Team:TU Munich/Project/Thaumatin
From 2012.igem.org
Nadine1990 (Talk | contribs) (→Background and principles) |
|||
| (165 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Team:TU_Munich/Header}} | {{Team:TU_Munich/Header}} | ||
| - | == | + | = Thaumatin = |
| + | <hr/> | ||
| + | [[File:gruppe_thaumatin_TUM12.jpg|350px|thumb||Responsible: Martin Schappert and Alois Bräuer]] | ||
| - | + | <div style="text-align:justify;">"'''Why'''? O WHY???" is the reaction we usually face when we tell our friends, that we '''genetically engineer yeast to secrete a sweetener'''. "Kruzifixnochemol" is another, more cryptic one. | |
| - | + | <br>We must admit, even we do not think that a "Münchner Hell" or a "Pils" would benefit from the distinct sweetness of Thaumatin, originally produced by ''Thaumatococcus daniellii''. | |
| + | <br>So, why, o why have we chosen Thaumatin? There are a '''variety of arguments''' that have to be taken into consideration: | ||
| - | Thaumatin | + | * Since experiments in the 1980ies, nobody tried to express Thaumatin via ''S. cerevisiae'' - so we saw the possibility to enhance the production and make it more efficient (as one of the biggest problems for industrial use of Thaumatin so far is the '''low yield efficiency''') by codon usage optimization. |
| - | + | * If you think of the beers of the Anglo-Saxon world - stouts and ales - these are the sorts that could '''directly profit from the licorice-like sweetness''', as they are generally more full-bodied and show a variety of caramel flavors. | |
| + | * It opens the world of brewage to a whole '''new generation of lifestyle drinks''' - perhaps a bit too innovative for the conservative german beer market, but nevertheless there is quite a potential there for cutting-edge beverages with the soul of beer and the savor of all the fruits you can imagine. Thaumatin might serve as a '''low-carb ingredient to balance out the bitter and sour flavors''' of guava, grapefruits, currant - ''or even horseradish''. | ||
| - | ''' | + | ==Background and Principles== |
| + | <hr/> | ||
| + | <div> | ||
| + | [[File:TUM12_structure_thaumatin.png|thumb|300px|]] | ||
| + | Thaumatin is a natural ''α+β-protein'' which is synthesized by the katamfe plant (''Thaumatococcus daniellii'') – a species of tropical flowering plants - and belongs to the thaumatin-like protein family. There exist different varieties of thaumatin, however, thaumatin I und thaumatin II are well characterized and differ only in one amino acid position (position 46 – without signaling sequence; thaumatin I Asn; thaumatin II Lys). Both are said to be '''22000 to 100000 times sweeter than sucrose''' on molar basis, but the sweetness builds slow and lasts long. | ||
| - | + | Thaumatin is a ''single chain with 207 amino acid residues'', ''eight disulfide bonds'' and a '''molecular weight of 22.2 kDa'''. It is highly water soluble, stable at heating (not for cooking, bakery, etc.) and stable under acidic conditions. The production of thaumatin is induced by an attack upon the plant by viroid pathogens. Thus it is involved in systematically acquired resistance and stress response. | |
| - | + | Thaumatin has been '''approved as a sweetener''' in the European Union (E957). | |
| - | + | The general idea is to create a system that expresses thaumatin via genetic engineering of ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', respectively the direct precursor ('''preprothaumatin'''). The N-terminal "pre" part is the internal signalling sequence for '''secretion''', the C-terminal "pro" sequence supports the correct and '''functional folding''' of thaumatin. | |
| + | Alternatively one could have used a fusion product of prothaumatin and the Mat-α-factor to achieve secretion. | ||
| - | + | The '''''natural'' preprothaumatin''' seems to be preferable, because of the expected '''higher yield''' [[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=21636903 Masuda et al., 2011]] and the possibility that the pre-sequence is necessary for the correct procession [[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=17897626 Ide et al., 2007]]. A similar construct was used by the Kyoto University (Ide ''et al.'', submitted) in ''Pichia pastoris'' with a ''pPIC6α expression vector'' and achieved a high yield (especially with the preprothaumatin I gene and without the α-factor secretion signal). | |
| - | The | + | |
| - | |||
| - | === | + | ===The molecular and physiological effects of thaumatin=== |
| - | + | The '''sweet taste receptor''' is a heterodimeric receptor composed of ''T1R2'' (also TAS1R2) and ''T1R3'' (also TAS1R3) subunits. The large amino-terminal domains (NTD) of the T1R2 and T1R3 subunits have shown to be responsible for the primary ligand binding [[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=22450161 Maîtrepierre et al., 2012]]. In addition these receptors have a heptahelical transmembrane domain. T1R receptors belong to the family of ''class C G-Protein coupled receptors'' (GPCRs), which in this case means that, through ligand binding, an elevation of cAMP concentration in the taste buds is induced [[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=19489607 Ide et al., 2009], [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=15087236 Ozeck et al., 2004]]. As a result a decrease in the intracellular cAMP accumulation is measured. Released calcium (Ca2+) seems to be another independent second messenger within the transduction of the taste response (downstream of taste receptors) [[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=16510847 Trubey et al., 2006]]. | |
| - | + | However, not only sucralose or other sugars can bind with the NTDs of the sweet taste receptor, but also thaumatin [[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=19489607 Ide et al., 2009]]. It seems to have a longer lasting and stronger effect than sucralose. | |
| - | + | </div> | |
| - | === | + | ===Theoretical consideration: How much thaumatin is needed in foodstuff?=== |
| - | + | The molecular weight of sucrose is 342,30 g/mol, respectively 22194,13 g/mol for thaumatin. This means that although the relative sweetness of thaumatin is 2000 to 10000 times the sweetness of sucrose '''on a molar basis''', it's ''only'' ~30 to 150 times the sweetness when measured in mass. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | Thus you need to put 0,07 to 0,35 g of thaumatin into 100 ml generic soft drink to create an equal level of sweetness. | |
| - | + | ==Results== | |
| - | + | <hr/> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | ===BioBricks planning=== | ||
| + | The BioBricks designed encode the '''Prepro-Thaumatin''' ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K801080 BBa_K801080]) that is believed to be exported on its own [[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6327079 Edens et al., 1984]]. The original gene sequence was optimized for best yeast codon usage using GeneArt® GeneOptimizer®. We ordered the gene synthesis and cloned this BioBrick into pSB1C3 and our galactose inducible yeast expression vector '''pTUM104'''. Furthermore we constructed an expression cassette with ''TeF1''-promoter and the ''TeF1''-terminator, which is also available as a protein generator (BBa_K801081). This expression cassette was subsequently cloned into the integration vector (BBa_K300001 ) assuring expression in brewing medium. | ||
| - | == | + | ===Expression of Thaumatin=== |
| - | === | + | We are planning a western blot of the supernatant to prove proper secretion. SDS page and coomassie/silver staining have proven to be too insensitive. |
| + | <div style="clear:both"> | ||
| + | ==== Ion exchange chromatography ==== | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | [[file:TUM12_ThaumatinIEC.png|600px|thump|right|Bildbeschreibung]] | ||
| + | Preprothaumatin will be posttranslationally modified by cleaving a part of the N- and the C-terminal polypeptide. Therefore it was not possible to add a tag for affinity chromatography. For this reason it was necessary to purify the protein from the cytoplasm of the disintegrated yeast cells using ion exchange chromatography for having a proof of principle. | ||
| - | + | '''Experimental details:''' | |
| + | *Samples: cell lysate, supernatant from culture, reference for thaumatin (MedHerbs) | ||
| + | *Dialysis against 20 mM MES buffer pH 6.0 (twice) using a 12-16 kDa dialysis membrane | ||
| + | *Chromatography with a Äkta purifier equipped with a Ressource S 6ml (S: Methyl sulfonate (strong cation exchanger)) | ||
| + | *Sample was applied using a super-loop | ||
| + | *Wash with two column volumes 20 mM MES buffer pH 6.0 | ||
| + | *Elution with a gradient of 0-500 mM NaCl over 5 column volumes | ||
| + | *Fractions of 1 ml were collected during the elution<br> | ||
| - | + | '''Experimental results:''' | |
| - | + | *Reference thaumatin (see figure A and B) | |
| - | + | **nearly no protein in the flow through during sample application (see figure A) | |
| - | + | **a major peak eluting at ~14 mS*cm-1 which corresponds to fraction No. 14, see figure A) | |
| - | + | **the corresponding SDS-PAGE showed a clear bond around fraction No. 14 corresponding the expected 22 kDa | |
| - | + | *Cell lysate | |
| - | + | **high concentration of protein in the flow through (see figure C and D) | |
| - | + | **no clear peak around fraction No. 14 could be detected | |
| - | + | **SDS-PAGE performed from the reference and the fractions No. 12 to 15 showed a weak bond having the same size as the reference (see running properties on SDS-PAGE in figure D) and the same isoelectric point (both eluted in fraction No. 14) | |
| - | + | *Supernatant of yeast culture (see figure E and F) | |
| - | + | **export of the protein in high concentrations was unlikely to happen, therefore 48 ml of supernatant were loaded on the column | |
| - | + | **ratio between flow through and eluted protein was less favorable compared to the cell lysate | |
| - | + | **total protein quantities were to low to be detected by coomassie stain, therefore a silver stain was performed (see figure F) | |
| - | + | **beside the reference no additional protein bonds could be detected on the silver stained SDS-PAGE<br> | |
| - | + | <br> | |
| - | + | <br> | |
| - | + | '''Conclusion of this experiment:'''<br> | |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | A '''proof of principle for the expression of thaumatin was achieved using ion exchange chromotography and comparison of bonds obtained on SDS-PAGE relatively to a standard of thaumatin'''. <br> | ||
| + | Further goals would include to increase the expression of thaumatin and to investigate the secretion. This could be achieved by improving the purification protocol to load more than 10 ml of cell lysate on the column in order to purify a sufficient amount of protein for a mass spectrum of the produced thaumatin. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ==== Toxicity Assay ==== | ||
| - | + | To check if thaumatin has an effect on yeast cells, we inoculated three different yeast strains with YPD including 45 mM of thaumatin and measured their growth rate after a defined period of time. The used yeast strains were the laboratory strain ''INVSc1'', a strain which is used for brewing beer and a strain which can be purchased in supermarkets. | |
| + | The growth rate of yeast cells which were incubated with thaumatin does not show a difference compared to the negative control (incubation of analogous strains with YPD without thaumatin). The small differences in doubling time are errors in measurement. | ||
| - | + | As expected, thaumatin does not have an effect on the growth rate of yeast cells. Hence we are not limited in over-expressing the sweetener in our beer. | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | [[File:TUM12_Toxicity_Thaumatin.png|500px|center|Evaluation of the Toxicity Assay for Thaumatin.]] | |
| - | + | </div> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | | | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| - | + | ---- | |
| - | + | *[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6327079 Edens et al., 1984]] Edens, L., Bom, I., Ledeboer, A. M., Maat, J., Toonen, M. Y., Visser, C., and Verrips, C. T. (1984). Synthesis and processing of the plant protein thaumatin in yeast. ''Cell'', 37(2):629–33. | |
| - | + | *[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17897626 Ide et al., 2007]] Ide, N., Masuda, T., and Kitabatake, N. (2007). Effects of pre- and pro-sequence of thaumatin on the secretion by ''Pichia pastoris''. ''Biochem Biophys Res Commun'', 363(3):708–14. | |
| - | * | + | *[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19489607 Ide et al., 2009]] Ide, N., Sato, E., Ohta, K., Masuda, T., and Kitabatake, N. (2009). Interactions of the sweet-tasting proteins thaumatin and lysozyme with the human sweet-taste receptor. ''J Agric Food Chem'', 57(13):5884–90. |
| - | * | + | *[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3167035 Lee et al., 1988]] Lee, J. H., Weickmann, J. L., Koduri, R. K., Ghosh-Dastidar, P., Saito, K., Blair, L. C., Date, T., Lai, J. S., Hollenberg, S. M., and Kendall, R. L. (1988). Expression of synthetic thaumatin genes in yeast. ''Biochemistry'', 27(14):5101–7. |
| - | * | + | *[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22450161 Maîtrepierre et al., 2012]] Maîtrepierre, E., Sigoillot, M., Le Pessot, L., and Briand, L. (2012). Recombinant expression, in vitro refolding, and biophysical characterization of the n-terminal domain of t1r3 taste receptor. ''Protein Expr Purif'', 83(1):75–83. |
| - | * | + | *[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21636903 Masuda et al., 2011]] Masuda, T., Ohta, K., Mikami, B., and Kitabatake, N. (2011). High-resolution structure of the recombinant sweet-tasting protein thaumatin i. ''Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun'', 67(Pt 6):652–8. |
| - | * | + | *[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14991654 Masuda et al., 2004]] Masuda, T., Tamaki, S., Kaneko, R., Wada, R., Fujita, Y., Mehta, A., and Kitabatake, N. (2004). Cloning, expression and characterization of recombinant sweet-protein thaumatin ii using the methylotrophic yeast pichia pastoris. ''Biotechnol Bioeng'', 85(7):761–9. |
| - | * | + | *[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10049878 Moralejo et al., 1999]] Moralejo, F. J., Cardoza, R. E., Gutierrez, S., and Martin, J. F. (1999). Thaumatin production in aspergillus awamori by use of expression cassettes with strong fungal promoters and high gene dosage. ''Appl Environ Microbiol'', 65(3):1168–74. |
| - | * | + | *[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15087236 Ozeck et al., 2004]] Ozeck, M., Brust, P., Xu, H., and Servant, G. (2004). Receptors for bitter, sweet and umami taste couple to inhibitory g protein signaling pathways. ''Eur J Pharmacol'', 489(3):139–49. |
| - | * | + | *[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16510847 Trubey et al., 2006]] Trubey, K. R., Culpepper, S., Maruyama, Y., Kinnamon, S. C., and Chaudhari, N. (2006). Tastants evoke camp signal in taste buds that is independent of calcium signaling. ''Am J Physiol Cell Physiol'', 291(2):C237–44. |
| - | * | + | |
=== Others === | === Others === | ||
| - | |||
* Thaumatococcus daniellii mRNA forpreprothaumatin I, comeplete cds [[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/121945717?report=genbank]] | * Thaumatococcus daniellii mRNA forpreprothaumatin I, comeplete cds [[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/121945717?report=genbank]] | ||
* Preprothaumatin I [Thaumatococcus daniellii], FASTA [[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/121945718?report=fasta]] | * Preprothaumatin I [Thaumatococcus daniellii], FASTA [[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/121945718?report=fasta]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
* yeastgenome.org [[http://www.yeastgenome.org/]] | * yeastgenome.org [[http://www.yeastgenome.org/]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:54, 26 October 2012



Contents |
Thaumatin
We must admit, even we do not think that a "Münchner Hell" or a "Pils" would benefit from the distinct sweetness of Thaumatin, originally produced by Thaumatococcus daniellii.
So, why, o why have we chosen Thaumatin? There are a variety of arguments that have to be taken into consideration:
- Since experiments in the 1980ies, nobody tried to express Thaumatin via S. cerevisiae - so we saw the possibility to enhance the production and make it more efficient (as one of the biggest problems for industrial use of Thaumatin so far is the low yield efficiency) by codon usage optimization.
- If you think of the beers of the Anglo-Saxon world - stouts and ales - these are the sorts that could directly profit from the licorice-like sweetness, as they are generally more full-bodied and show a variety of caramel flavors.
- It opens the world of brewage to a whole new generation of lifestyle drinks - perhaps a bit too innovative for the conservative german beer market, but nevertheless there is quite a potential there for cutting-edge beverages with the soul of beer and the savor of all the fruits you can imagine. Thaumatin might serve as a low-carb ingredient to balance out the bitter and sour flavors of guava, grapefruits, currant - or even horseradish.
Background and Principles
Thaumatin is a natural α+β-protein which is synthesized by the katamfe plant (Thaumatococcus daniellii) – a species of tropical flowering plants - and belongs to the thaumatin-like protein family. There exist different varieties of thaumatin, however, thaumatin I und thaumatin II are well characterized and differ only in one amino acid position (position 46 – without signaling sequence; thaumatin I Asn; thaumatin II Lys). Both are said to be 22000 to 100000 times sweeter than sucrose on molar basis, but the sweetness builds slow and lasts long.
Thaumatin is a single chain with 207 amino acid residues, eight disulfide bonds and a molecular weight of 22.2 kDa. It is highly water soluble, stable at heating (not for cooking, bakery, etc.) and stable under acidic conditions. The production of thaumatin is induced by an attack upon the plant by viroid pathogens. Thus it is involved in systematically acquired resistance and stress response.
Thaumatin has been approved as a sweetener in the European Union (E957).
The general idea is to create a system that expresses thaumatin via genetic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, respectively the direct precursor (preprothaumatin). The N-terminal "pre" part is the internal signalling sequence for secretion, the C-terminal "pro" sequence supports the correct and functional folding of thaumatin. Alternatively one could have used a fusion product of prothaumatin and the Mat-α-factor to achieve secretion.
The natural preprothaumatin seems to be preferable, because of the expected higher yield [Masuda et al., 2011] and the possibility that the pre-sequence is necessary for the correct procession [Ide et al., 2007]. A similar construct was used by the Kyoto University (Ide et al., submitted) in Pichia pastoris with a pPIC6α expression vector and achieved a high yield (especially with the preprothaumatin I gene and without the α-factor secretion signal).
The molecular and physiological effects of thaumatin
The sweet taste receptor is a heterodimeric receptor composed of T1R2 (also TAS1R2) and T1R3 (also TAS1R3) subunits. The large amino-terminal domains (NTD) of the T1R2 and T1R3 subunits have shown to be responsible for the primary ligand binding [Maîtrepierre et al., 2012]. In addition these receptors have a heptahelical transmembrane domain. T1R receptors belong to the family of class C G-Protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), which in this case means that, through ligand binding, an elevation of cAMP concentration in the taste buds is induced [Ide et al., 2009, Ozeck et al., 2004]. As a result a decrease in the intracellular cAMP accumulation is measured. Released calcium (Ca2+) seems to be another independent second messenger within the transduction of the taste response (downstream of taste receptors) [Trubey et al., 2006].
However, not only sucralose or other sugars can bind with the NTDs of the sweet taste receptor, but also thaumatin [Ide et al., 2009]. It seems to have a longer lasting and stronger effect than sucralose.
Theoretical consideration: How much thaumatin is needed in foodstuff?
The molecular weight of sucrose is 342,30 g/mol, respectively 22194,13 g/mol for thaumatin. This means that although the relative sweetness of thaumatin is 2000 to 10000 times the sweetness of sucrose on a molar basis, it's only ~30 to 150 times the sweetness when measured in mass.
Thus you need to put 0,07 to 0,35 g of thaumatin into 100 ml generic soft drink to create an equal level of sweetness.
Results
BioBricks planning
The BioBricks designed encode the Prepro-Thaumatin (BBa_K801080) that is believed to be exported on its own [Edens et al., 1984]. The original gene sequence was optimized for best yeast codon usage using GeneArt® GeneOptimizer®. We ordered the gene synthesis and cloned this BioBrick into pSB1C3 and our galactose inducible yeast expression vector pTUM104. Furthermore we constructed an expression cassette with TeF1-promoter and the TeF1-terminator, which is also available as a protein generator (BBa_K801081). This expression cassette was subsequently cloned into the integration vector (BBa_K300001 ) assuring expression in brewing medium.
Expression of Thaumatin
We are planning a western blot of the supernatant to prove proper secretion. SDS page and coomassie/silver staining have proven to be too insensitive.
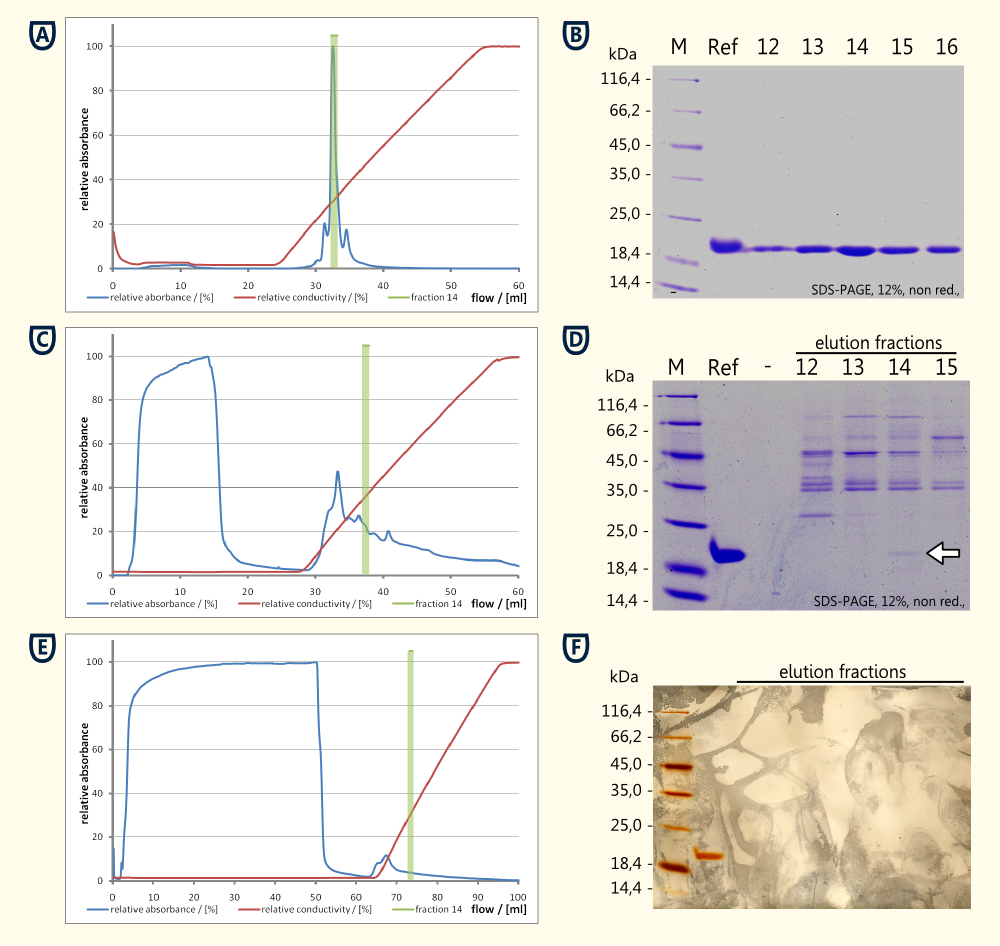
Ion exchange chromatography
Preprothaumatin will be posttranslationally modified by cleaving a part of the N- and the C-terminal polypeptide. Therefore it was not possible to add a tag for affinity chromatography. For this reason it was necessary to purify the protein from the cytoplasm of the disintegrated yeast cells using ion exchange chromatography for having a proof of principle.
Experimental details:
- Samples: cell lysate, supernatant from culture, reference for thaumatin (MedHerbs)
- Dialysis against 20 mM MES buffer pH 6.0 (twice) using a 12-16 kDa dialysis membrane
- Chromatography with a Äkta purifier equipped with a Ressource S 6ml (S: Methyl sulfonate (strong cation exchanger))
- Sample was applied using a super-loop
- Wash with two column volumes 20 mM MES buffer pH 6.0
- Elution with a gradient of 0-500 mM NaCl over 5 column volumes
- Fractions of 1 ml were collected during the elution
Experimental results:
- Reference thaumatin (see figure A and B)
- nearly no protein in the flow through during sample application (see figure A)
- a major peak eluting at ~14 mS*cm-1 which corresponds to fraction No. 14, see figure A)
- the corresponding SDS-PAGE showed a clear bond around fraction No. 14 corresponding the expected 22 kDa
- Cell lysate
- high concentration of protein in the flow through (see figure C and D)
- no clear peak around fraction No. 14 could be detected
- SDS-PAGE performed from the reference and the fractions No. 12 to 15 showed a weak bond having the same size as the reference (see running properties on SDS-PAGE in figure D) and the same isoelectric point (both eluted in fraction No. 14)
- Supernatant of yeast culture (see figure E and F)
- export of the protein in high concentrations was unlikely to happen, therefore 48 ml of supernatant were loaded on the column
- ratio between flow through and eluted protein was less favorable compared to the cell lysate
- total protein quantities were to low to be detected by coomassie stain, therefore a silver stain was performed (see figure F)
- beside the reference no additional protein bonds could be detected on the silver stained SDS-PAGE
Conclusion of this experiment:
A proof of principle for the expression of thaumatin was achieved using ion exchange chromotography and comparison of bonds obtained on SDS-PAGE relatively to a standard of thaumatin.
Further goals would include to increase the expression of thaumatin and to investigate the secretion. This could be achieved by improving the purification protocol to load more than 10 ml of cell lysate on the column in order to purify a sufficient amount of protein for a mass spectrum of the produced thaumatin.
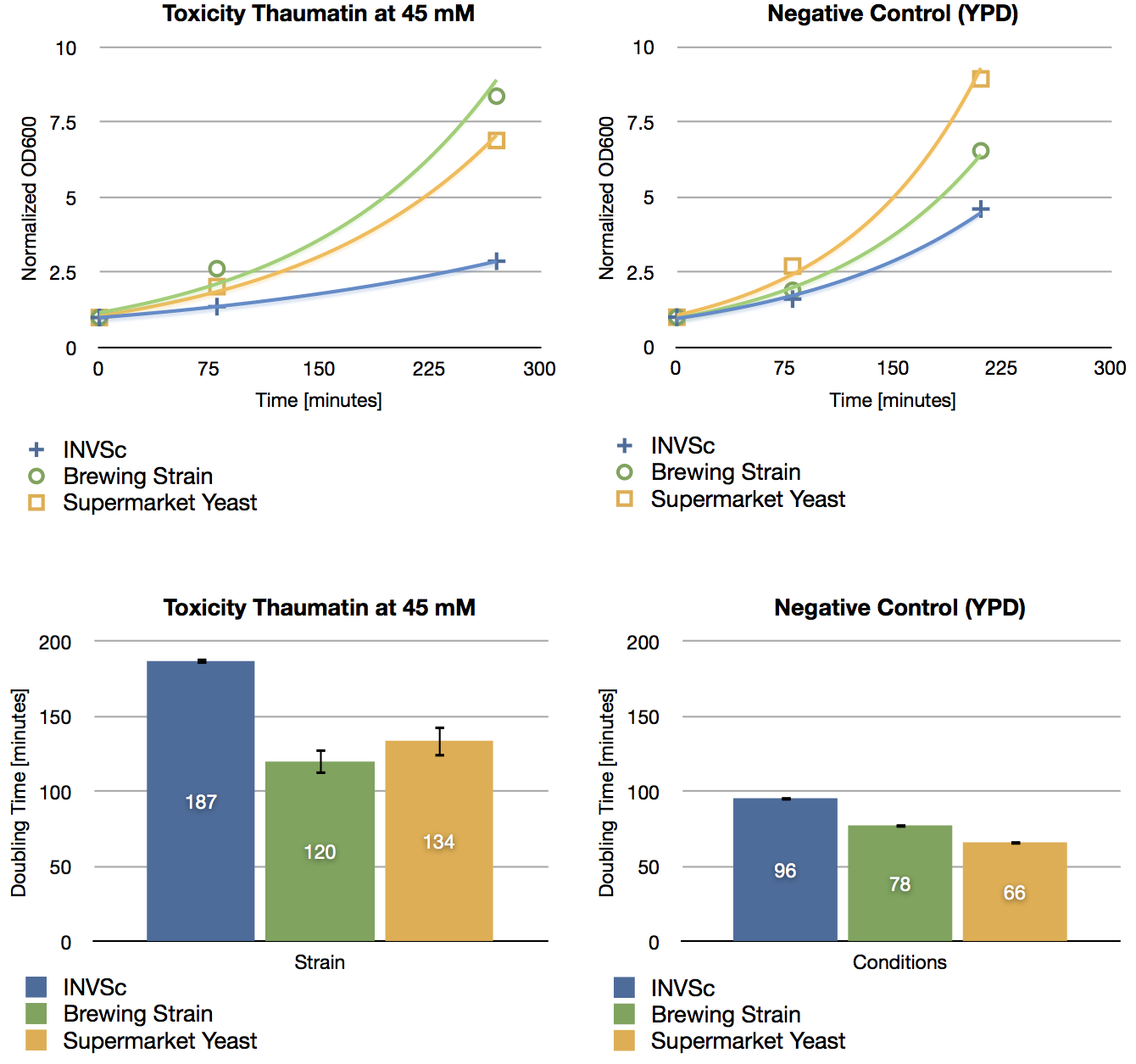
Toxicity Assay
To check if thaumatin has an effect on yeast cells, we inoculated three different yeast strains with YPD including 45 mM of thaumatin and measured their growth rate after a defined period of time. The used yeast strains were the laboratory strain INVSc1, a strain which is used for brewing beer and a strain which can be purchased in supermarkets. The growth rate of yeast cells which were incubated with thaumatin does not show a difference compared to the negative control (incubation of analogous strains with YPD without thaumatin). The small differences in doubling time are errors in measurement.
As expected, thaumatin does not have an effect on the growth rate of yeast cells. Hence we are not limited in over-expressing the sweetener in our beer.
References
- [Edens et al., 1984] Edens, L., Bom, I., Ledeboer, A. M., Maat, J., Toonen, M. Y., Visser, C., and Verrips, C. T. (1984). Synthesis and processing of the plant protein thaumatin in yeast. Cell, 37(2):629–33.
- [Ide et al., 2007] Ide, N., Masuda, T., and Kitabatake, N. (2007). Effects of pre- and pro-sequence of thaumatin on the secretion by Pichia pastoris. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 363(3):708–14.
- [Ide et al., 2009] Ide, N., Sato, E., Ohta, K., Masuda, T., and Kitabatake, N. (2009). Interactions of the sweet-tasting proteins thaumatin and lysozyme with the human sweet-taste receptor. J Agric Food Chem, 57(13):5884–90.
- [Lee et al., 1988] Lee, J. H., Weickmann, J. L., Koduri, R. K., Ghosh-Dastidar, P., Saito, K., Blair, L. C., Date, T., Lai, J. S., Hollenberg, S. M., and Kendall, R. L. (1988). Expression of synthetic thaumatin genes in yeast. Biochemistry, 27(14):5101–7.
- [Maîtrepierre et al., 2012] Maîtrepierre, E., Sigoillot, M., Le Pessot, L., and Briand, L. (2012). Recombinant expression, in vitro refolding, and biophysical characterization of the n-terminal domain of t1r3 taste receptor. Protein Expr Purif, 83(1):75–83.
- [Masuda et al., 2011] Masuda, T., Ohta, K., Mikami, B., and Kitabatake, N. (2011). High-resolution structure of the recombinant sweet-tasting protein thaumatin i. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun, 67(Pt 6):652–8.
- [Masuda et al., 2004] Masuda, T., Tamaki, S., Kaneko, R., Wada, R., Fujita, Y., Mehta, A., and Kitabatake, N. (2004). Cloning, expression and characterization of recombinant sweet-protein thaumatin ii using the methylotrophic yeast pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Bioeng, 85(7):761–9.
- [Moralejo et al., 1999] Moralejo, F. J., Cardoza, R. E., Gutierrez, S., and Martin, J. F. (1999). Thaumatin production in aspergillus awamori by use of expression cassettes with strong fungal promoters and high gene dosage. Appl Environ Microbiol, 65(3):1168–74.
- [Ozeck et al., 2004] Ozeck, M., Brust, P., Xu, H., and Servant, G. (2004). Receptors for bitter, sweet and umami taste couple to inhibitory g protein signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol, 489(3):139–49.
- [Trubey et al., 2006] Trubey, K. R., Culpepper, S., Maruyama, Y., Kinnamon, S. C., and Chaudhari, N. (2006). Tastants evoke camp signal in taste buds that is independent of calcium signaling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 291(2):C237–44.
Others
- Thaumatococcus daniellii mRNA forpreprothaumatin I, comeplete cds [[1]]
- Preprothaumatin I [Thaumatococcus daniellii], FASTA [[2]]
- yeastgenome.org [[3]]
 "
"