Team:Stanford-Brown/Biomining/Harvesting
From 2012.igem.org
Michelleyu (Talk | contribs) (→Harvesting) |
Michelleyu (Talk | contribs) (→Harvesting) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
<li id="active"><a href="#" id="current">Harvesting</a></li> | <li id="active"><a href="#" id="current">Harvesting</a></li> | ||
<li><a href="/Team:Stanford-Brown/Parts">BioBricks</a></li> | <li><a href="/Team:Stanford-Brown/Parts">BioBricks</a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://docs.google.com/a/stanford.edu/document/d/1RfsxBERl_GZoXgjWbqzlezqknuxjKNX8bjLudxNzz9U/edit">Notebook</a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="/Team:Stanford-Brown/Protocols">Protocols</a></li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 20: | ||
| - | Engineered MCS FliC: | + | Engineered MCS FliC ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K847101 BBa_K847101]): |
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:FliC MCS.001.tiff]] |
| Line 31: | Line 33: | ||
We inserted the following metal-binding sequences into the FliC disposable region. Nucleotide sequences were obtained by reverse translating peptide sequences with codons optimized for E. coli. | We inserted the following metal-binding sequences into the FliC disposable region. Nucleotide sequences were obtained by reverse translating peptide sequences with codons optimized for E. coli. | ||
| - | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align: | + | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" |
!colspan="3"|Metal Ion-Binding Peptides | !colspan="3"|Metal Ion-Binding Peptides | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | |Peptide Name | + | |'''Peptide Name''' |
| - | |Binds to | + | |'''Binds to ''' |
| - | |Sequences | + | |'''Sequences''' |
|- | |- | ||
|rowspan="2"|HTTC | |rowspan="2"|HTTC | ||
|rowspan="2"|Cu 2+ | |rowspan="2"|Cu 2+ | ||
| - | |'''Peptide''': HNLGMNHDLQGERPYVTEGC | + | | align="left"|'''Peptide''': HNLGMNHDLQGERPYVTEGC |
|- | |- | ||
| - | |'''Nucleotide''': CATAACCTGGGCATGAACCATGATCTGCAGGGCGAACGCCCGTATGTGACCGAAGGCTGC | + | | align="left"|'''Nucleotide''': CATAACCTGGGCATGAACCATGATCTGCAGGGCGAACGCCCGTATGTGACCGAAGGCTGC |
|- | |- | ||
|rowspan="2"|HypB1 | |rowspan="2"|HypB1 | ||
|rowspan="2"|Cu 1+ | |rowspan="2"|Cu 1+ | ||
| - | |'''Peptide''': CTTCGCG | + | | align="left"|'''Peptide''': CTTCGCG |
|- | |- | ||
| - | |'''Nucleotide''': TGCACCACCTGCGGCTGCGGC | + | | align="left"|'''Nucleotide''': TGCACCACCTGCGGCTGCGGC |
|- | |- | ||
|rowspan="2"|HypB2 | |rowspan="2"|HypB2 | ||
|rowspan="2"|Cu 1+ | |rowspan="2"|Cu 1+ | ||
| - | |'''Peptide''': MCTTCGCGEG | + | | align="left"|'''Peptide''': MCTTCGCGEG |
|- | |- | ||
| - | |'''Nucleotide''': ATGTGCACCACCTGCGGCTGCGGCGAAGGC | + | | align="left"|'''Nucleotide''': ATGTGCACCACCTGCGGCTGCGGCGAAGGC |
|} | |} | ||
| - | + | We are currently working on metal-binding assays and flagella imaging on SEM. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Latest revision as of 03:39, 4 October 2012
Harvesting
The FliC gene codes for flagellin, a protein that arranges itself in a hollow cylinder to form the filament of a bacterial flagellum. The N and C termini of flagellin and alpha-helices flanking the termini form the inner core of the filament cylinder (Bergman). The central portion, or “dispensable region,” forms the outer surface of the filament, and is highly variable.
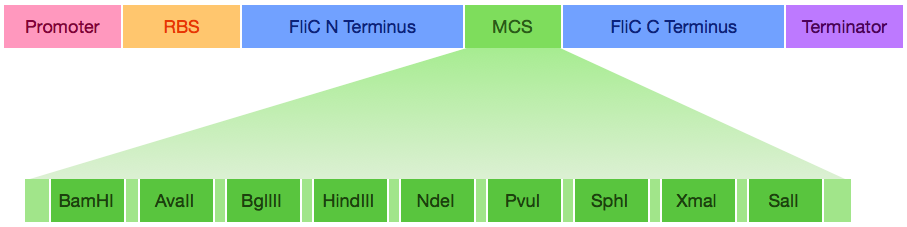
iGEM Team Slovenia 2008 used the FliC gene to design a chimeric fusion protein expressing the antigenic segment of H. pylori on E. coli flagella ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K133038 BBa_K133038]). Our team wanted to use the same flagellar expression mechanism to express metal binding sequences, and our part is an improvement on the Slovenian biobrick. In the process, we designed the FliC gene with a multiple cloning site (MCS) in the dispensable region so that any iGEM team can insert a protein to be expressed in the dispensable region.
Engineered MCS FliC ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K847101 BBa_K847101]):
Biobricks used:
[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J23100 Promoter J23100],
[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0030 RBS B0030],
[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0015 Terminator B0015]
We inserted the following metal-binding sequences into the FliC disposable region. Nucleotide sequences were obtained by reverse translating peptide sequences with codons optimized for E. coli.
| Metal Ion-Binding Peptides | ||
|---|---|---|
| Peptide Name | Binds to | Sequences |
| HTTC | Cu 2+ | Peptide: HNLGMNHDLQGERPYVTEGC |
| Nucleotide: CATAACCTGGGCATGAACCATGATCTGCAGGGCGAACGCCCGTATGTGACCGAAGGCTGC | ||
| HypB1 | Cu 1+ | Peptide: CTTCGCG |
| Nucleotide: TGCACCACCTGCGGCTGCGGC | ||
| HypB2 | Cu 1+ | Peptide: MCTTCGCGEG |
| Nucleotide: ATGTGCACCACCTGCGGCTGCGGCGAAGGC | ||
We are currently working on metal-binding assays and flagella imaging on SEM.
CITATIONS
Molly A. Bergman,Lisa A. Cummings,Robert C. Alaniz,Laura Mayeda,Ivana Fellnerova,Brad T. Cookson. CD4+-T-Cell Responses Generated during Murine Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Infection Are Directed towards Multiple Epitopes within the Natural Antigen FliC. 2005 Infect Immun. 73(11): 7226–7235
E.Coli FliC gene: http://biocyc.org/ECOLI/sequence-rc?type=GENE&object=EG10321
Kouichi Kuroda and Mitsuyoshi Ueda. Molecular design of the microbial cell surface toward the recovery of metal ions. Current Opinion in Biotechnology 2011, 22:427–433
Benita Westerlund-Wikstro ̈m, Jarna Tanskanen, Ritva Virkola, Jo ̈rg Hacker, Martin Lindberg, Mikael Skurnik and Timo K.Korhonen. Functional expression of adhesive peptides on flagellin (Section - Purification of Chimeric Flagella) Protein Engineering vol.10 no.11 pp.1319-1326, 1997
 "
"