Team:Tokyo Tech/Projects/PHAs/detail/index.htm
From 2012.igem.org
Other Teams
| Part number | Description | States | experience |
| BBa_K338003 | PHA Synthase Composite, Part 1/2 | planning | |
| BBa_K338004 | PHA Synthase Composite, Part 1/2 | Available |
They couldn’t prove that their engineered bacteria produced PHB according to the team wiki.
| Part number | Description | States | experience |
| BBa_K342001 | Pha C (poly-β-hydroxybutyrate polymerase) | available |
They registered and submitted a part, which contains only phaC sequence, as worked. But the team wiki shows that the part doesn’t meet the standard which is required in iGEM because they couldn’t cut their part with Xba1.
| Part number | Description | States | experience |
| BBa_K282000 | phaAB | available |
| Part number | Description | States | experience |
| BBa_K089001 | phaA gene | planning | |
| BBa_K089002 | phaB gene | planning | |
| BBa_K089003 | phaC gene | planning |
| Part number | Description | States | experience |
| BBa_K125801 | RBS-phaA | available | |
| BBa_K125802 | RBS-phaB | Planning | |
| BBa_K125803 | RBS-phaC | Available | |
| BBa_K125804 | RBS-phaE | Available | |
| BBa_K125501 | phaA BioPlastic polyhydroxybutyrate synthesis pathway (origin PCC6803 slr1994) | Available | |
| BBa_K125502 | phaB BioPlastic polyhydroxybutyrate synthesis pathway (origin PCC6803 slr1994) | Available | |
| BBa_K125503 | phaC BioPlastic polyhydroxybutyrate synthesis pathway (origin PCC6803 slr1994) | Available | |
| BBa_K125504 | phaE BioPlastic polyhydroxybutyrate synthesis pathway (origin PCC6803 slr1994) | Available |
| Part number | Description | States | experience |
| BBa_K156031 | RBS + phaA + double terminator | available | |
| BBa_K156033 | RBS + phaB1 + double terminator | available | |
| BBa_K156034 | RBS + phaC1 + double terminator | available | |
| BBa_K156012 | phaA (acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase) | available | |
| BBa_K156013 | phaB1 (acetyacetyl-CoA reductase) | available | |
| BBa_K156014 | phaC1 (Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) polymerase) | available | |
| BBa_K156021 | Promoter + RBS + phaA + double terminator | available | |
| BBa_K156018 | Promoter + RBS + phaA | planning | |
| BBa_K156019 | Promoter + RBS + phaB1 | planning | |
| BBa_K156020 | Promoter + RBS + phaC1 | planning | |
| BBa_K156022 | Promoter + RBS + phaB1 + double terminator | planning | |
| BBa_K156023 | Promoter + RBS + phaC1 + double terminator | planning |
Production of PHAs by E.coli
Construction of pha-C1-A-B1 in Biobrick format
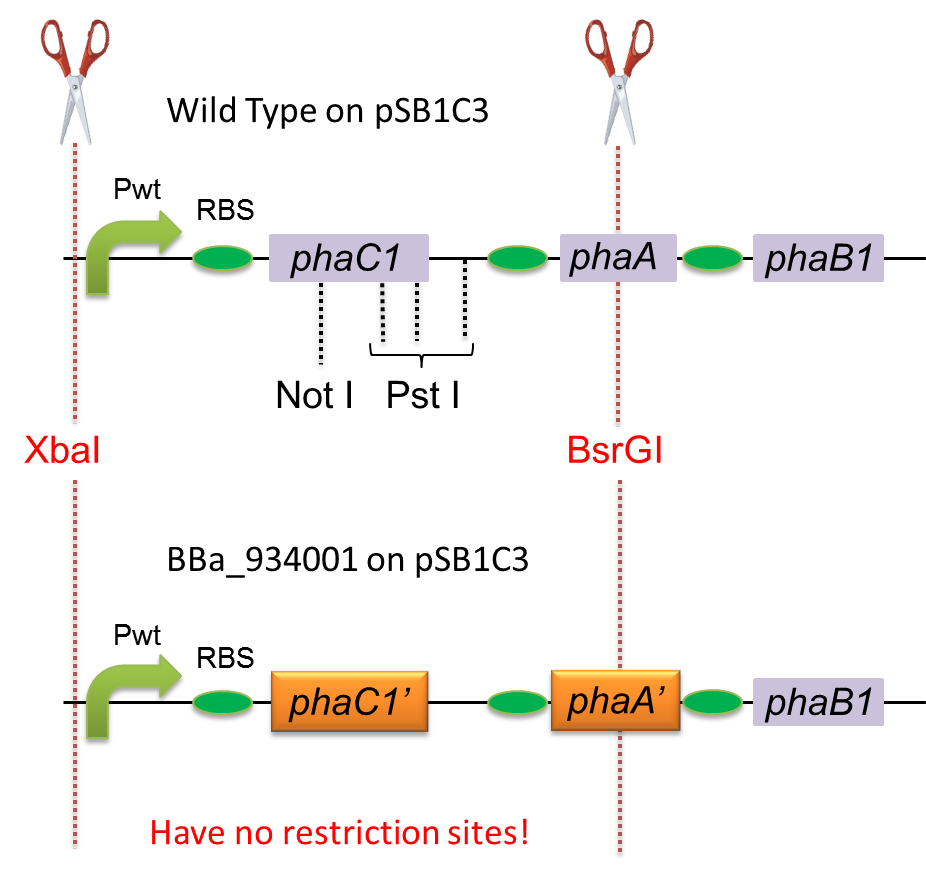
To construct a part that meets Biobrick format, we have modified the pha-C1-A-B1 operon not to contain forbidden restriction enzyme sites. First, we cloned the wild type gene pha-C1-A-B1 from R.eutropha H16 by using PCR and inserted the gene into pSB1C3. However, wild type pha-C1-A-B1 gene sequence contains one NotI and three PstI recognition sites that are not allowed in Biobrick format. To get pha-C1-A-B1 sequence without these recognition sites, we ordered the chemically synthesized DNA from IDT/MBL. In this chemically synthesized DNA, coding is optimized for E.coli. That is to say, we got PHB synthesizing gene in Biobrick format(BBa_K934001).
Production of PHAs by E.coli
(ⅰ)
We observed the accumulation of PHB in the E.coli colonies on Nile red positive medium under UV .Nile red has been widely used to stain colonies and distinguish between PHA-accumulating and non-accumulating colonies. Nile red produces a strong orange fluorescence (emission maximum,598nm) with an excitation wavelength of 543nm (maximum) upon binding to PHA-granules in cells of R.eutropha (Degelau et al.1995) H16. Nile red in the agar medium doesn’t affect the growth of the cells, and the occurrence of PHAs in the colonies can be directly monitored. This method is quite sensitive and results in fluorescent colonies of PHA-positive strains. So we cultured the transformant on LB agar medium plates with 0.5μg/ml Nile Red and 2% glucose at 37℃ for 30 hours, then we transferred the plates to 4℃ room. After 115 hours, colonies with PHB would be stained Red by Nile red when observed under UV. This showed that the transformant had stored PHB.FIG1 is the photograph of E.coli(with phaC1AB1 gene) colonies on Nile Red positive medium taken under UV. The fluorescent area in the figure showed the accumulated PHBs stained by Nile red in cells. This indicated that part BBa_K934001 functioned correctly.FIG2 is the photograph of negative control cells. In this figure we observed that there was no remarkable fluorescent area.
(ⅱ)
To confirm the accumulation condition of PHB in E.coli with a microscope, we stained the PHB with Nile blue A reagent. Nile blue A is also used to detect the existence of PHBs and has no toxicity to the cells. We carried out the observation after the procedures stated below. First,We cultured a small amount of the transformant (3ml) in LB medium for 17 hrs. Then,we added the cultured trandformant(1%) into LB medium(with 2% glucose) and shaking cultured it under aerobic condition with an air permeable lid for 96 hrs. After the cultivation we recovered the bacteria with PHA accumulation by centrifugation. We were able to get the dried cells after the procedure of lyophilization. Before taking the photographs,we stained the dried cells with 1% Nile blue A solution for 8 minutes and washed the extra Nile blue with 8% acetic acid solution afterwards. We then took photographs of the sample under fluorescence microscope. FIG1 is the photograph of E.coli(with phaC1AB1 gene) colonies on Nile Red positive medium taken under UV. The fluorescent area in the figure showed the accumulated PHBs stained by Nile red in cells. This indicated that part BBa_K934001 functioned correctly.FIG2 is the photograph of negative control cells. In this figure we observed that there was no remarkable fluorescent area.
 "
"