Team:Wellesley HCI/MoClo Planner
From 2012.igem.org

MoClo Planner
Tool Overview
The MoClo planner is a collaborative, touch-enabled software tool that simplifies information gathering and design steps of Golden Gate Modular Cloning; a hierarchical cloning method that relies on biological “parts” to create multi-gene constructs. Users can browse through a library of biological parts using filters, search for a specific part using the part’s name or registry ID, access a data sheet for each part, and view relevant publications from Pubmed. The layered workspaces allows for efficient and organized transfer of information from one level of the cloning method to another without distracting from the primary workspace. Furthermore, the built-in primer designer allows for the generation of primer sequences and lab protocols without ever leaving the workspace.
Implementation
The MoClo planner is being implemented on a 40 inch Microsoft Surface. The software tool is programmed using the Microsoft Surface SDK written in C#. Eugene is used to generate and regulate Level 1 permutation from Level 0 BioBricks. We also use Visual Sbol to visually represent the distinct parts in the standard way.
Golden Gate Modular Cloning
Golden Gate Modular Cloning is a DNA construction method that allows for the assembly of any multi-gene construct from a library of biological parts. The method is hierarchical, allowing the user to link the standard biological parts (promoters, ribosome binding sites, coding sequences, and terminators) in order to create genes, and then use these genes to assemble multi-gene constructs.
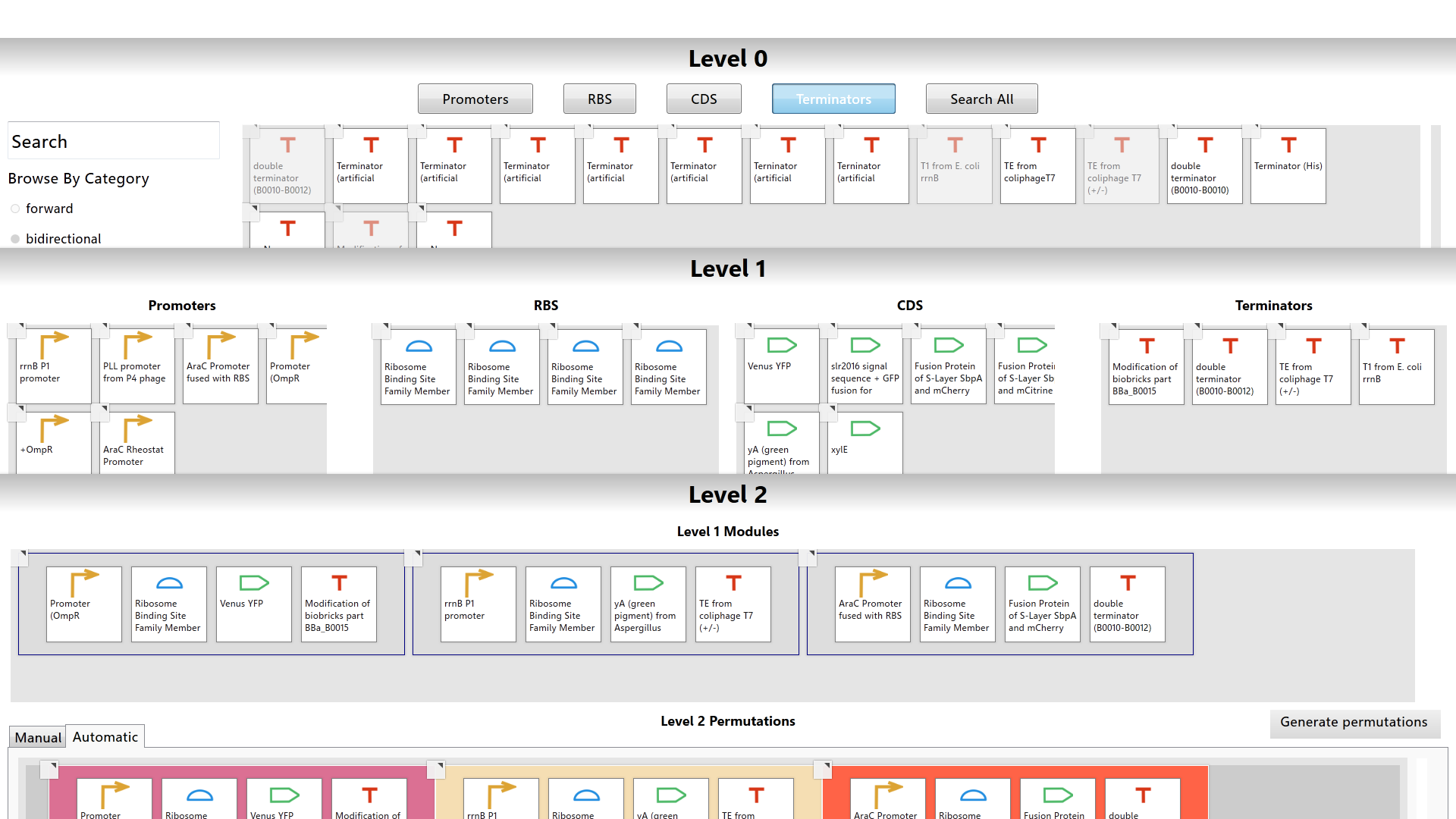
The Interface
The MoClo planner has three layered workspaces called the Level 0, Level 1, and Level 2 workspaces. Each workspace represents one level of the modular cloning method. Basic biological parts are handled in Level 0. The construction of genes is managed in Level 1. The assembly of multi-gene networks is done in Level 2. The user can work in multiple workspaces at a time. While working in any workspace, the user can arrange the workspaces to fit the screen so that each workspace is seen simultaneously.
How It Works
The Level 0 workspace contains a library populated with over 2000 biological parts from the Registry of Standard Biological Parts. The user can utilize filters or search for a specific part using the part’s common name or registry id to browse the library. Each biological part is color-coded based on its type.
Drag-and-drop functionality is used to transfer information from one workspace to another.
Within the Level 1 and Level 2 workspaces, the user can utilize two methods of construct assembly: manual assembly and automatic assembly. Manual assembly allows the user to create specific constructs from specific parts whereas automatic assembly will generate all possible constructs from the selected biological parts.
Information for each part is easily accessed by pulling up a data sheet and publications list from the element menu. The data sheet is populated with standard information about the part from the parts registry. The publications are fetched from Pubmed and parsed for abstracts and publication info.
At any point in the design process, the user can launch the primer designer. Similar to the Level 1 and Level 2 workspaces, primers can be created manually or automatically. By including a built-in primer designer, the MoClo planner efficiently encompasses all steps of the design and build process.

 |
Results
We conducted several user studies this summer and refined our evaluation and design to reflect the user feedback with each study. We had six groups of Wellesley undergraduates (who had exposure to introductory biology classes), the BU iGem team, and four pairs from the MIT iGEM team construct a multi-gene network using MoClo Planner. While everyone found the interface of the layered workspaces to be intuitive, the BU iGem team had some concern with the program’s criteria for creation of primers. Since then, we have revamped the algorithms for the processing and creation of primers to include specific regulations unique to Golden Gate Modular Cloning primers.

An example of a collection showing parts, vectors, and features
A DNA sequence opened in sequence viewer with features highlighted.
 "
"