, F., & Knight, D. P. (2001). Liquid crystalline spinning of spider silk. Nature, 410(6828), 541-8. doi:10.1038/35069000
Winkler, S., Szela, S., Avtges, P., Valluzzi, R., Kirschner, D. a, & Kaplan, D. (1999). Designing recombinant spider silk proteins to control assembly. International journal of biological macromolecules, 24(2-3), 265-70. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10342773
 "
"