Team:TU-Eindhoven/Parts
From 2012.igem.org

To start off with, the iGEM team decided to prepare BioBricks of the GECO proteins since the BioBricks of the calcium channels CCH1 and MID1 (<partinfo>BBa_K363008</partinfo> and <partinfo>BBa_K363009</partinfo> respectively) are already available and able to ligate directly into bacterial plasmids. Moreover, to ligate these calcium channels into yeast plasmids, it's more practical to order the sequences directly from Iida[1], because then the sequence is immediately available for yeast plasmid ligation.
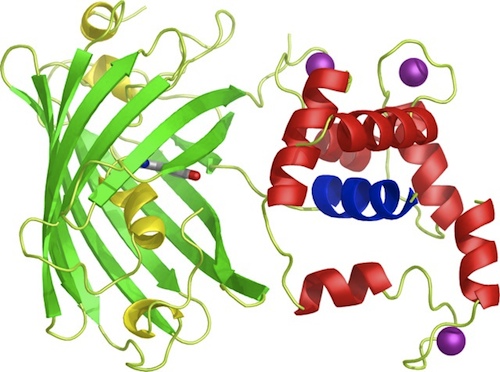
Our iGEM team prepared three different BioBricks: BBa_K881000 (R-GECO), BBa_K881001 (G-GECO), BBa_K881002 (B-GECO). These three GECO proteins, which are obtained from Zhao et al. 2011[2], are red, green and blue fluorescent respectively. The protocol for ligation and restriction obtained from the BioBrick library didn't work for our Biobricks. Therefore, we designed our own protocol, which can be found at the 'Protocol' page, and is shortly described here. The coding DNA for these three proteins was ligated into a <partinfo>pSB1C3</partinfo> vector. After culturing, the vectors were restricted with restriction enzymes XbaI en PstI. These enzymes restricted the vector nicely, however, the DNA sequence coding for the fluorescent GECO proteins appears to contain a restriction site for PstI aswell. Therefore, this procedure was repeated with restriction enzymes XbaI and SpeI. Using this restriction method, the BioBricks can be used in yeast cells and E. coli bacteria.
Although, these BioBricks are prepared in a more efficient way using our own protocol, the permission we needed to apply the GECO BioBricks to registry library was more difficult than expected. You can read more about this struggle at the 'Other Thoughts' page.
Characterization
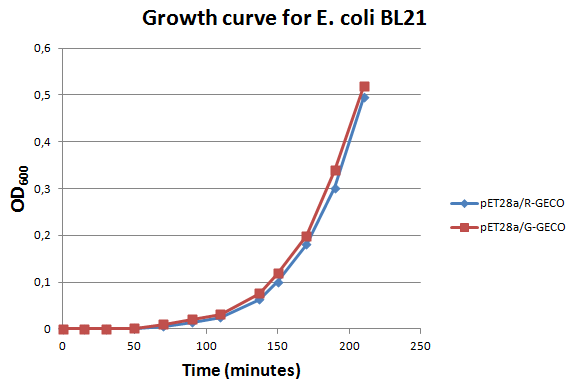
E. coli strain BL21 transformed with Part BBa_K881000 and Part BBa_K881001 ligated into vector pET_28a were cultured in LB media containing 100 µg/ml kanamycin for ~4 hours at 37°C. The growth rate was followed by use of OD600 measurements (see figure on the right). Then the culture was induced at an OD600 of 0,82 absorption units with 100 µg/ml IPTG.
Harvesting and Purification
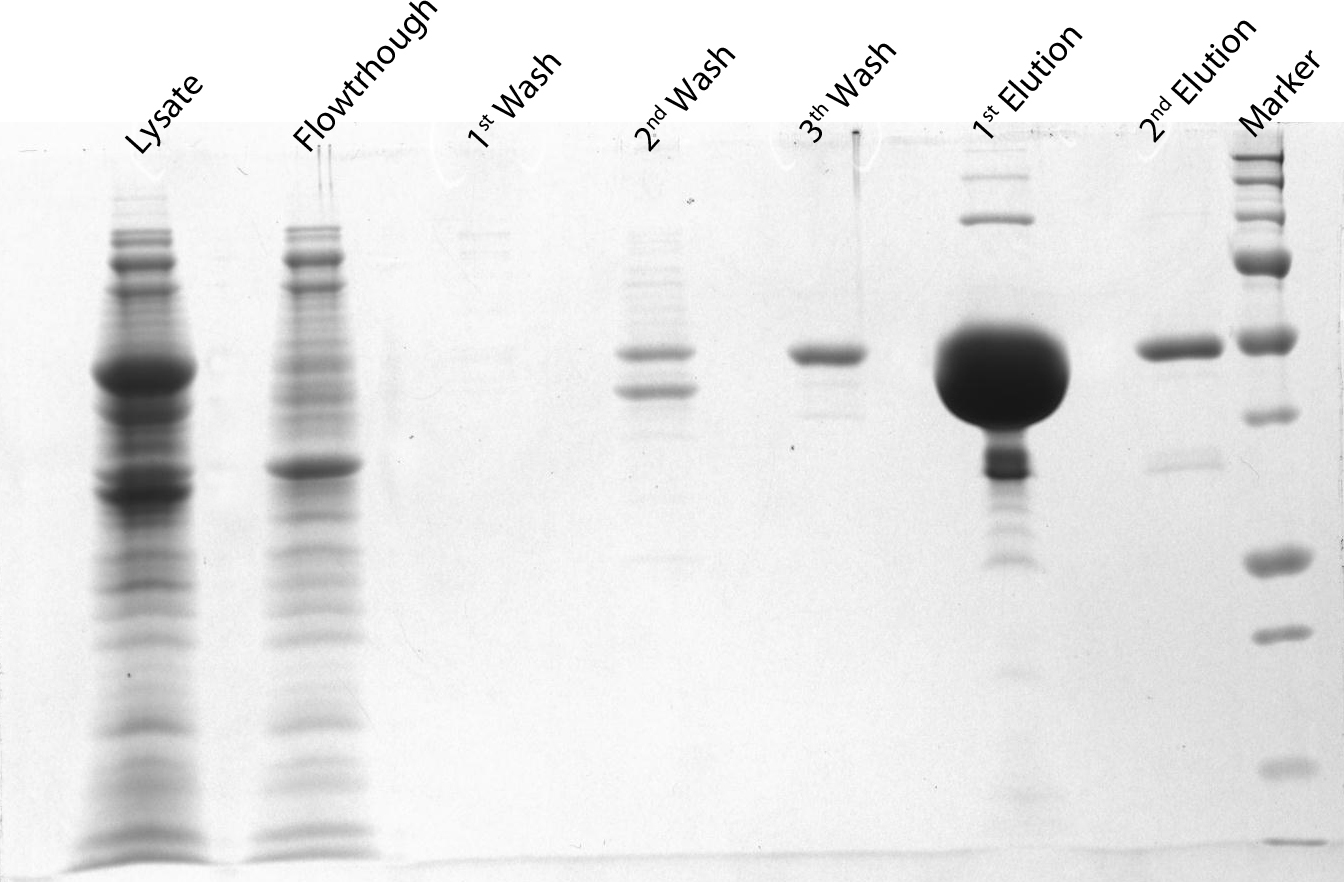
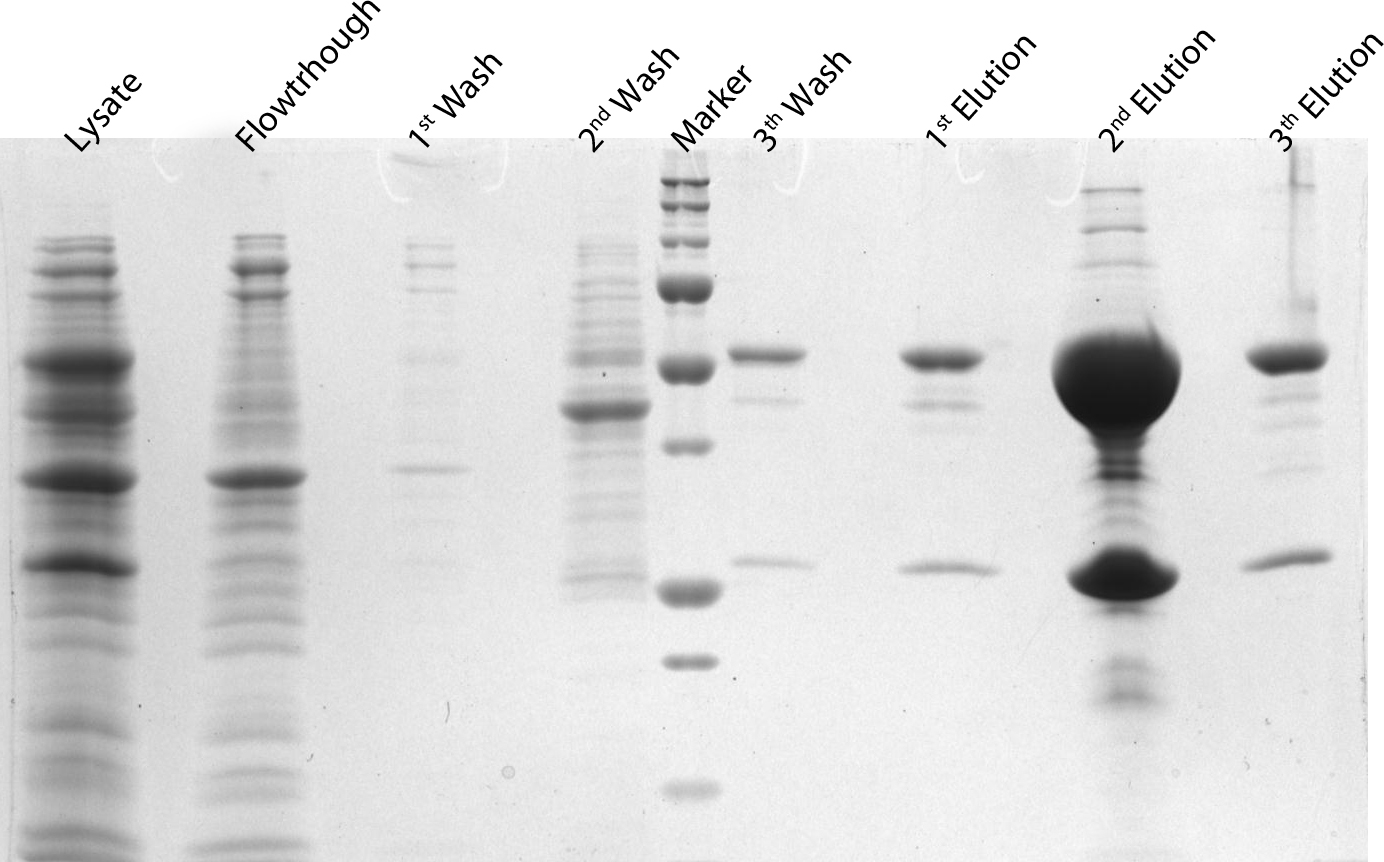
After induction for 15 hours, the cells were harvested and lysed with 5ml BugBuster containing 1µl/ml Benzonase. The supernatant of this suspension was put on a Ni-NTA column for purification and afterwards put on a PD10 column and washed with a TRIS buffer containing NaCl to remove all the calcium molecules. Then, an SDS-gel was prepared to check the abundance and the purity of the GECO proteins (See figure below). As can be seen in the gels, the GECO proteins are present in abundance.
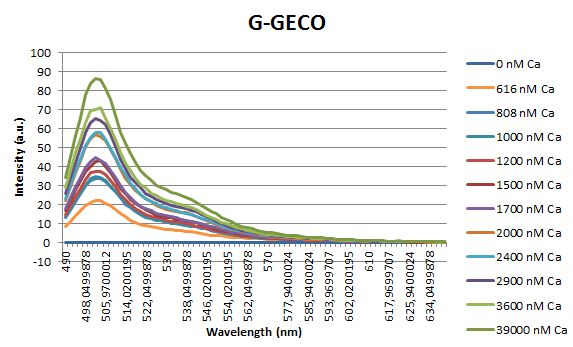
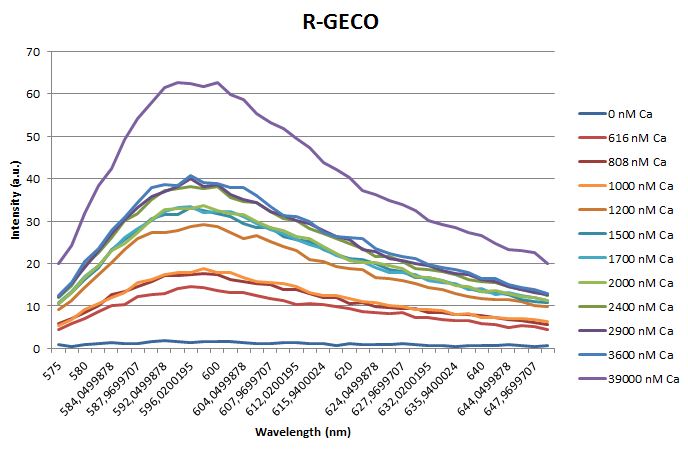
Calcium titration
Before measuring the fluorescence, the samples were prepared first. A 30mM MOPS buffer was prepared containing 100mM KCl and 10mM EGTA. Since EGTA has a high affinity for calcium, in this buffer the GECO proteins will be discomposed from calcium completely. Then 1μl 1mg/ml protein was added to this buffer aswell as a range of calcium concentrations ranging from 0nM to 3,900nM free calcium. Then, the fluorescence of the two GECO proteins, G-GECO and R-GECO, was measured at 20°C. The proteins were excited at 485nm and 565nm respectively. In the figure below, it can be seen that the intensity of the fluorescence increases upon increasing free calcium concentration, suggesting our BioBricks are indeed sensitive to calcium concentrations.
References
- [1] K. Iida, et al., Essential, completely conserved glycine residue in the domain III S2S3 linker of voltage-gated calcium channel α1 subunits in yeast and mammals, Journal of Biological Chemistry 282: 25659-25667, (2007)
- [2] Y. Zhao, et al., An expanded palette of genetically encoded Ca2+ indicators, Science 333: 1888-1891, (2011)
 "
"