Team:Osaka/Tests
From 2012.igem.org
Tests
Damage tolerance assay
Radioresistance parts contain codon rarely used in E.coli. Codon optimization and a better expression system are needed to make our parts functional, so we transformed plasmid DNA into E.coli Rosetta.
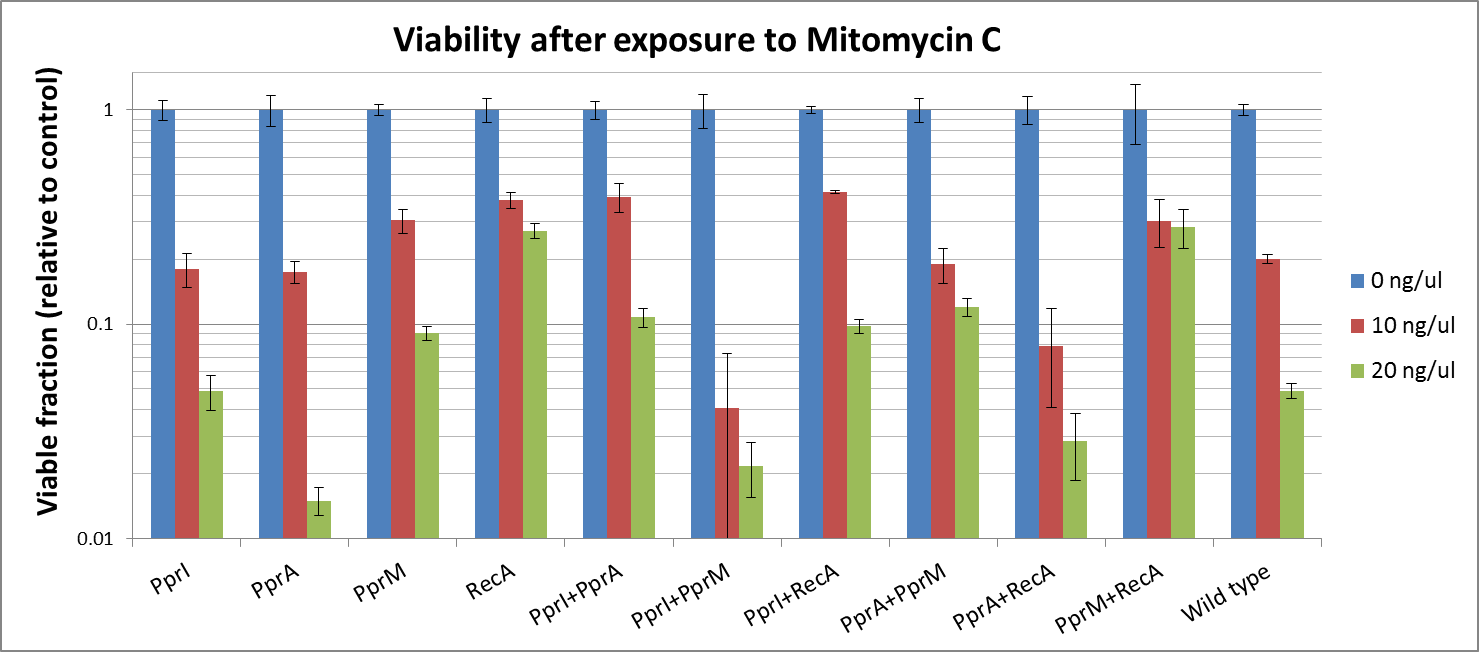
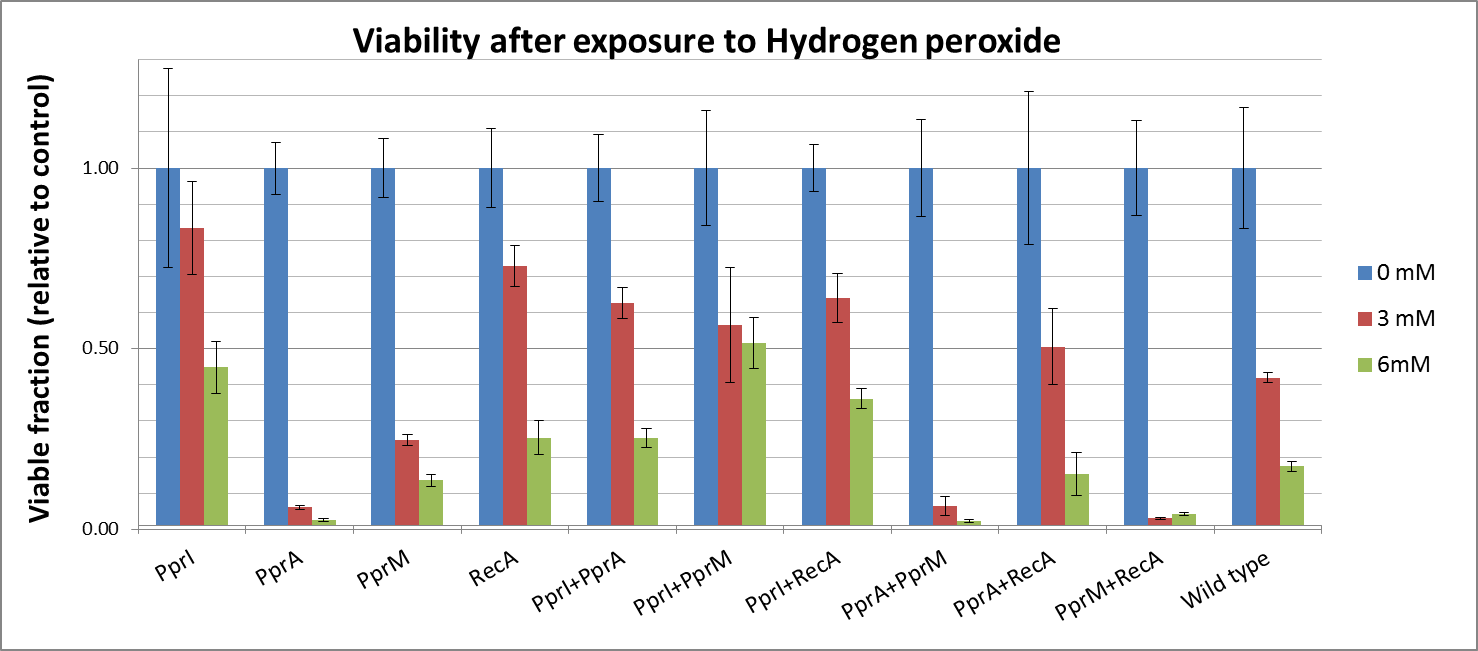
To measure the DNA damage tolerance conferred by each part, we used DNA damaging agents (such as Mitomycin C and Hydrogen peroxide) as a source of DNA damage and then assayed the survival rates. Transformed E. coli was exposed to the DNA damaging agents and then incubated for 2 hours. Cells were plated on agar plates at different dilutions and air dried. Plates were wrapped with aluminum foil and incubated in the dark. Colony-forming units were scored after 16h incubation at 37°C. For detailed protocols, refer to the Protocols page.
The tolerance parts tested were as follows:
Parts containing one gene each
- CDS: [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602005 PprI], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602006 PprA], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602007 PprM] or [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602008 RecA]
Parts containing two genes
- CDS1+2: [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602016 PprI+RecA], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602017 PprA+RecA], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602020 PprM+RecA], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602015 PprI+PprA],[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602018 PprI+PprM], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602019 PprA+PprM],
Discussion
Single-gene parts
Against Mitomycine C
- PprI itself did not increase tolerance, since its known role is an inducer of other radiotolerance proteins. As E. coli lacks downstream proteins of D. radiodurans, it is expected that PprI would not be able to confer tolerance on its own.
- PprA, which repairs blunt-ended breaks, also did not confer tolerance. PprA may not protect against interstrand crosslinks and single strand breaks induced by Mitomycin C
- In our previous experiment using UV irradiation, PprM showed to confer tolerance slightly. Though it is said that PprM is a modulator of the PprI-dependent damage response that depends on downstream effector such as PprA, our resultsindicates that is protective for E.coli by itself.
- In our previous experiments, RecA of D. radiodurans was indicated to confer the highest tolerance among the four radiotolerance genes (against UV irradiation). We should that RecA much increased tolerance against DNA damaging agents, too.. Maybe, it supports the effect of E. coli RecA each other.
Against Hydrogen peroxide
- Actually, each PprA and PprM alone decreased tolerance. It may be due to the cost of their expression.
- On the other hand, both PprI and RecA significantly increased tolerance, which agrees with the role of PprI as an enhancer of enzyme activities of catalases
Two-gene combinations
Against Mitomycine C
- While PprI alone did not confer any tolerance, the combination of PprI and PprA somehow increased the. tolerance This is in accordance with the role of PprI as an inducer of PprA.
- The fact that this combination much increased the tolerance, agrees with the role of PprI as an inducer of D. radiodurans RecA.
- Though it is said that PprM is not a modulator of RecA, here we shiowed a significant increase in tolerance when these two genes are coupled. It could be explained by the fact that PprM is known to induce/modulate other, unknown proteins and some of these proteins may have homologs in E. coli that benefit from the presence of PprM
Against Hydrogen peroxide
- Though PprA or PprM alone did not increase tolerance, the combination of PprI and other radiotolerance genes somehow improved the tolerance. This agrees with the role of PprI as an enhancer of enzyme activities of catalases.
Conclusion
First, PprM appears to protect against to interstrand crosslinks and single strand breaks induced by Mitomycin C. Perhaps its role as a mere modulator of the PprI-dependent DNA damage response needs to be revised, or perhaps it is capable of regulating certain E. coli genes to advantageous effect.
In addition, our results indicated that PprI, as a global regulator of the DNA repair system, alone does not secure against Mitomycin C and UV irradiation. This is in contradiction to a previous report that PprI confers radiotolerance to E. coli.
Finally, D. radiodurans's RecA confer resistance to any mutagen despite past reports that this protein is lethal to E. coli
Promoter assay
We assayed the promoter of the SOS gene RecA ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J22106 J22106]) and sulA ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K518010 K518010]). To measure the DNA damage detection, we used antibacterial agents as a source of DNA damage. To quantitatively and accurately evaluate the promoter activity, dual luciferase assay method was employed. Transformed E. coli was exposed to DNA damaging agents and then incubated for 2 hours. For details check the Protocols page.
We were going to assemble the Dual Luciferase Assay System from existing Biobrick parts, but not yet finished.
Future work
1, Complete the Dual Luciferase Assay System
As we mentioned before, we tried to assemble the Dual Luciferase Assay System from existing Biobrick parts, but have not finished it yet. So, we will go on our experiments and complete it.
2, Quantification of damages to "Bio-dosimeter"
One of the weak point of our "Bio-dosimeter" is impossibility of quantifying the damages. Therefore, for practical use, we need to add some mechanisms that quantify the stresses to "Bio-dosimeter".
 "
"