Team:Peking/Modeling/Luminesensor
From 2012.igem.org
m |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
</script> | </script> | ||
<div class="PKU_context floatR first"> | <div class="PKU_context floatR first"> | ||
| - | <h3 id=" | + | <h3 id="title1">Summary</h3> |
<p> | <p> | ||
| - | Firstly we established a reaction network for the DNA binding process of <i>Luminesensor</i> | + | We have managed to conduct a series of modeling simulations to guide the optimization of our <i>Luminesensor</i>, combining protein kinetics, thermodynamics, and stochastic simulation with molecular docking together. The modeling results also shows the system still works well even if considering noise and endogenous competition. |
| + | </p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="PKU_context floatR"> | ||
| + | <h3 id="title2">Kinetic Network</h3> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | Firstly we established a reaction network for the DNA binding process of the <i>Luminesensor</i> (For details see <a href="/Team:Peking/Project/Luminesensor/Design#title4" title="">Project Luminesensor Design</a>). Previous works by other scientists indicate that the Vivid (VVD) protein, the sensing domain of the <i>Luminesensor</i>, dimerizes in the presence of light,<sup><a href="#ref1" title="Zoltowski, B.D., Crane, B.R.(2008)Light Activation of the LOV Protein Vivid Generates a Rapidly Exchanging Dimer.Biochemistry, 47: 7012: 7019">[1]</a></sup> and the LexA protein, the binding domain of the <i>Luminesensor</i>, binds at specific sequences on DNA predominantly when coupled<sup><a href="#ref2" title="Mohana-Borges, R.,et al.(2000). The LexA repressor forms stable dimers in solution. The role of specific DNA in tightening protein-protein interactions. J. Biol. Chem., 275: 4708: 4712">[2]</a></sup> and subsequently represses the interest gene. By combining with the mechanisms of the two functional domains of the <i>Luminesensor</i>, we concluded with the following kinetic network (Figure 1): | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<div class="floatC"> | <div class="floatC"> | ||
<img src="/wiki/images/3/3a/Peking2012_LuminesensorNodes.png" alt="Network System Fig" style="width:500px;"/> | <img src="/wiki/images/3/3a/Peking2012_LuminesensorNodes.png" alt="Network System Fig" style="width:500px;"/> | ||
| - | <p class="description"> | + | <p class="description" style="text-align:center;width:350px;">Figure 1. Kinetic Network of our Luminesensor</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<p>where</p><ul><li> | <p>where</p><ul><li> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 30: | ||
Since no multi-intermediate reactions are hidden in the network above, all reactions can be regarded as elementary reactions. | Since no multi-intermediate reactions are hidden in the network above, all reactions can be regarded as elementary reactions. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="PKU_context floatR"> | ||
| + | <h3 id="title3">Reference</h3> | ||
| + | <p></p> | ||
| + | <ul class="refer"><li id="ref1"> | ||
| + | 1. Zoltowski, B.D., Crane, B.R.(2008)Light Activation of the LOV Protein Vivid Generates a Rapidly Exchanging Dimer.<i>Biochemistry</i>, 47: 7012: 7019 | ||
| + | </li><li id = "ref2"> | ||
| + | 2. Mohana-Borges, R., Pacheco, A.B., Sousa, F.J., Foguel, D., Almeida, D.F., and Silva, J.L. (2000). LexA repressor forms stable dimers in solution. The role of specific DNA in tightening protein-protein interactions. <i>J. Biol. Chem.</i>, 275: 4708: 4712 | ||
| + | </li></ul> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</html>{{Template:Peking2012_Color_Epilogue}} | </html>{{Template:Peking2012_Color_Epilogue}} | ||
Latest revision as of 03:39, 25 October 2012
Summary
We have managed to conduct a series of modeling simulations to guide the optimization of our Luminesensor, combining protein kinetics, thermodynamics, and stochastic simulation with molecular docking together. The modeling results also shows the system still works well even if considering noise and endogenous competition.
Kinetic Network
Firstly we established a reaction network for the DNA binding process of the Luminesensor (For details see Project Luminesensor Design). Previous works by other scientists indicate that the Vivid (VVD) protein, the sensing domain of the Luminesensor, dimerizes in the presence of light,[1] and the LexA protein, the binding domain of the Luminesensor, binds at specific sequences on DNA predominantly when coupled[2] and subsequently represses the interest gene. By combining with the mechanisms of the two functional domains of the Luminesensor, we concluded with the following kinetic network (Figure 1):
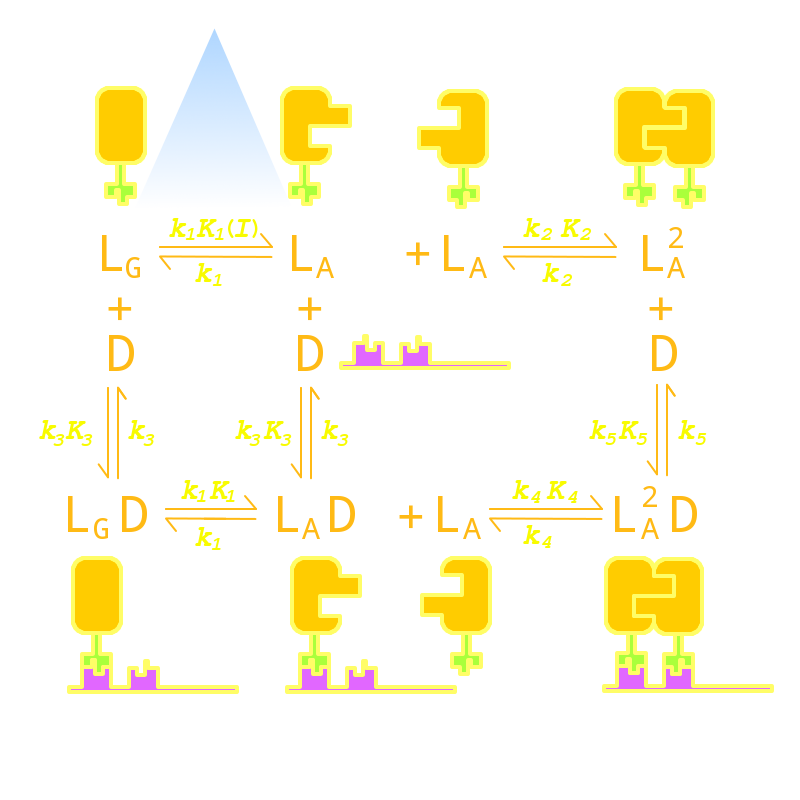
Figure 1. Kinetic Network of our Luminesensor
where
- L : Luminesensor,
- LG : the ground state --- with its VVD N-cap locked,
- LA : the active state --- with its VVD N-cap released,
- DL : the specific DNA binding site to Luminesensor.
Since no multi-intermediate reactions are hidden in the network above, all reactions can be regarded as elementary reactions.
Reference
- 1. Zoltowski, B.D., Crane, B.R.(2008)Light Activation of the LOV Protein Vivid Generates a Rapidly Exchanging Dimer.Biochemistry, 47: 7012: 7019
- 2. Mohana-Borges, R., Pacheco, A.B., Sousa, F.J., Foguel, D., Almeida, D.F., and Silva, J.L. (2000). LexA repressor forms stable dimers in solution. The role of specific DNA in tightening protein-protein interactions. J. Biol. Chem., 275: 4708: 4712
 "
"