Team:TU Darmstadt/Project/Material Science
From 2012.igem.org
(→Material Science) |
(→Material Science) |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
Our group is the intermediator between the theoretic [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Project/Simulation simulation] and applied [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Project/Degradation degradation] group. With our investigation of surface interactions of the degradation enzymes on different surface structures of PET we are able to supply data to both teams. Using atomic-force-microscopy (AFM) and sanning electron microscopy (SEM) the [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Labjournal/Material_Science resulting data] we will provide will contain information about if the enzyme works and how the degradation mechanism depends on different PET modifications. This [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Labjournal/Material_Science data] is essential feedback to both the simulation and degradation department for it poses a chance to verify the [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Modeling simulated models] and the choice of enzyme for [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Project/Degradation PET degradation]. | Our group is the intermediator between the theoretic [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Project/Simulation simulation] and applied [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Project/Degradation degradation] group. With our investigation of surface interactions of the degradation enzymes on different surface structures of PET we are able to supply data to both teams. Using atomic-force-microscopy (AFM) and sanning electron microscopy (SEM) the [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Labjournal/Material_Science resulting data] we will provide will contain information about if the enzyme works and how the degradation mechanism depends on different PET modifications. This [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Labjournal/Material_Science data] is essential feedback to both the simulation and degradation department for it poses a chance to verify the [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Modeling simulated models] and the choice of enzyme for [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Project/Degradation PET degradation]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Material_science_project.png]] | ||
Due to the crystalline nature of [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Materials/PET PET] a huge variety of PET structures with different characteristics may exist. We try to explain how the crystallinity, the surface character of the PET and the additives (crystal nucleus, plasticizers) effect the degradation process. | Due to the crystalline nature of [https://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/Materials/PET PET] a huge variety of PET structures with different characteristics may exist. We try to explain how the crystallinity, the surface character of the PET and the additives (crystal nucleus, plasticizers) effect the degradation process. | ||
Revision as of 19:09, 20 September 2012
Material Science
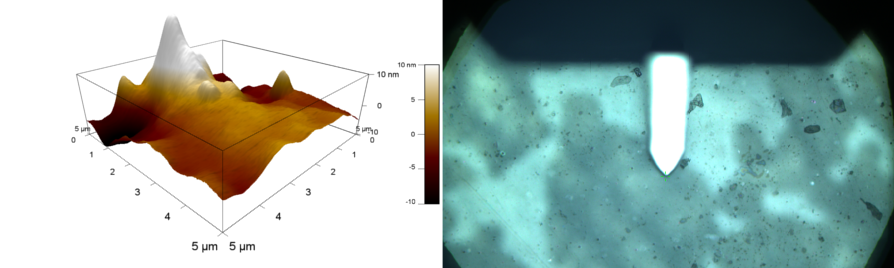
The material science group main focus is the synthesis of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and structural analoga for the study of the degradation mechanism. To accomplish this challenging task we work with a spectra of methods ranging from (an-)organic synthesis to atomic force - and electron microscopy. The interaction of the synthetic (PET) and the biological polymer (enzyme) was a matter of particular interests.
Our group is the intermediator between the theoretic simulation and applied degradation group. With our investigation of surface interactions of the degradation enzymes on different surface structures of PET we are able to supply data to both teams. Using atomic-force-microscopy (AFM) and sanning electron microscopy (SEM) the resulting data we will provide will contain information about if the enzyme works and how the degradation mechanism depends on different PET modifications. This data is essential feedback to both the simulation and degradation department for it poses a chance to verify the simulated models and the choice of enzyme for PET degradation.
Due to the crystalline nature of PET a huge variety of PET structures with different characteristics may exist. We try to explain how the crystallinity, the surface character of the PET and the additives (crystal nucleus, plasticizers) effect the degradation process.
First we characterize the PET with light microscope detection and determination the crystallinity. For exact analysis of different PET modifications it is necessary to know their specific compositions. Therefore our group will synthesise pure PET and serveral analogs. The analogs are used for characterizing the enzyme function and kinetics with UV-VIS-detection. To understand the degradation mechanism on the molecular level we analyze the decomposition products with GPC (Gel permeation chromatography).
Check out or labbook for the details: Labjournal Material Science or continue to 5. Simulation for more details about our iGEM contribution.
 "
"