Team:TU Munich/Project/Limonene
From 2012.igem.org
(→Toxicity Assay) |
(→Toxicity Assay) |
||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
Limonene at high concentrations affects the growth of yeast cells. We could show an inhibition of growth at 1 mM and even a lethal effect at 100 mM. At lower concentrations (1 µM, 10 µM, 100 µM) no inhibition could be observed. | Limonene at high concentrations affects the growth of yeast cells. We could show an inhibition of growth at 1 mM and even a lethal effect at 100 mM. At lower concentrations (1 µM, 10 µM, 100 µM) no inhibition could be observed. | ||
| - | + | The in vivo GCMS detection of limonene [B] displayed a concentration of 50 µM. Hence the amount of limonene we will produce with the modified yeast will not reach a toxic concentration at all. | |
Revision as of 20:17, 25 September 2012



Contents |
Limonene
Limonene is a cyclic terpene and a major constituent of several citrus oils. D-Limonene is used as a component of flavorings and fragrances since it has a orange/lemon-like odor. Limonene has been shown to inhibit rat mammary and other tumor development (Tsuda et al. 2004). Being an excellent solvent of cholesterol, d-limonene also has been used clinically to dissolve cholesterol-containing gallstones. Because of its gastric acid neutralizing effect and its support of normal peristalsis, it has also been used for relief of heartburn (Sun 2007).
Producing the flavoring substance limonene in our beer might result in a fresh, lemon-like taste on the one hand. On the other hand, we might have beneficial effects on health such as preventive activity against cancer, dissolution of gallstones and relief of heartburn.
Background and principles
Limonene is a cyclic terpene and a major constituent of several citrus oils (orange, lemon, mandarin, lime and grapefruit). It is a chiral molecule with the molecular mass of 136.24 g/mol; citrus fruits contain the (R)-enantiomer. The (R)-enantiomer smells like oranges, while the (S)-enantionmer has a piney odor. D-Limonene ((+)-Limonene, (R)-enantiomer) is used as a component of flavorings and fragrances.
Biosynthesis
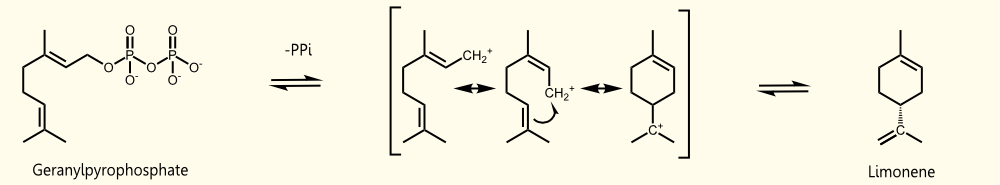
Limonene is produced by limonene synthase which uses geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) as educt. Geranyl pyrophosphate is the universal precursor of monoterpenoids. In yeast it occurs exclusively as an intermediate of farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) synthesis (Oswald et al. 2007). (+)-limonene synthase from Citrus limon consists of 606 aminoacids (EC=4.2.3.20) and catalyzes the following reaction: Geranyl pyrophosphate = (+)-(4R)-limonene + diphosphate.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae produces geranyl pyrophosphate via the mevalonate pathway. It has been established that S. cerevisiae has enough free GPP to be used by exogenous monoterpene synthases to produce monoterpenes under laboratory and vinification conditions (Herrero et al. 2008, Oswald et al. 2007).

The molecular and physiological effects of limonene
It has been shown to inhibit rat mammary and other tumor development (Tsuda et al. 2004). Being an excellent solvent of cholesterol, d-limonene also has been used clinically to dissolve cholesterol-containing gallstones. Because of its gastric acid neutralizing effect and its support of normal peristalsis, it has also been used for relief of heartburn (Sun 2007).
- elaborate a bit more
Results
BioBricks
Characterization
Gel Picture of finished construct
SDS Page of Limonene Synthase
InVitro detection of limonene
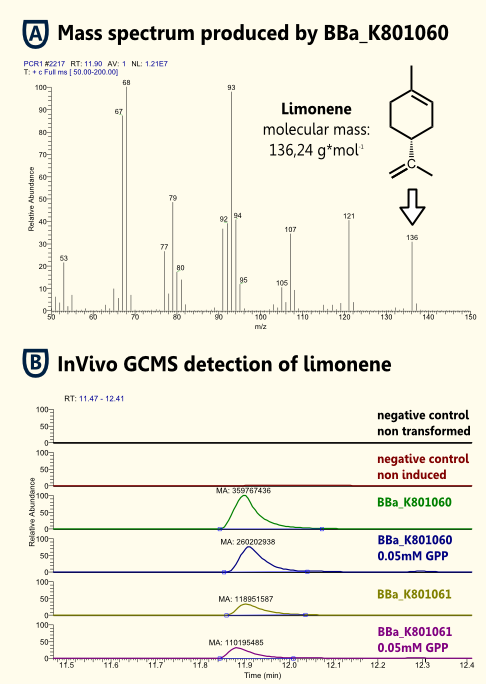
InVivo detection of limonene
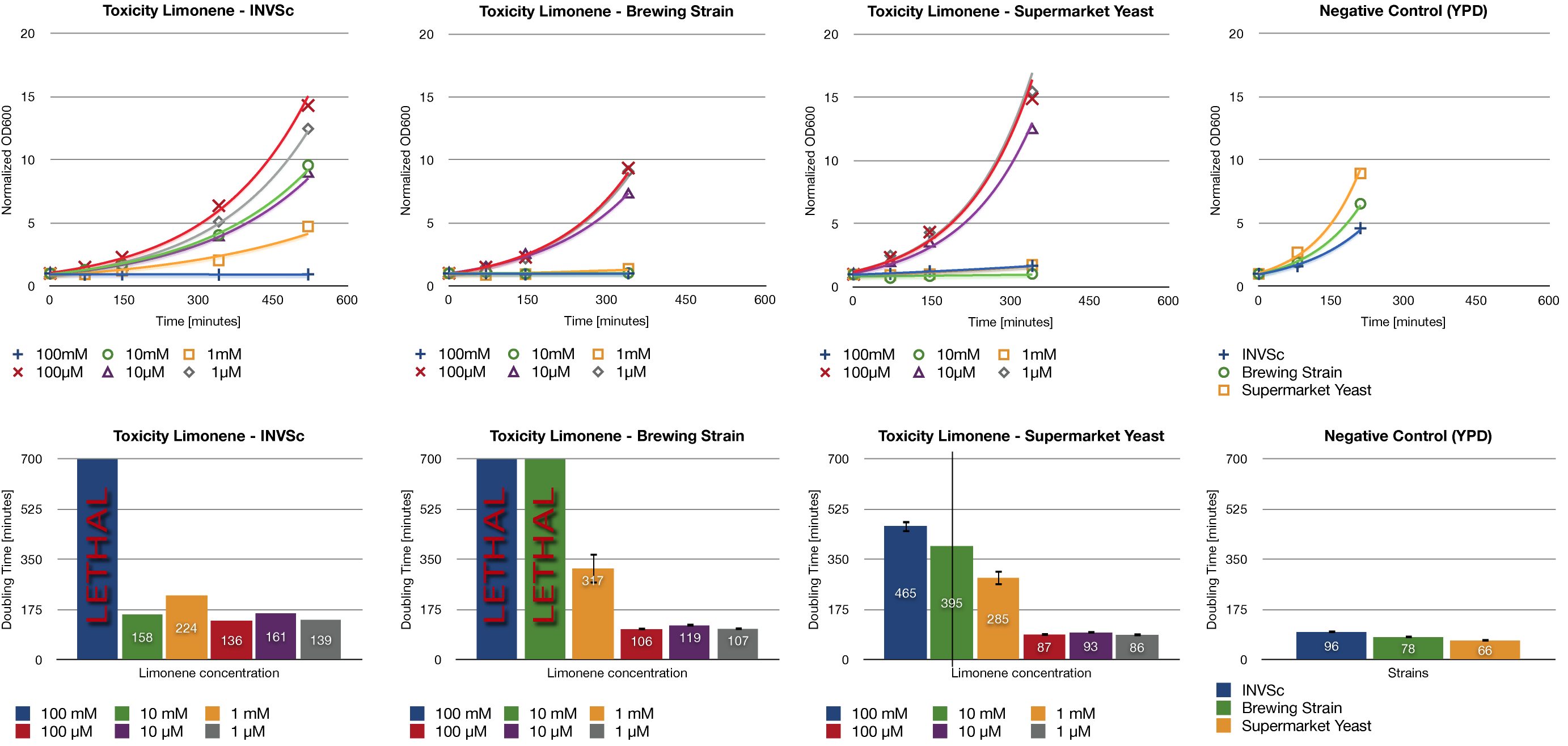
Toxicity Assay
To establish whether limonene has an effect on yeast cells , we inoculated three different yeast strains with different concentrations of limonene. Limonene was added to the medium and the used yeast strains were the laboratory strain INVSc1, a strain which is used for brewing beer and a strain which can be purchased in a supermarket.
Limonene at high concentrations affects the growth of yeast cells. We could show an inhibition of growth at 1 mM and even a lethal effect at 100 mM. At lower concentrations (1 µM, 10 µM, 100 µM) no inhibition could be observed.
The in vivo GCMS detection of limonene [B] displayed a concentration of 50 µM. Hence the amount of limonene we will produce with the modified yeast will not reach a toxic concentration at all.
References
- Herrero O, Ramón D, Orejas M (2008) Engineering the Saccharomyces cerevisiae isoprenoid pathway for de novo production of aromatic monoterpenes in wine. Metab Eng 10:78-86.
- Lücker J, Tamer M, Schwab W, Verstappen F, Van der Plas L, Bouwmeester H, Verhoeven H (2002) Monoterpene biosynthesis in lemon (Citrus limon) cDNA isolation and functional analysis of four monoterpene synthases. Eur J Biochem 269:3160-3171.
- Sun J (2007) D-Limonene: Safety and Clinical Applications. Altern Med Rev 12(3):259-264.
- Tsuda H, Ohshim Y, Nomoto H, Fujita K, Matsuda E, Iigo M, Takasuka N, Moore M (2004) Cancer Prevention by Natural Compounds. Drug Metab Pharmacokin 19(4):245-263.
- Landmann C, Fink B, Festner M, Dregus M, Engel KH, Schwab W (2007) Cloning and functional characterization of three terpene synthases from lavender (Lavandula angustifolia). Arch Biochem Biophys 467:417–429.
- William DC, McGarvey DJ, Katahira EJ, Croteau R (1998) Truncation of Limonene Synthase Preprotein Provides a Fully Active ‘Pseudomature’ Form of This Monoterpene Cyclase and Reveals the Function of the Amino-Terminal Arginine Pair. Biochem 37:12213-12220.
- Oswald M, Fischer M , Dirninger N, Karst F (2007) Monoterpenoid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Lett. 7:413-421.
- Rico J, Pardo E, Orejas M (2010) Enhanced Production of a Plant Monoterpene by Overexpression of the 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase Catalytic Domain in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 76(19): 6449–6454.
older blocks
- please integrate the informations into the other blocks
Idea
Limonene can be produced by (R)-limonene synthase.
- state how we want to indtroduce this biobrick in S. cerevisiae
 "
"