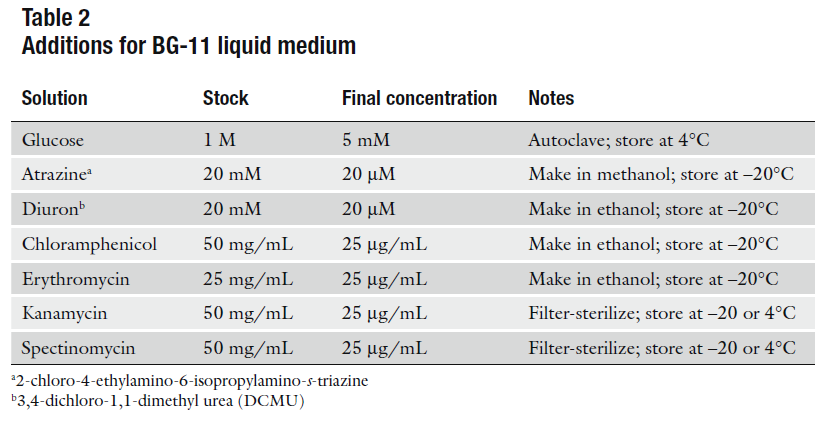
Autoclave and store at 4°C.
The standard assembly reaction relies on the standarization of Biobricks to join different DNA parts. Plasmids from the registry of standard parts allow joining of DNA parts by using a combination of specific enzymes to cut a Upstream Biobrick with the restriction enzymes EcoRI and SpeI, and a Downstream Biobrick with the restriction enzymes XbaI and PstI into a Destination plasmid which has been cut with the restriction enzymes EcoRI and PstI. The reaction yields the Upstream and Downstream part joined by a mixed restriction site and allows further elongation of the construct by the same strategy. It is important to notice that such a reaction requires purification of the digested parts if any of the plasmids (Upstream, Downstream or Destination) share a resistance marker.
Gibson Assembly is a DNA assembly method created by Daniel Gibson during the development of the first Synthetic Genome (Synthia) 2. Its adaptation to a cloning method allows fast and accurate production of increasingly complex constructions. The strategy behind the method relies on PCR to obtain different parts which share a 40bp homology region, and a 3 enzyme reaction which produces cohesive ends, fills the gaps between the parts and ligates the resulting construct into a scarless assembly of various (>2) parts.
The easiest way to design primers to obtain amplicons with the required overlaps (40bp final overlaps) is to make an in sillico design of the final construct
The assembly reaction is composed of 9uL of 1.33X Gibson assembly master mix + 3uL of purified parts DNA
Chemically Competent cells
To prepare our competent cells we used a protocol we found in openwetware.org. Starting from commercial TOP10 cells as the starting inoculus for the whole protocol, we get competence levels close to 5*10⁸ cfu/ug pUC19 DNA
[http://openwetware.org/wiki/TOP10_chemically_competent_cells Openwetware protocol here]
Cyanobacteria Protocols
Transformation of Synechocystis PCC. 6803
By iGEM - UC_Chile Team 2012 (Based on 1)
Materials
- Liquid BG-11 Media
- Solid BG-11 Media
- Sterile 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask
- Sterile 50 mL Falcon tube (2)
- Sterile 1.5ml Eppendorf tubes
- Petri Dishes
- Millipore Membrane Filters, 0.45um HA (HAWP09000)
- Pasteur pipette
- Antibiotics (according to your selection resistance)
- DNA for transformation
To be prepared previously
Concentrate the DNA to be transformed into Synechocystis to 1µg/µL in 10µL for each transformation (A total of 10 ug of the transformation plasmid).
Inoculate Synechocystis PCC 6803 into a sterile 250mL Erlenmeyer flask with 150mL* of liquid BG-11 and grow culture until you reach an OD730nm of 0.8 – 1.0 (That should take between 6 to 10 days dependending on the amount of initial inoculum).
- For each 50 mL of Synechocystis PCC 6803 you will have 5 individual transformations.
Once you have reached the OD730nm and have enough DNA, proceed to transform.
Transformation
All subsequent actions are to be realized under sterile conditions.
Plate preparation
Prepare 50 mL BG-11 plates with no antibiotic for the transformation day.
Put Millipore membrane filters on BG-11 plates.
- 9.- After the 5 hours of recuperation, take the celular suspension and spread over the Millipore membrane. The suspension is to be spreaded carefully over the whole membrane using a sterile bended Pasteur pipete.
- 10.- Let the membranes dry before transfering the plates to the growth chamber.
- 11.- Transfer plates to the growth chamber putting the membrane facing up and leave at 30°C for 12 hours in light.
- 12.- Transfer membranes to BG-11 plates that contain half of the concentration of the antibiotic (12.5 ug/mL of antibiotic) and leave growing for 3 days at 30°C in light.
- 13.- After the 3 days have passed, transfer the membrane to BG-11 plates with full concentration of antibiotic (25ug/mL).
Colonies should appear between 1 to 2 weeks after the transformation. First you will see most of the cellular suspension dissapear and slowly small colonies should appear in the plate.
Reinoculation
Protocol right here!
Protocol goes here!
Bactomithril Protocols
You can find a complete protocol to produce spider-silk fibers in the following paper:
Teulé, F., Cooper, A. R., Furin, W. a, Bittencourt, D., Rech, E. L., Brooks, A., & Lewis, R. V. (2009). A protocol for the production of recombinant spider silk-like proteins for artificial fiber spinning. Nature protocols, 4(3), 341-55. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.250
Other easier protocols are in the following adresses:
http://www.pnas.org/content/107/32/14059.long
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jbm.a.34353/full
Characterization Protocols
Methods for the characterization of Synechocystis PCC 6803 growth curve
This are the methods we used for setting up the growth curve experiment of our Synechocystis PCC 6803 which is further described here .
Materials
- 4 sterile (autoclaved) 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks
- 1 liter of BG-11
- 250 mL of BG-110
- Axenic culture of Synechocystis PCC 6803
- Sterile filtered 1 mL tips
- Spectrophotometer
- 5 1 mL Cuvettes
All procedures should be realized under sterile conditions, preferably in a laminar flow hood.
- Measure 150 mL of BG-11 with a sterile 50 mL Falcon tube and put into each of the 3 Erlenmeyer flasks.
- Measure 150 mL of BG-110 with a sterile 50 mL Falcon tube and put into the remaining Erlenmeyer flask.
- Inoculate 1 mL of axenic Synechocystis PCC 6803 with and OD730 of X to each flask (including the one with BG-110).
- Place flasks in rotating incubator and try to avoid leaving them out of the incubator for long when taking measurements
- Measure OD600 and OD730 twice a day (preferably with at least 8 hours of difference between measurements)
- Repeat measurements for 14 days
Methods for [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K325909 BBa_K325909 (LuxBrick)] characterization
- Pick a single colony from a transformed plate of K325909. Grow in LB media with chloramphenicol 30ug/mL O/N at 30°C.
- Measure OD at 600nm, then dilute to OD600 = 0.6 with growth media following direct C*V ratio to obtain bacterial stock for experiments.
- Induce with 3mM (L)-Arabinose (final concentration)
- Alicuot 600uL of bacteria and add LB media with chloramphenicol 30ug/mL + additives and inducers up to 1.5mL. This will yield a 0.24 OD600nm.
- Grow at 30°C for 1.5 hours (or at chosen T° condition for characterization).
- Alicuot 100uL into 4 wells of a 96 well falcon plaque.
- Measure luminescence in a ThermoScientific Luminoskan Ascent Microplate Luminometer.
Methods for Gibson Assembly for small parts characterization
The experiment for the characterization of T5 exonuclease concentration in Gibson Assembly for small parts was set as follows:
- After the design of the segment to be assembled as described in the Characterization section, amplification of the parts was done using standard Phusion Polymerase PCR conditions but with a total amount of template of 0.05ng
- Bands where cut and purification of DNA from agarose gel was realized using a Promega's Wizard SV Gel and PCR Clean-Up System, final elution volume of 20 ul
- Purified DNA was quantified using a Nanodrop 2000
- According to concentration of DNA, the amount of pmoles/uL of each part was calculated using the following formulae:
pmoles of DNA = weigth in ng * 1000 (conversion factor from nano to pico) / (650 Daltons * base pair length of part)
- Volumes of each part were calculated to obtain a final amount of 0.0125 pmoles of the small part and 0.0025 pmoles of the backbone in a final volume of 3 uL (add nuclease-free water to reach 3 uL) for each reaction
- For the preparation of Gibson Assembly Master Mixes, different volumes of a 10X T5 exonuclease 1.33X Gibson Assembly Master Mix were mixed with T5 exonuclease-free 1.33X Gibson Assembly Master Mix until appropriate concentrations were reached. If mixing volumes of any of the Master Mixes was lower than 1 uL, then one of the diluted T5 exonuclease 1.33X Master Mixes was used for the mix.
- Gibson Assembly was done as described here, and transformation proceeded as described here
- Each of the concentration points of the experiment was done in triplicate
- Red colonies and white colonies were counted 20 hours post-transformation
References
[1]Julian J. Eaton-Rye , “Construction of Gene Interruptions and Gene Deletions in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. Strain PCC 6803 ”, Photosynthesis Research Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 684, DOI 10.1007/978-1-60761-925-3_22
[2]Gibson DG, Young L, Chuang RY, Venter JC, Hutchison CA 3rd, Smith HO. (2009). "Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases". Nature Methods 6 (5): 343–345. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1318
 "
"