Team:TU Darmstadt/Project/Transport
From 2012.igem.org
(→Transport) |
(→Transport) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
== Transport == | == Transport == | ||
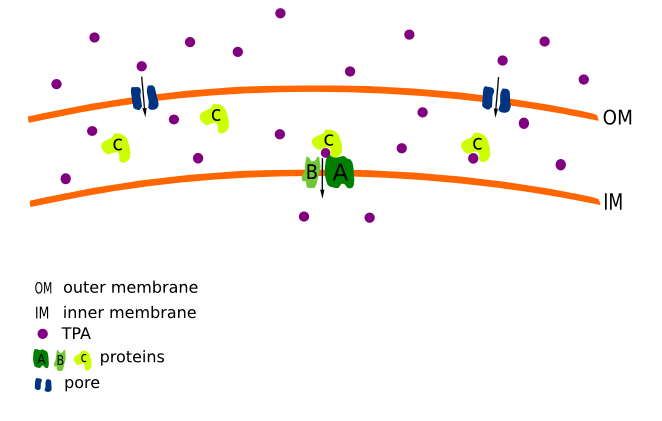
| - | + | The goal for group "Transport" is to express ''comamonas testosteroni'' KF-1 transport proteins in ''Escherichia coli''. The target proteins are regulating the Terephthalic acid (TPA) transport. The TPA transport is crucial to make it accessible for metabolism to useful substances in ''E. coli''. | |
| - | + | TPA can only pass the membrane at low pH values, which negatively affect the growth of ''E. coli''. Therefore, a suitable transport system is needed that operates under good growth conditions for ''E. coli''. | |
| - | + | Based on literature the proteins from ''C.testosteroni'' are forming a tripartite tricarboxylate transport system. The system consists of three subunits called A, B and C. A is a large transmembrane protein with 12 transmembrane domains. It is acompanied by a smaller transmembrane protein with only 4 transmembrane domains. C is a specific periplasmatic bonding protein, which is moving freely in the periplasm and bonds to the AB units. The function is similar to ABC transporters, however the sequences are unrelated. ''C.testosteroni'' KF-1 owns two different A and B proteins (A1 with 505 aa, B1 with 197 aa and A2 with 503 aa, B2 with 162 aa). The proteins are naturally unspecific and can transport different substrates. Initially A1B1C and A2B2C shall be insert on pSB1C3 and pSB1A2 plasmides in ''E. coli'' DH5α. Afterwards they will be transferred in an overexpression strain like BL21(DE3)pLysS or c43 (de3) and expressed under arabinose promotor regulation. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
:[[File:Ttt_v2.png]] | :[[File:Ttt_v2.png]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
continue with [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Project/Metabolism 3. Metabolism] | continue with [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Project/Metabolism 3. Metabolism] | ||
Revision as of 22:30, 19 September 2012
Transport
The goal for group "Transport" is to express comamonas testosteroni KF-1 transport proteins in Escherichia coli. The target proteins are regulating the Terephthalic acid (TPA) transport. The TPA transport is crucial to make it accessible for metabolism to useful substances in E. coli. TPA can only pass the membrane at low pH values, which negatively affect the growth of E. coli. Therefore, a suitable transport system is needed that operates under good growth conditions for E. coli. Based on literature the proteins from C.testosteroni are forming a tripartite tricarboxylate transport system. The system consists of three subunits called A, B and C. A is a large transmembrane protein with 12 transmembrane domains. It is acompanied by a smaller transmembrane protein with only 4 transmembrane domains. C is a specific periplasmatic bonding protein, which is moving freely in the periplasm and bonds to the AB units. The function is similar to ABC transporters, however the sequences are unrelated. C.testosteroni KF-1 owns two different A and B proteins (A1 with 505 aa, B1 with 197 aa and A2 with 503 aa, B2 with 162 aa). The proteins are naturally unspecific and can transport different substrates. Initially A1B1C and A2B2C shall be insert on pSB1C3 and pSB1A2 plasmides in E. coli DH5α. Afterwards they will be transferred in an overexpression strain like BL21(DE3)pLysS or c43 (de3) and expressed under arabinose promotor regulation.
continue with 3. Metabolism
 "
"