Team:TU-Eindhoven/LEC/Lab
From 2012.igem.org
Nickveeken (Talk | contribs) |
Nickveeken (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
<p>Fluorescent proteins like our GECOs can be detected by spectrophotometry if the intensity is insufficient to be observed by the naked eye. If many samples have to be measured these can be put onto a 96-wells plate and measured all at once in a special type of spectrophotometer called a plate reader. A plate reader is also convenient for use with small sample volumes, which was beneficial in our case, since it allowed us to concentrate the yeast from a large culture volume into a small volume through centrifugation and obtain a better measurement.</p> | <p>Fluorescent proteins like our GECOs can be detected by spectrophotometry if the intensity is insufficient to be observed by the naked eye. If many samples have to be measured these can be put onto a 96-wells plate and measured all at once in a special type of spectrophotometer called a plate reader. A plate reader is also convenient for use with small sample volumes, which was beneficial in our case, since it allowed us to concentrate the yeast from a large culture volume into a small volume through centrifugation and obtain a better measurement.</p> | ||
| - | <p>The expression of GECOs in yeast did not yield obvious fluorescence when [[Team:TU-Eindhoven/LEC/Device#practice|stimulated in the device]]. To check if the protein was actually present in our cells, we made spectrograms of cells concentrated to 1.25 x 10<sup>8</sup> cells/ml, which amounts to an | + | <p>The expression of GECOs in yeast did not yield obvious fluorescence when [[Team:TU-Eindhoven/LEC/Device#practice|stimulated in the device]]. To check if the protein was actually present in our cells, we made spectrograms of cells concentrated to 1.25 x 10<sup>8</sup> cells/ml, which amounts to an OD<sub>600</sub> of approximately 125.</p> |
[[File:GECO_on_plate_reader_96_wells.jpg|thumb|Samples of yeast on a 96-wells plate. Samples contain either the GECO-plasmid and CCH-MID1 channel plasmids (columns 5 to 10), only a GECO plasmid (column 3), only CCH1-MID1 plasmids (column 4), or no plasmids at all (column 2). Column 1 contains PBS. Furthermore, cells containing all three plasmids were cultured on medium with 2% glucose (column 5 to 7) or on medium with 2% galactose (column 8 to 10). Since the GECO protein is under control of the GAL-promotor, only in galacose medium the GECO protein is expressed. Vertically, cells are put into either PBS (row A), PBS+0.5% Tween (row B), PBS+0.1 mM calcium acetate (row C) and PBS+0.5% Tween+0.1 mM calcium acetate (rowD). Rows E to H are filled with supernatant of induced cells to determine the background fluorescence of the medium.]] | [[File:GECO_on_plate_reader_96_wells.jpg|thumb|Samples of yeast on a 96-wells plate. Samples contain either the GECO-plasmid and CCH-MID1 channel plasmids (columns 5 to 10), only a GECO plasmid (column 3), only CCH1-MID1 plasmids (column 4), or no plasmids at all (column 2). Column 1 contains PBS. Furthermore, cells containing all three plasmids were cultured on medium with 2% glucose (column 5 to 7) or on medium with 2% galactose (column 8 to 10). Since the GECO protein is under control of the GAL-promotor, only in galacose medium the GECO protein is expressed. Vertically, cells are put into either PBS (row A), PBS+0.5% Tween (row B), PBS+0.1 mM calcium acetate (row C) and PBS+0.5% Tween+0.1 mM calcium acetate (rowD). Rows E to H are filled with supernatant of induced cells to determine the background fluorescence of the medium.]] | ||
Revision as of 01:17, 27 September 2012

GECO protein expression and isolation

The three GECOs have been expressed in E. coli BL21 to yield a large amount of the proteins for characterization. Cells were cultured in large Erlenmeyer flasks. The results were visually impressive: After lysis the flasks turned vibrantly red and green respectively. The blue GECO however looked much the same as the green GECO.
More information about the GECOs can be found at Our BioBricks.
Yeast transformation
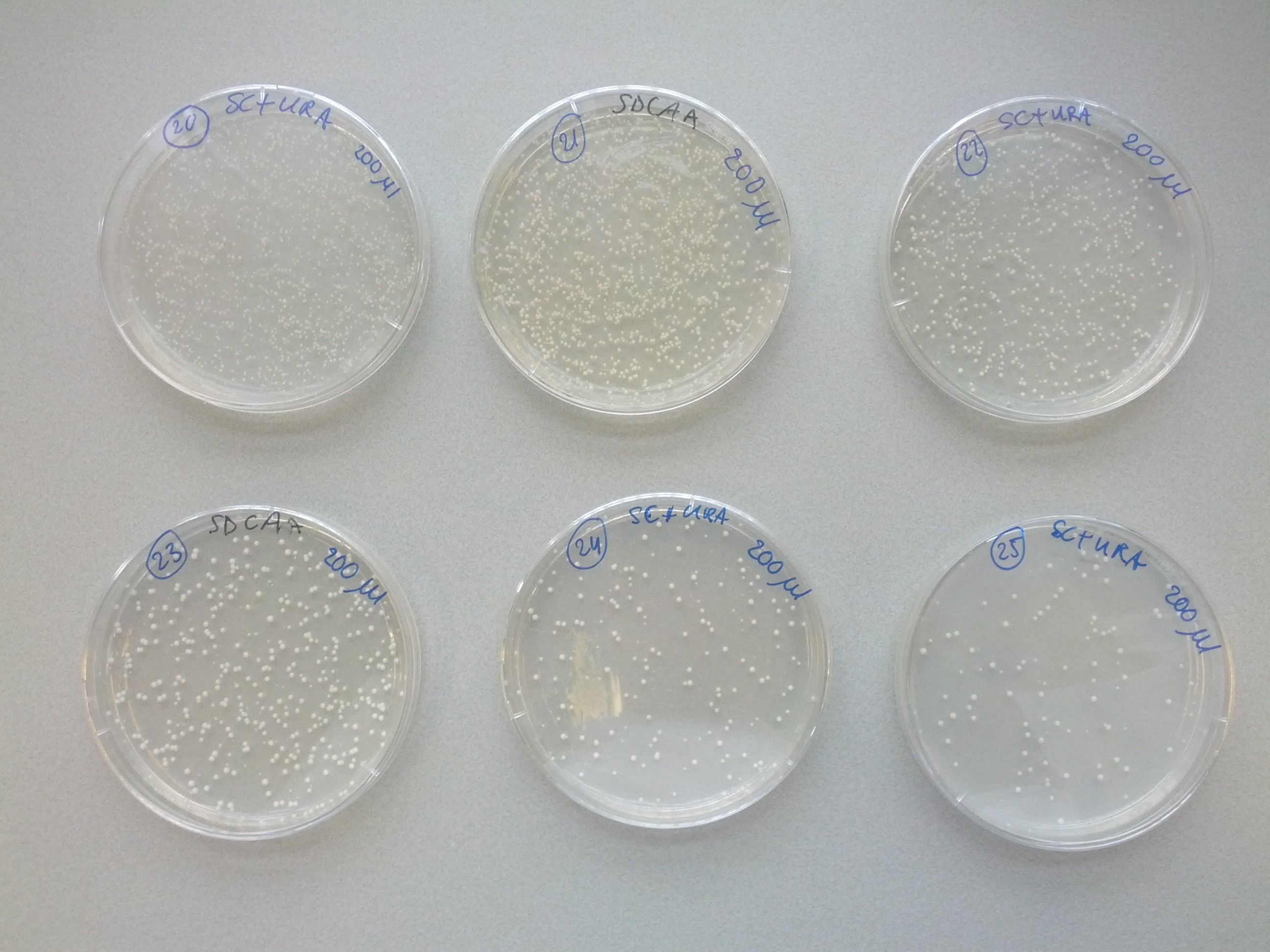
A weekly item on our schedule was yeast transformation. It takes about a week to complete a transformation, that is, to add one plasmid to an existing strain variant. Because success is not guaranteed we choose to introduce plasmids in various orders in parallel. This resulted in many variants that we assigned a unique number for convenience. The same number was used on plates, cultures and cryostocks. In total 49 variants were made.
To reach the aim of this project and prepare a multi-colored screen, three kind of cells, each with a different color, are needed. Therefore, one single plasmid strain would have to consist of both calcium channel parts MID1 and CCH1 sequences and one of the fluorescent GECO protein sequence. Each of these DNA sequences, coding for the three different parts, is transformed into a yeast plasmid (InvSC1). Moreover, each of these sequences contain a small sequence coding for an amino acid, causing the yeast strain to be able to synthesize this specific amino acid. The synthesis of this specific amino acid will allow strain selection by retaining this amino acid from the culture media. Cells containing the coding CCH1, MID1 and GECO sequence are able to synthesize leucine, uracil and tryptophan respectively.
Looking at Scheme 1, which represents the transformations needed to come to the desired yeast strain, it seems and is logical to start with the MID1 or CCH1 vectors. By doing so, less transformations can be performed due to the transformation intensive introduction of the three different GECO proteins at last. To make sure that the transformations would lead to the desired strain, it was decided to start the first step with transforming all possibilities. When step one was transformed successfully, visualized by the arrows in Scheme 1, the transformation of step two was performed and so on.

Scheme1: Transformation Scheme
The several transformation steps are clarified in Scheme 1. The arrows represent a successful transformation as at the same time the lack of an arrow represents a transformation failure. Of course, not every transformation was needed to obtain the desired strain. E.g. in step one the transformation of the R-GECO failed, however, the strain containing the R-GECO was obtained in step two due to other successful transformations. As can be seen, in step 2 the first co-transformation are performed. This brought some complications because the regular transformation protocol did not work for these co-transformations. For the co- and co-co-transformations (performed in step 3) we used another high-efficiency transformation protocol which worked out successfully. After 3 steps of transformations, a couple of different transformation paths reached the three desired strains a complete calcium channel and one of the three GECO proteins.
Initially, yeast transformations failed or yielded only several colonies, a lot less than expected. A review of transformation protocols showed that the shock protocol we used should be more efficient than electroporation or other common methods. We tried to transform another yeast strain with our plasmids which yielded the expected high transformation efficiency. Unfortunately that strain was not compatible with the auxotrophic markers on the plasmids we wanted to introduce. Our problem was remedied by using more plasmid DNA for the transformation, as described in our modified yeast transformation protocol.
Device tests
The device was tested with yeast containing all three plasmids, thus over expressing channels and expressing GECOs. A quick inspection with the naked eye did not show any sign of visual light coming off the device, not even in a dark room. We think that the yeast was not concentrated enough to show a clear response.
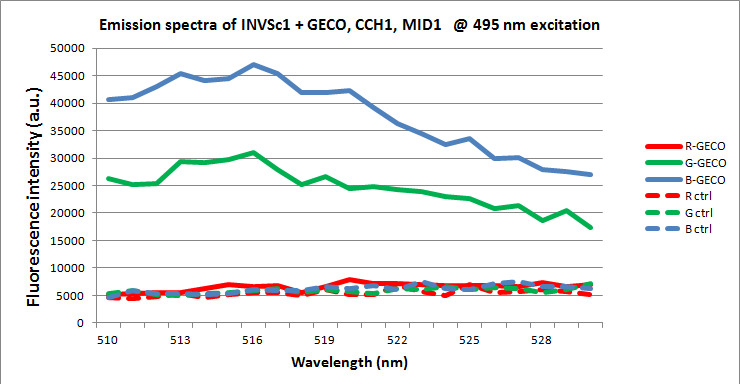
Detection of GECO protein in yeast
Fluorescent proteins like our GECOs can be detected by spectrophotometry if the intensity is insufficient to be observed by the naked eye. If many samples have to be measured these can be put onto a 96-wells plate and measured all at once in a special type of spectrophotometer called a plate reader. A plate reader is also convenient for use with small sample volumes, which was beneficial in our case, since it allowed us to concentrate the yeast from a large culture volume into a small volume through centrifugation and obtain a better measurement.
The expression of GECOs in yeast did not yield obvious fluorescence when stimulated in the device. To check if the protein was actually present in our cells, we made spectrograms of cells concentrated to 1.25 x 108 cells/ml, which amounts to an OD600 of approximately 125.

We wanted to demonstrate the presence of GECOs in yeast cells carrying GECO, CCH1, and MID1 plasmids, cultured on induction medium. For this we used a plate reader to detect the possible fluorescence of any GECO protein present within the cells. To exclude other sources of fluorescence we also measured yeast cells without either GECOs, without over expressed CCH1-MID1 or without any plasmids. Furthermore we compared cells carrying GECO- and CCH1-MID1 plasmids cultured in 2% galactose induction medium with cells cultured in 2% glucose growth medium, which represses induction.
When excited at 495 nm, around the peak in the excitation spectrum of G-GECO, both cells carrying G-GECO and cells carrying B-GECO plasmids cultured in induction medium fluoresced, whereas cells carrying R-GECO cultured in induction medium did not fluoresce. Cells cultured in medium that represses the expression of GECO protein did not fluoresce. Furthermore the spectra of G-GECO and B-GECO seem to overlap, which confirms our earlier observation that spectra of G-GECO and B-GECO protein produced in E. coli overlapped.
When excited at 565 nm, around the peak in the excitation spectrum of R-GECO, only cells carrying R-GECO plasmids cultured in induction medium fluoresced, whereas cells carrying G-GECO or B-GECO plasmids cultured in induction medium did not fluoresce. Cells cultured in medium that represses the expression of GECO protein did not fluoresce.
There is a clear difference in spectra between R-GECO and G-GECO, which means they can be used together in a multi-color screen without disturbing each other’s emission. The difference between G-GECO and B-GECO is very small, perhaps another excitation wavelength could better separate the emission spectra and make them better suited for simultaneous use in the same screen.
| name | vector | inserts | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| pYES2/CT-X-GECO | pYES2/CT | R-GECO1, G-GECO1.1, B-GECO1 | High copy-number shuttle vector |
| pYES3/CT-X-GECO | pYES3/CT | R-GECO1, G-GECO1.1, B-GECO1 | High copy-number shuttle vector |
| pET28a | X-GECO/pET28a | R-GECO1, G-GECO1.1, B-GECO1 | Expression vector for E. coli |
The following plasmids were received from addgene.org:
| name | vector | inserts | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMV-X-GECO | CMV | R-GECO1, G-GECO1.1, B-GECO1 | Shipping vector use by addgene.org, CMV vector was not used in this project |
These plasmids were kindly donated by H. Iida & K. Iida:
| name | vector | inserts | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| pBCT -CCH1H | pBCT | CCH1H | Low copy-number shuttle vector, encodes the CCH1 protein |
| pBCT-CCH1H-HA4 | pBCT | CCH1H-HA4 | Low copy-number shuttle vector, encodes HA4-tagged CCH1 |
| pBCT-CCH1H-EGFP | pBCT | CCH1H-EGFP | Low copy-number shuttle vector, encodes EGFP-tagged CCH1 |
| YCpT-MID1 | YCpT | MID1 | Low copy-number shuttle vector, encodes the MID1 protein |
| YCpT-MID1-EGFP | YCpT | MID1-EGFP | Low copy-number shuttle vector, encodes EGFP-tagged MID1 |
References
 "
"