Team:Austin Texas/Caffeinated coli
From 2012.igem.org
PeterOtoupal (Talk | contribs) (→Results) |
PeterOtoupal (Talk | contribs) (→Growth of cells expressing both GuaB knockout and our deccaffeination operon) |
||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
==<div style="font-size:130%;text-align:center">'''Results</div>== | ==<div style="font-size:130%;text-align:center">'''Results</div>== | ||
| - | ===Growth | + | ===Cell Growth when Expressing both GuaB Knockout and our Deccaffeination Operon=== |
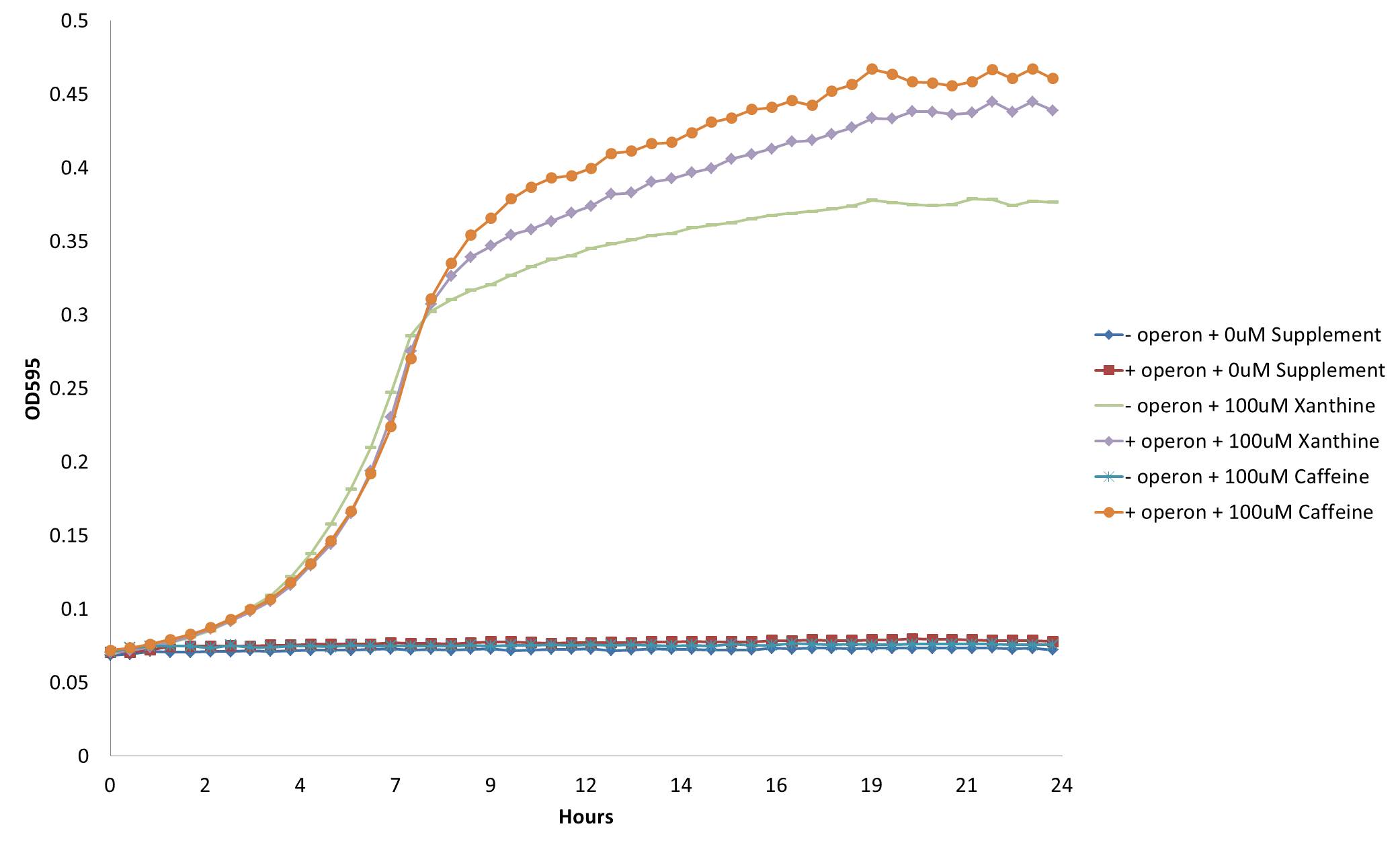
The GuaB gene was successfully knocked out of E. coli cells through use of the BW25113 Keio Knockout Collection. This strain was then transformed with cells from our refactored CBB5 decaffeination operon. Both strains were then grown on M9 minimal media containing 0.2% Caesin as the cell’s only carbon source. The results are shown below. | The GuaB gene was successfully knocked out of E. coli cells through use of the BW25113 Keio Knockout Collection. This strain was then transformed with cells from our refactored CBB5 decaffeination operon. Both strains were then grown on M9 minimal media containing 0.2% Caesin as the cell’s only carbon source. The results are shown below. | ||
Revision as of 22:45, 2 October 2012

Contents |
Project: Caffeinated Coli
Introduction
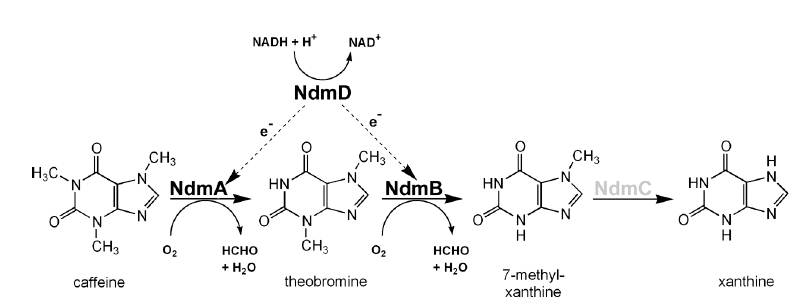
Pseudomonas putida CBB5, discovered by Ryan Summers and Mani Subramanian at the University of Iowa can live on caffeine as the sole carbon and nitrogen source. CBB5 uses a Nitrogen demethylation pathway to convert caffeine to xanthine with formaldehyde side products. The xanthine and formaldehyde are then used as the nitrogen and carbon sources respectively.
The N-demethylation pathway consists of four demethylation genes, ndmA, ndmB, ndmc, and ndmD. ndmA, B, and C remove the methyl group from the N-1, N-3, and N-7 respectively. This is done with the help of a reductase, ndmD.
Strategy
Refactoring Decaffeination Operon
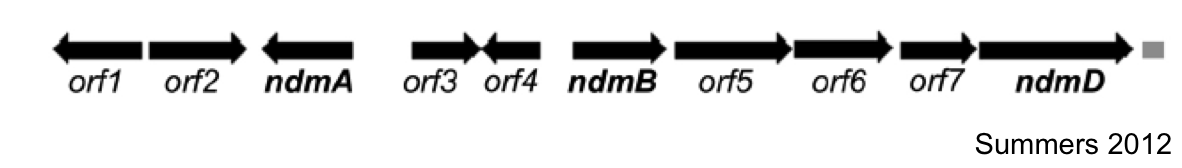
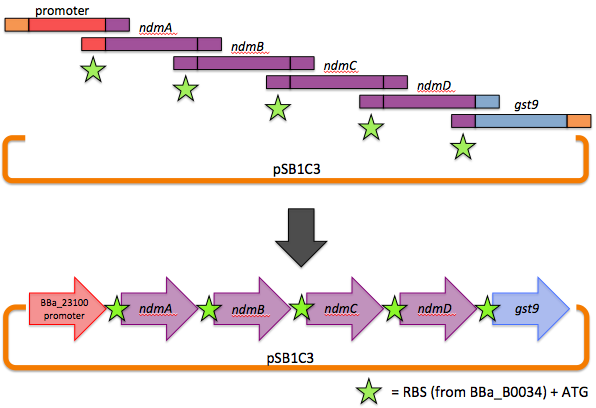
The first goal of this project involves refactoring the caffeine operon from the caffeine utilization pathway from Psuedomonas putida CBB5, first characterized by Summers et al. in early 2012. The operon, shown below, will be incorporated into the well characterized bacterium, Escherichia coli [3].
Directly importing the operon into E. coli was determined impractical, as the strength and regulation of the ribosome binding sites (rbs) and operon-controlled promoters in the CBB5 operon may not be optimized for function in E. coli. Additionally, the use in CBB5 of GTG start codons conflicts with E. coli’s preference for ATG – leading to problems in translation initiation.
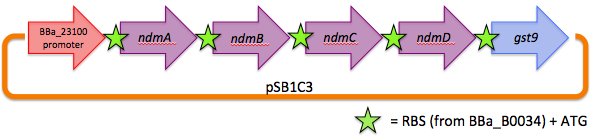
We therefore decided to separate out open reading frames for the genes of interest in the CBB5 operon and put them under controlled regulation in a refactored caffeine utilization operon for import into E. coli. The operon's design, shown below and submitted as [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K734000 BBa_K734000], aims to optimize its functionality in its new host.
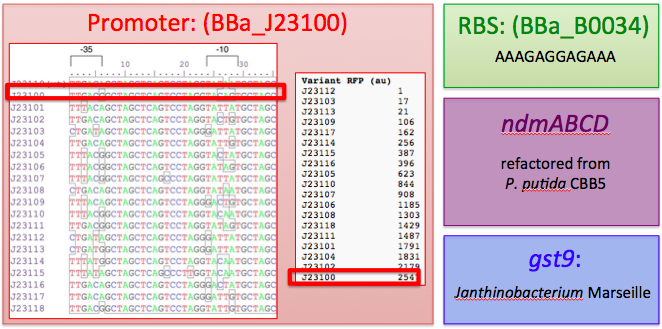
This includes the N-demethylase proteins: ndmA, ndmB, ndmC, and the putative assisting protein ndmD. Also included is the glutathione S-transferase from Janthinobacterium sp. strain Marseille, necessary for functionality of NdmC. Constitutive expression occurs with a strong, well-characterized promoter ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php/Part:BBa_J23100 BBa_J23100]) and a strong, well-characterized RBS ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0034 BBa_B0034]). Finally, all GTG start codons have been replaced with ATG.
Sources of parts used in our synthetic decaffeination circuit:
Assembly
Our operon was assembled via a one-step, six-piece Gibson assembly. Briefly, genes to be stitched together were PCR amplified with overhangs homologous to adjacent genes (or homologous to the vector backbone in the case of the 5' end of the promoter and the 3' end of gst9). The forward primers also contained our chosen RBS and ATG. In a one-pot reaction, a 5'-exonuclease chewed back on the homologous overhangs, allowing adjacent fragments to base pair, and a DNA ligase stitched them together. An overview is shown here.
Operon Testing and Optimization
We will employ two different assays for operon functionality; growth on caffeine as a sole carbon source, and a genetic selection for caffeine demethylation to xanthine. To evaluate the ability to use caffeine as a sole carbon source we will transform TOP 10 E.coli electrocompetent cells with the refactored caffeine utilization operon, grow transformed cells in rich media to saturation and then dilute 1:100 into M9 mineral media. Varying levels of caffeine concentrations will be used to determine the degree of caffeine utilization, and the optimal limit for growth.
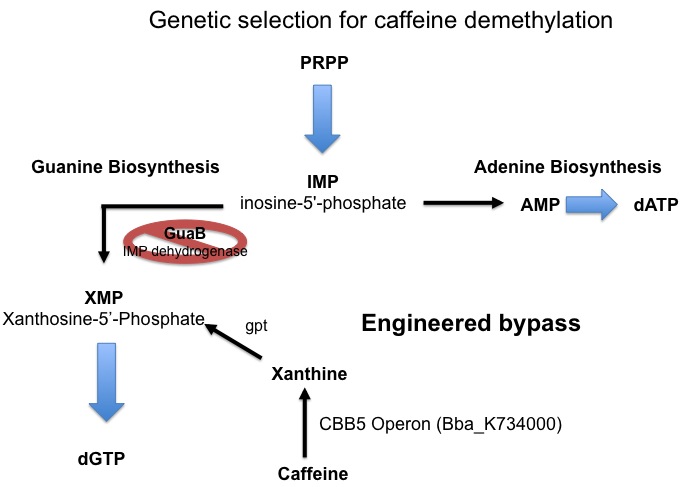
Since the cell has an extremely large requirement for carbon, the energy derived from demethylation may not be enough to support growth. For this reason a second assay for caffeine demethylation based on guanine auxotrophy has been devised. E. coli synthesizes the nucleotide guanine de novo via a pathway that involves Xanthosine-5’-phosphate (XMP) as an essential intermediate. The enzyme responsible for the formation of XMP (from inosine-5’-phosphate[IMP]) is IMP dehydrogenase, which is encoded by the GuaB gene. If GuaB is knocked out, the cell is unable to synthesize guanine and is therefore unable to grow on media lacking guanine. We plan to take advantage of this engineered auxotrophy and use it as a way to select for cells that are able to demethylate caffeine to xanthine which can then be converted to XMP by xanthine-guanine phosphoribotransferase (gpt) and thereby relieve the metabolic block and restore guanine synthesis allowing for cell growth.
Finally, after construction and preliminary testing of the caffeine degradation operon inE. coli, we will attempt to grow our cells in the presence of various commercial caffeinated beverages.
Characterizing Inducible Promoters
In Summmers et al., the two open reading frames orf1 and orf4 are thought to be putative regulators of the caffeine degradation operon's N-demethylase proteins due to the proximity of their genes. They are hypothesized to bind to operator sequences in the intergenic regions between genes in the operon, which may serve as promoters for the various demethylases of the operon.
Analysis of the sizes of the intergenic regions of the CBB5 caffeine utilization operon shows that the regions upstream of the ndm genes are all greater than 150bp. The large size of these intergenic regions and the fact that they precede the catabolic enzyme gene leads us to hypothesize that there are caffeine (or other methylxanthine) regulatory elements in these sequences.
We will clone these open reading frames into the reporter plasmid pRA301. pRA301 contains a promoterless lacZ gene, preceded by a multiple cloning site (MCS). DNA fragments hypothesized to contain promoter elements can be cloned into the MCS and assayed for lacZ expression by Miller assay. Using this method, we can determine the regulatory functionality of each open reading frame by examining varying fluorescence levels.
Results
Cell Growth when Expressing both GuaB Knockout and our Deccaffeination Operon
The GuaB gene was successfully knocked out of E. coli cells through use of the BW25113 Keio Knockout Collection. This strain was then transformed with cells from our refactored CBB5 decaffeination operon. Both strains were then grown on M9 minimal media containing 0.2% Caesin as the cell’s only carbon source. The results are shown below.
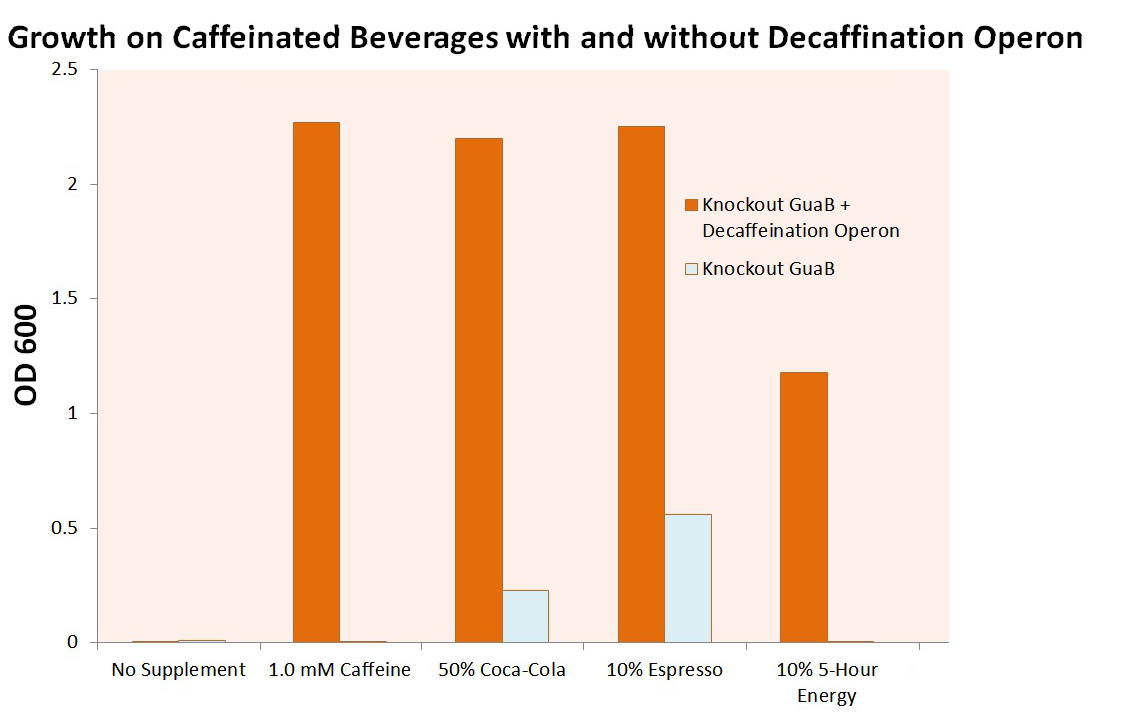
From this figure, we see that our decaffeination operon allows cells that are unable to survive in carbon limited conditions to grow in the presence of xanthine or its derivatives. This not only confirms the functionality of our refactored decaffeination operon, but proves a method by which we can use it to auxotrophically select for cells.
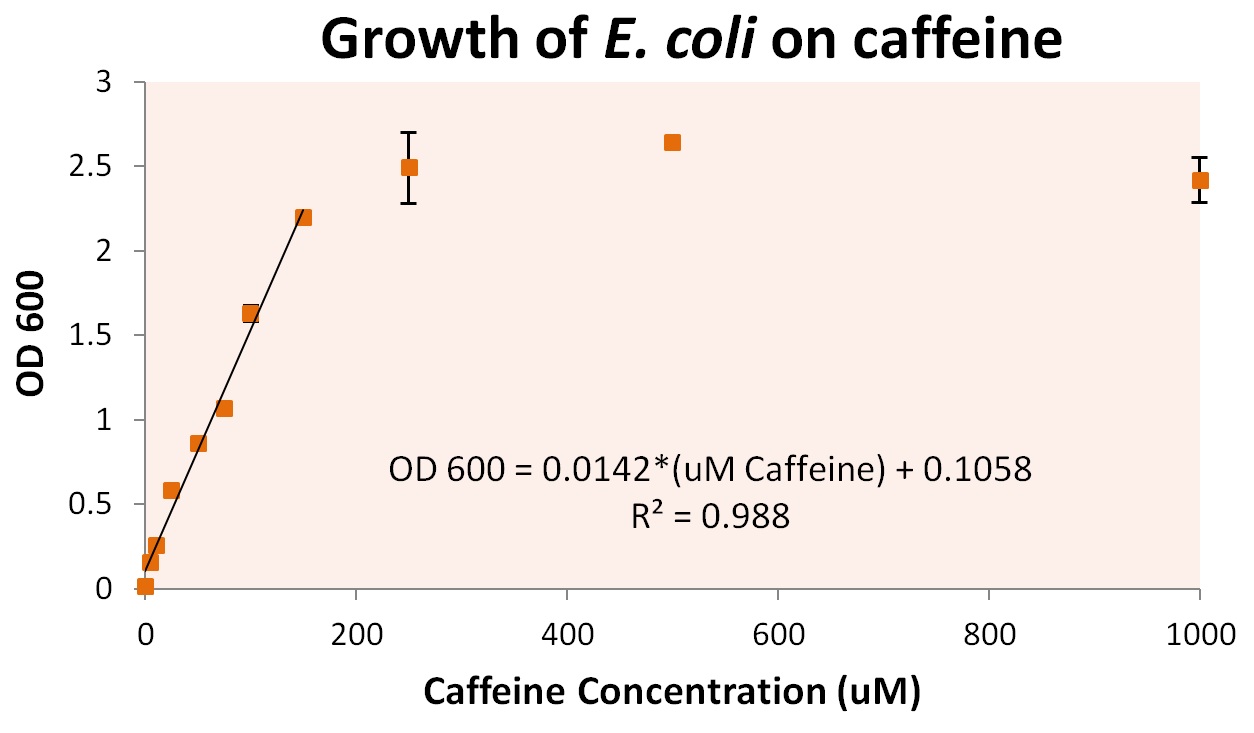
To more accurately determine the utilization of caffeine by our operon, we tested the growth of our E. coli cells containing refactored operon and the knocked out GuaB gene under multiple caffeine concentration conditions. We found that our cells were able to grow at conditions as low as 10uM of caffeine, and peaked at a caffeine concentration of approximately 250uM. Concentrations were grown as high as 5000uM, at which point cells began to die.
From these growth conditions, we plated dilutions of up to 10^7 dilution. This was used to determine individual cell growth based on caffeine. Approximately 7.6 +/- 0.8 pg of caffeine were utilized per cell. Assuming the use of guanine in E. coli DNA that is roughly 9.2 Mb and 50% GC, approximately 2.3 *10 ^6 guanines derived from caffeine are shown to be utilized per cell in our engineered organisms. As there are roughly 10^11 bases of RNA per E. coli cell, and approximately ¼ of these are guanine, there are approximately 2.55*10^10 guanines required for E. coli cell growth. From this calculation, we can include that our cells are scavenging and utilizing approximately all the caffeine present in the system.
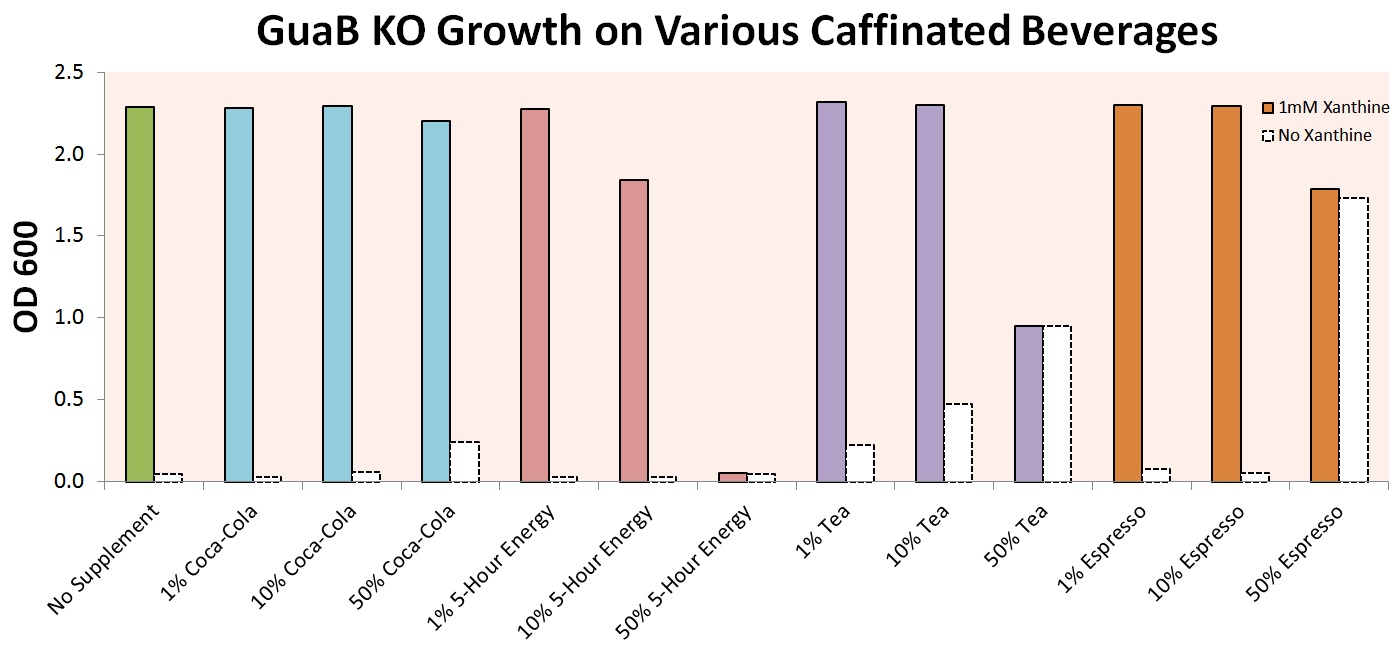
Growth in Caffeinated Beverages (Aurko)
Initial growth tests for guaB KO cells in M9 media supplemented with give supplements, by volume. Growth on various caffeinated beverages with and without xanthine added. Shows if cells are viable in certain beverages, and at what concentrations lethality occurs. Basically proving for next graph that the cells could grow. May or may not even want to include this. :
Final growth tests for guaB KO cells in M9 media supplemented with given supplements, by volume. Note: THIS is when we used the decaffeination operon. Proves cells can scavenge xanthine from caffeine using the decafienation operon. Goes with the pretty pictures Erik and I (mostly Erik) took.
Lots of pictures! You should have all of them in the dropbox folder.
Transcriptional Regulators
As described earlier, we hypothesize that the large intergenic regions upstream of various genes in the CBB5 decaffeination operon, particularly upstream of ndmA, may contain methylxanthine regulated promoters. We propose that orf1 and orf4, which were annotated as putative regulators based on sequence homology, act as repressors for the promoters contained in the operon.
To test these hypotheses, we cloned the intergentic region upstream of the ndmA gene into a promoterless LacZ reporter plasmid, pRA301. This vector enabled quantitative measurement of promoter strength using the β-galactosidase Miller Assay. Additionally, we created compatible biobrick plasmids of each putative repressor, orf1 and orf4, in order to assay their effect on ndmA promoter strength in the presence or absence of methylxanthine supplementation.
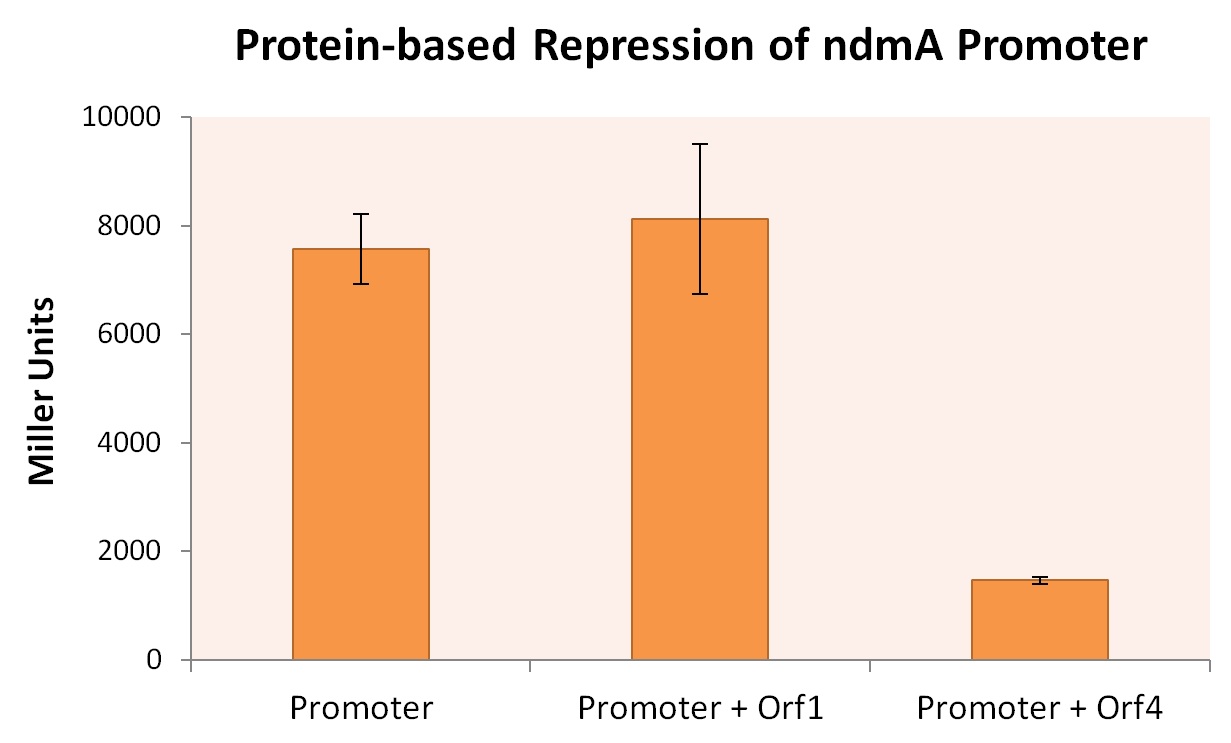
We transformed these plasmids into the Top10 E.coli strain to create three strains: one containing only the ndmA-LacZ reporter plasmid, and cotransformants containing both the ndmA-LacZ plasmid and either orf1 or orf4 biobrick plasmids. All three E. coli strains were grown in M9 minimal media + .2% casein (+ appropriate supplement) at 30oC for 48 hrs, after which time Miller assays were performed. The results, summarized in the figure below, provide strong evidence that expression of orf4 leads to inhibited ndmA promoter functionality, while orf1 expression provides negligible influence on the ndmA promoter.
A higher Miller Unit correlates to a higher level of lacZ production, effectively quantifying the degree of gene expression. As the Miller Unit of the strain co-expressed ndmA promoter with orf4 is lower by a factor of roughly 4, it can be inferred that the protein encoded by orf4 regulates the degree to which the ndmA promoter is expressed during transcription.
It should be noted that while expression of ndmA drops significantly in this experiment, this does not imply that orf4 only inhibits the expression of ndmA. This is discussed in the next section: Inducible Promoters.
Inducible Promoters
As shown above, it appears that orf4 acts as a transcriptional regulator of ndmA expression. One would expect a transcriptional regulator to regulate transcription in a way that is beneficial to the overall fitness of the organism. In certain situations in which a protein is necessary for survival, the transcriptional factor should up-regulate the production of said gene. Likewise, when a protein is not necessary, the transcriptional factor should down-regulate its production.
We hypothesize that this is the way in which orf4 regulates transcription of ndmA. In situations of high caffeine and related xanthine concentrations, the protein encoded by orf4 up-regulates the expression of ndmA. In the experiment listed above, in which no xanthine derivative was added to the media, the expression of ndmA is inhibited (as shown).
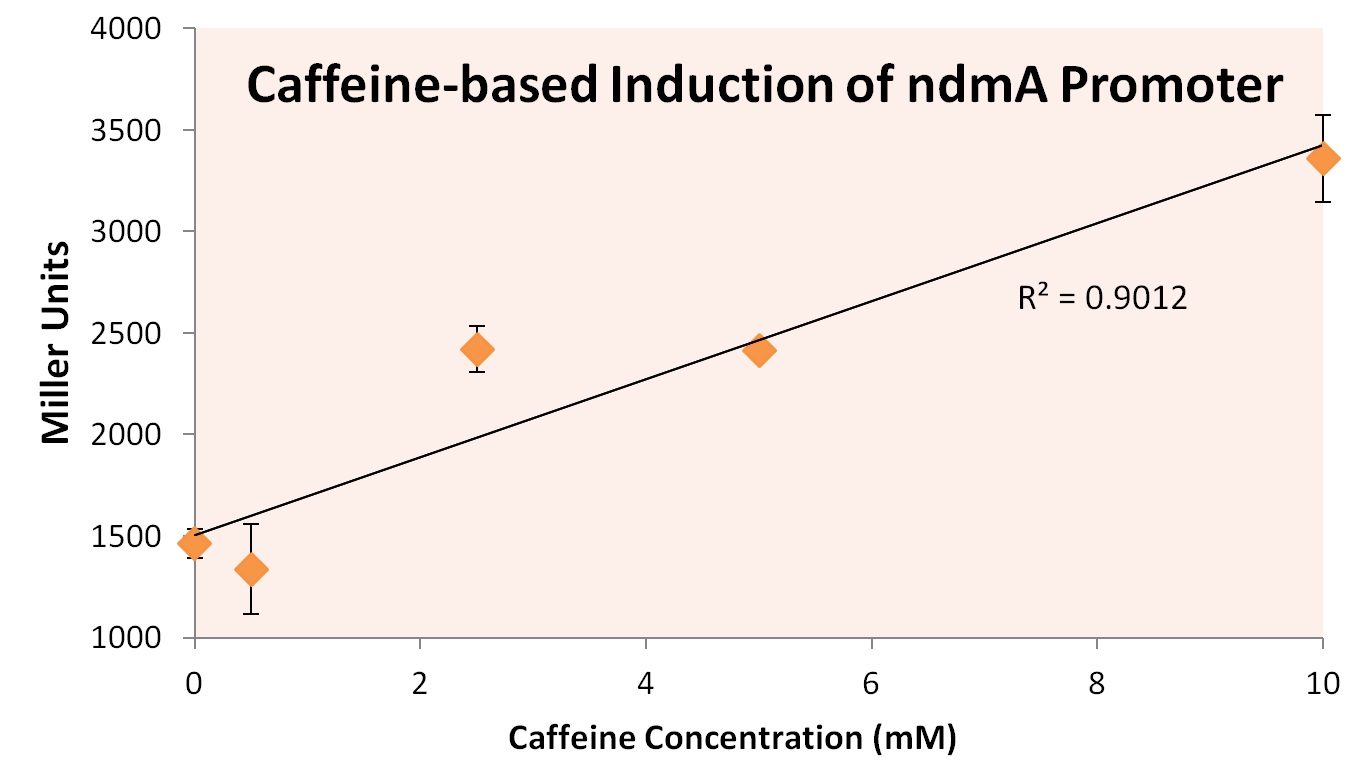
In order to test this hypothesis, we subjected a strain of Top10 E. coli cells containing the orf4 gene and the ndmA promoter containing the lacZ gene to varying supplements of caffeine, theobromine, theophylline, and xanthine. Xanthine was shown to be insoluble at high concentratinos, and was therefore removed from the experiment. The results of exposure to varying concentration levels is shown below.
As predicted, the expression of ndmA appears to rise at higher caffeine concentrations. Similarly, higher concentrations of theobromine and theophylline also appear to increase the expression of ndmA.
From these experiments we conclude that the ndmA intergenic region contains a promoter that is negatively-regulated by the orf4 protein in the absence of methylxanthines. Upon exposure to methylxanthines, it appears that orf4-mediated repression is relieved, leading to induction.
 "
"