Team:Peking/Modeling/Luminesensor
From 2012.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
m |
m |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
<h3 id="title2">Kinetic Network</h3> | <h3 id="title2">Kinetic Network</h3> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| - | Firstly we established a reaction network for the DNA binding process of <i>Luminesensor</i> | + | Firstly we established a reaction network for the DNA binding process of <i>Luminesensor</i>. Previous works by other scientists indicate that the Vivid (VVD) protein, a sensing domain of <i>Luminesensor</i>, dimerizes in the presence of light,<sup><a href="#ref1" title="Light Activation of the LOV Protein Vivid Generates a Rapidly Exchanging Dimer. B. D. Zoltowski etc. Biochemistry">[1]</a></sup> and the LexA protein, a binding domain of <i>Luminesensor</i>, binds at specific sequences on DNA predominantly when coupled<sup><a href="#ref2" title="LexA Repressor Forms Stable Dimers in Solution. R. Mohana-Borges etc. THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY">[2]</a></sup> and subsequently represses the interest gene. By combining with the mechanisms of the two functional domains of Luminesensor, we concluded with the following kinetic network: |
</p> | </p> | ||
<div class="floatC"> | <div class="floatC"> | ||
Revision as of 01:50, 25 September 2012
Kinetic Network
Firstly we established a reaction network for the DNA binding process of Luminesensor. Previous works by other scientists indicate that the Vivid (VVD) protein, a sensing domain of Luminesensor, dimerizes in the presence of light,[1] and the LexA protein, a binding domain of Luminesensor, binds at specific sequences on DNA predominantly when coupled[2] and subsequently represses the interest gene. By combining with the mechanisms of the two functional domains of Luminesensor, we concluded with the following kinetic network:
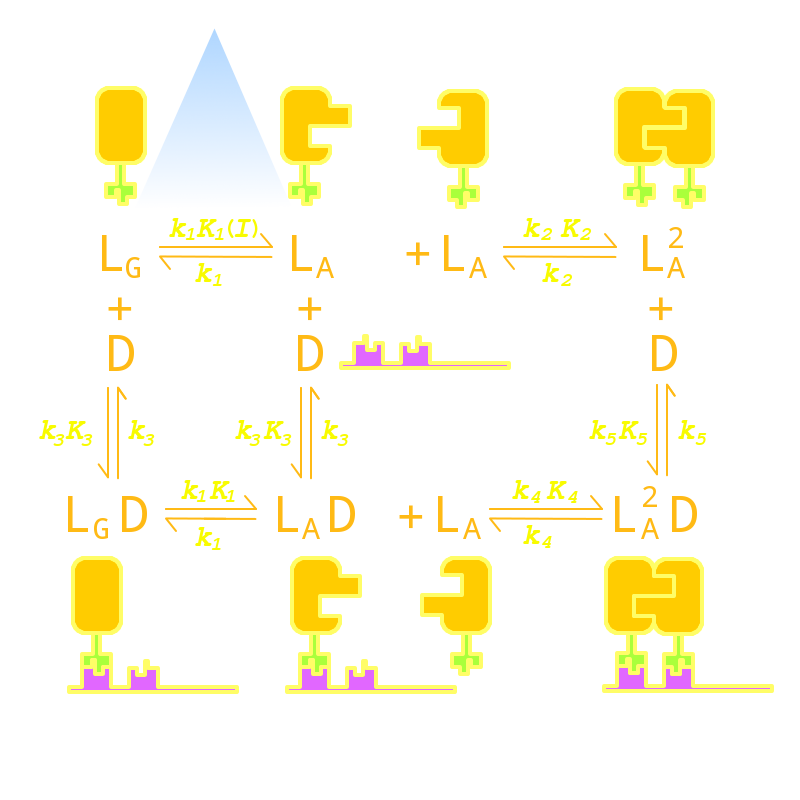
Fig 1. Kinetic Network of our Luminesensor
where
- L : Luminesensor,
- LG : the ground state --- with its VVD N-cap locked,
- LA : the active state --- with its VVD N-cap released,
- DL : the specific DNA binding site to Luminesensor.
Since no multi-intermediate reactions are hidden in the network above, all reactions can be regarded as elementary reactions.
 "
"