Team:Evry/FrenchFrog
From 2012.igem.org
The French froggies: an artificial hormonal system in tadpoles
Establishment of a new chassis
So far, the engineering of living organsims has moslty been focuced on bacteria, as beeing the simplest organism to engineer. iGEM teams and laboratories have focuced on unicellular organisms in order to understand the principles underlying biology and has developped a quite comprehensive database of molecular part. Some work has been started on engineering mammalian cells and a few iGEM team had followed this trend. It is generally admitted that synthetic biology is now heading toward rational design of mulicellular organisms with numerous applications ranging from gene therapy, drug production or environmental applications. This year, our team would like to be part of that challenge.
Frogs, as well as nematodes, flies and mouses has been used for a long time as organisms of choice to study the fundamental principles of biology in multicellular organisms, and an all range of genetic and micro injection techniques has been developped for them. But so far, very little work has been done in engineering de-novo systems in these organisms, as we are aming at in synthetic biology.
This year, the Evry iGEM team iq going to be the very first iGEM team to work on a vertabrate, and our work is focuced both on developping genetic tools and standard protocols for the iGEM community. We beleive the tadpole is a chassis of choice for iGEM on multi cellular organisms, and we would like to demonstrate the feasibility of engineering Xenopus Laevis and Xenopus trocicalis in the iGEM time and technological constraints through the development of a very original project: the development of a new orthogonal hormonal system in Xenopus.
An new engineered orthogonal hormonal system
Our project this year is to demonstrate the feasibility of building de-novo a new hormonal system, in Xenopus Tropicalis, orthogonal to any endogenous hormonal system existing in the tadpole. A hormone (from Greek ὁρμή, "impetus") is a chemical released by a cell or a gland in one part of the body that sends out messages that affect cells in other parts of the organism. In essence, it is a chemical messenger that transports a signal from one tissue to another. In a synthetic biology approach, it is a communication device, and an extensive work has been done on bacteria to engineer such systems, mostly using quorum sensing molecules.
We had to choose 2 organs we would like to make communicate. The choice of these organs has been set on the specific properties of the tissues in term of function and blod irrigation as well as on the existance of reported functionnig tissue specific promotors. As an emitter, we choosed to use the skin, and as a receiver, the kidney. We are going to described the reason of these choices now.
In orted to trigger the emission of the hormone in our synthetic hormonal system we wanted to dissolve a chemical in the water of the tadpole that would activate an indicible promoter. The most exposed tissue to the chemical environment is undoubtely the epithelium, because of the important surface exposed to the water. On the top of it, this tissue is highly vascularized, which is important in order to acheive a high concentration of auxin in the blood. An important library of promoter has also been identified for this tissue.
The problem of introducing a non native hormon into the blood is that the kidney is likely to eliminate it from the blood. The kidney works as an inverted filter, in the sense that it takes out every molecule from the blood and reintroduce only the one it knows, and our hormon does not nessarily belongs to these molecule. Therefore, we can anticipate that the course of your molecule will ends up there and it will be the place where it is the most concentrated. This organ seems to be the best place for expressing our receiver system. There are also good promoters coming from the different ion channels that are know to work there.
Auxin as a new hormonal system in Xenopus
The molecule we have choosen to use as an hormon is a plant hormon called Auxin (IAA) well known for beeing gesponsible of the plant and the roots growth. A very extensive work has been done on this hormon in E. coli and Arabidopsis Thaliana last year by the 2011 Imperial College of London iGEM team [1].
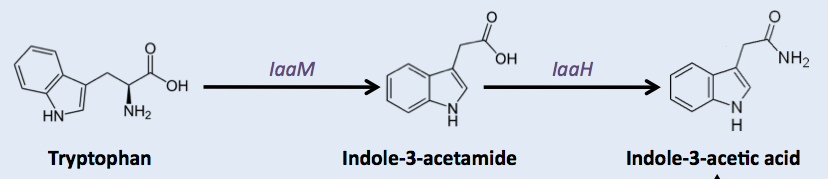
Auxin is a molecule of choice for working on tadpole becaus of its similarity to tryptophane. It is amphiphilic and hydrophobic so we assume it can cross the biological membrane easily but its toxicity is reported to be very weak. It can be synthetized in a two step pathway from a tryprophane precursor and a cytosolic receptor for this hormone from the rice has been shown to work in mammalian cells successfully [2].
This project is the first known example of a rationally designed homonal system in a pluricellular organism. On the top of being an important technological acheivement, it demonstrates the capability to engineer deeply fundamental mechanisms in pluricellular organisms and demonstrate further that the tadpole is a good system to engineer biosensors
Auxin Inductible Degron system
Modeling
Biosensors
We will then create the "biosensors" and "biomonitors", capable of detecting pollutants in water by human societies. Its metabolism is similar to humans, but with a shorter life cycle, it is more readily possible to evaluate the impact of these molecules in animals and human beings who consume the contaminated water.References:
- Paper, author, journal, 2011
 "
"