Team:Osaka/Tests
From 2012.igem.org
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
The DNA-damaging agent mitomycin C is known to introduce interstrand cross-links into duplex DNA. | The DNA-damaging agent mitomycin C is known to introduce interstrand cross-links into duplex DNA. | ||
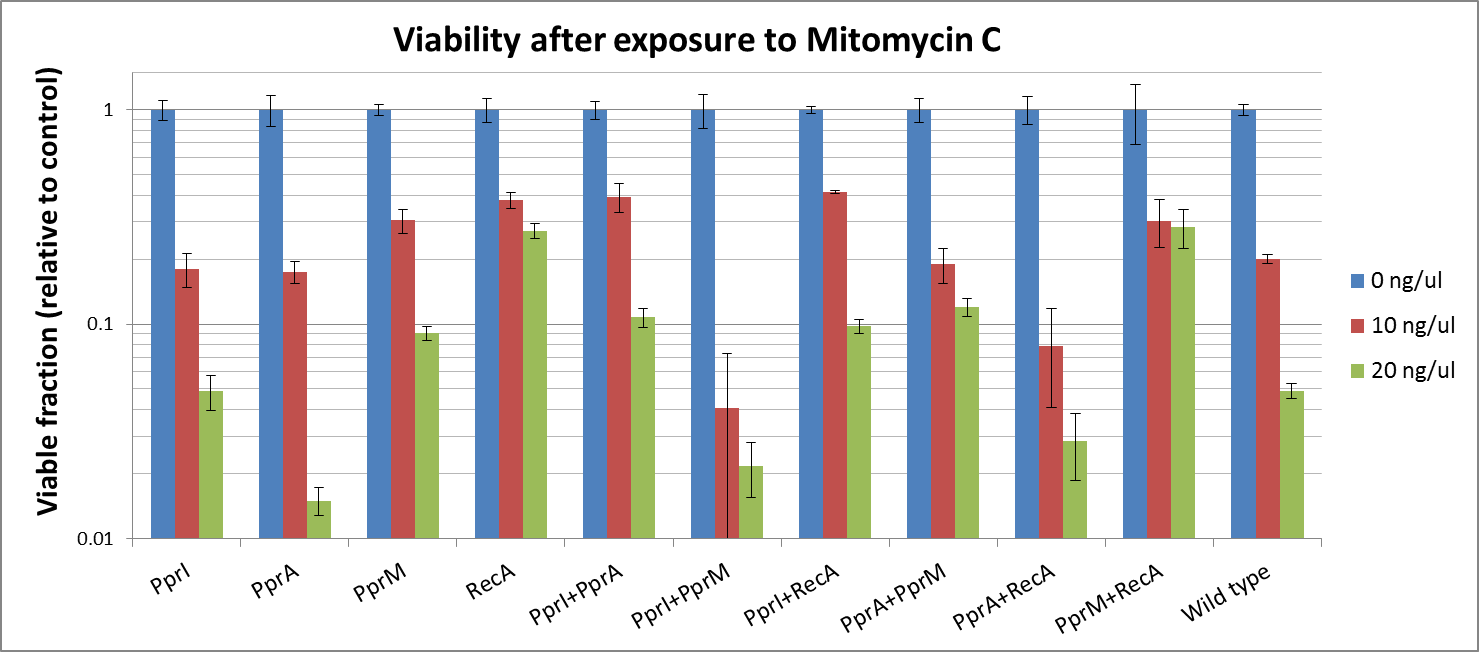
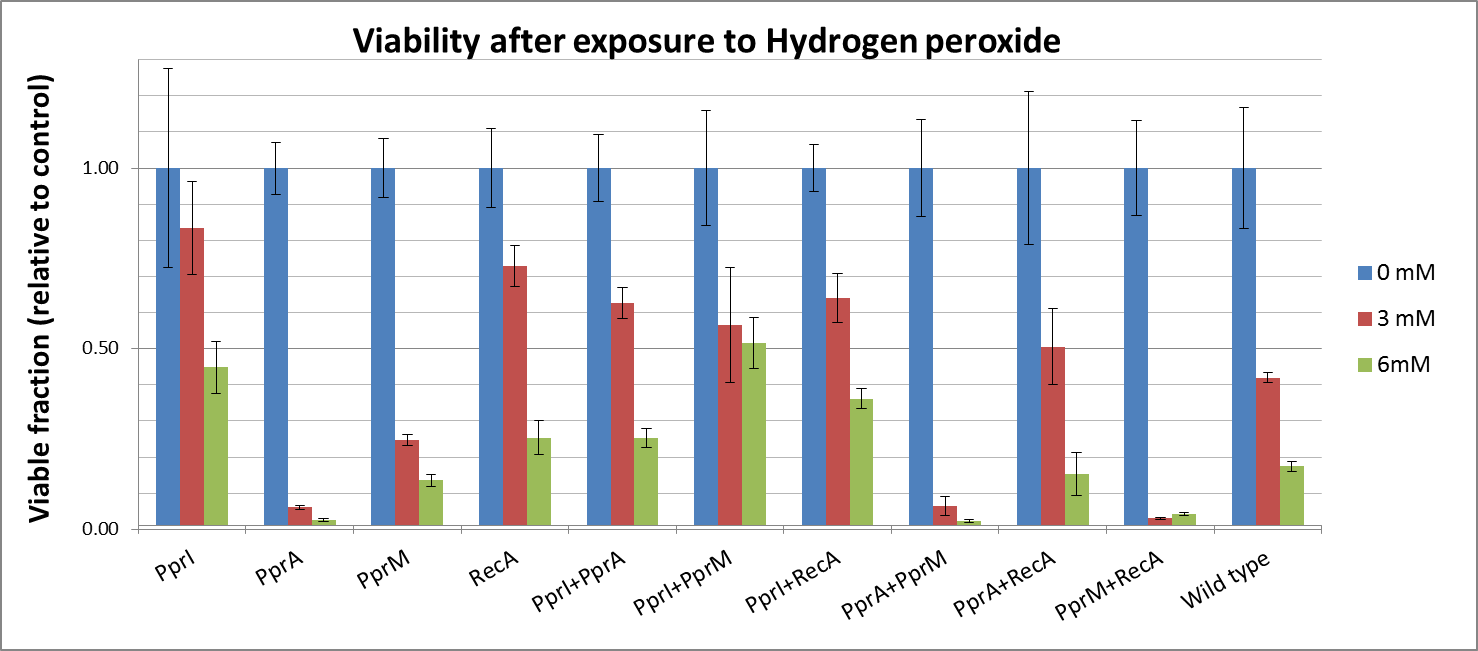
| - | + | A single crosslink per genome has shown to be effective in killing bacteria. This is accomplished by reductive activation followed by two N-alkylations. Both alkylations are sequence specific for a guanine nucleoside in the sequence 5'-CpG-3'. Potential bis-alkylating heterocylic quinones were synthetised in order to explore their antitumoral activities by bioreductive alkylation. Mitomycin is also used as a chemetherapeutic agent in Glaucoma Surgery | |
[[File:Viability after exposure to Hydrogen peroxide.png|800px]] | [[File:Viability after exposure to Hydrogen peroxide.png|800px]] | ||
Revision as of 06:51, 25 September 2012
Tests
Damage tolerance assay
Radioresistance parts contain codon rarely used in E.coli, so we transformed plasmid DNA into E.coli Rosetta.
To measure the DNA damage tolerance conferred by each part, we used antibacterial agents (We used Mitomycin C and Hydrogen peroxide) as a source of DNA damage and then assayed the survival rates. Transformed E. coli was exposed to antibacterial agents and then incubated for 2 hours. Cells were plated on agar plates at different dilutions and air dried. Plates were wrapped with aluminum foil and incubated in the dark. Colony-forming units were scored after 16h incubation at 37°C. For detailed protocols, refer to the Protocols page.
The tolerance parts tested were as follows:
Parts containing one gene each
- CDS: [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602005 PprI], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602006 PprA], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602007 PprM] or [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602008 RecA]
Parts containing two genes
- CDS1+2: [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602016 PprI+RecA], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602017 PprA+RecA], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602020 PprM+RecA], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602015 PprI+PprA],[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602018 PprI+PprM], [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K602019 PprA+PprM],
The DNA-damaging agent mitomycin C is known to introduce interstrand cross-links into duplex DNA. A single crosslink per genome has shown to be effective in killing bacteria. This is accomplished by reductive activation followed by two N-alkylations. Both alkylations are sequence specific for a guanine nucleoside in the sequence 5'-CpG-3'. Potential bis-alkylating heterocylic quinones were synthetised in order to explore their antitumoral activities by bioreductive alkylation. Mitomycin is also used as a chemetherapeutic agent in Glaucoma Surgery
Discussion
Single-gene parts
Two-gene combinations
Conclusion
Promoter assay
We assayed the promoter of the SOS gene RecA ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J22106 J22106]) and sulA ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K518010 K518010]). To measure the DNA damage detection, we used antibacterial agents as a source of DNA damage. To quantitatively and accurately evaluate the promoter activity, dual luciferase assay method was employed. Transformed E. coli was exposed to antibacterial agents and then incubated for 2 hours. For details check the Protocols page.
We were going to assemble the Dual Luciferase Assay System from existing Biobrick parts, but did not make it.
 "
"