Team:USP-UNESP-Brazil/Plasmid Plug n Play/Background
From 2012.igem.org
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
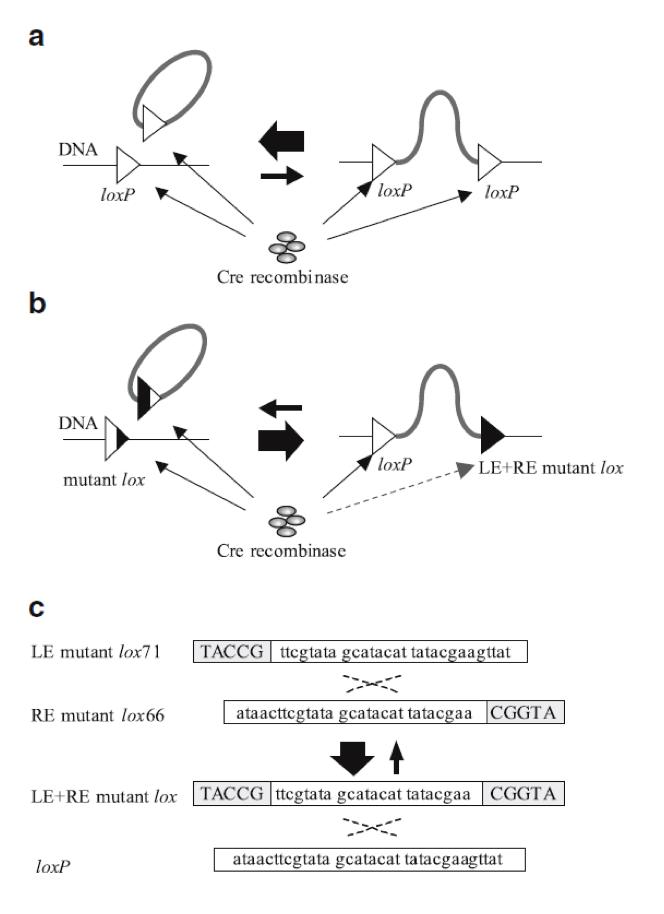
However, insertion of a circular DNA carrying a loxP into a loxP site on a chromosome (integrative recombination) is quite inefficient because unimolecular reactions are kinetically favored over bimolecular reactions, causing that the inserted DNA will often be excised (6) (Fig. 2a). To tackle this problem we have used loxP mutant sites (2). These sites help to maintain the inserted DNA in the chromosome (Fig. 2b).In our project we used one loxP site and two loxP mutant sites (lox71 and lox66) (Fig. 2c). | However, insertion of a circular DNA carrying a loxP into a loxP site on a chromosome (integrative recombination) is quite inefficient because unimolecular reactions are kinetically favored over bimolecular reactions, causing that the inserted DNA will often be excised (6) (Fig. 2a). To tackle this problem we have used loxP mutant sites (2). These sites help to maintain the inserted DNA in the chromosome (Fig. 2b).In our project we used one loxP site and two loxP mutant sites (lox71 and lox66) (Fig. 2c). | ||
| - | {{:Team:USP-UNESP-Brazil/Templates/RImage | image=fig2plugplay.JPG | caption=Illustration of Cre/loxP and Cre/LE- and RE-mutant lox system. Black regions of the triangles represent sites at which nucleotide sequence changes occurred. a Recombination between loxP sites. b Recombination between a LE mutant lox71 and a RE mutant lox66 produces a loxP and a LE + RE mutant lox. c Gray boxes indicate sites at which nucleotide sequence changes occurred (6). | size=600px }} | + | {{:Team:USP-UNESP-Brazil/Templates/RImage | image=fig2plugplay.JPG | caption= Fig 2. Illustration of Cre/loxP and Cre/LE- and RE-mutant lox system. Black regions of the triangles represent sites at which nucleotide sequence changes occurred. a Recombination between loxP sites. b Recombination between a LE mutant lox71 and a RE mutant lox66 produces a loxP and a LE + RE mutant lox. c Gray boxes indicate sites at which nucleotide sequence changes occurred (6). | size=600px }} |
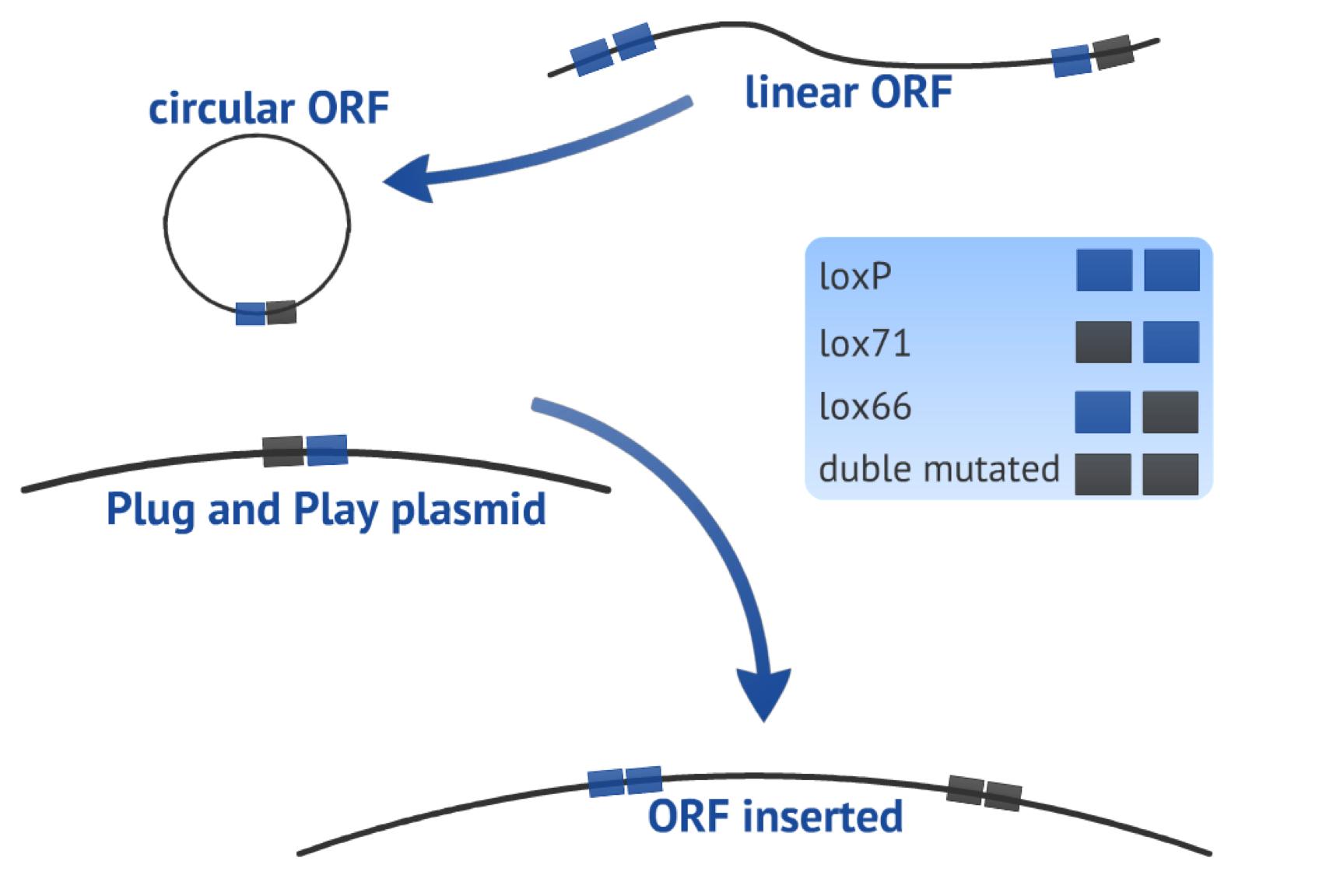
The first recombination consists in a circularization of the linearized PCR product (target-gene flanked by one loxP site upstream and one lox66 site downstream, both in the same orientation) in order to form a plasmid. The result of this step is one 8bp loxP fragment that is released and one circular fragment with the target gene and one lox61 newly created (Fig. 3). | The first recombination consists in a circularization of the linearized PCR product (target-gene flanked by one loxP site upstream and one lox66 site downstream, both in the same orientation) in order to form a plasmid. The result of this step is one 8bp loxP fragment that is released and one circular fragment with the target gene and one lox61 newly created (Fig. 3). | ||
Revision as of 19:03, 21 September 2012
 Introduction
Introduction Project Overview
Project Overview Plasmid Plug&Play
Plasmid Plug&Play Associative Memory
Associative MemoryNetwork
 Extras
ExtrasThe Plug and Play project is base on the Cre-lox recombination mechanism, which occurs between the Cre Recombinase enzyme and the loxP sites.
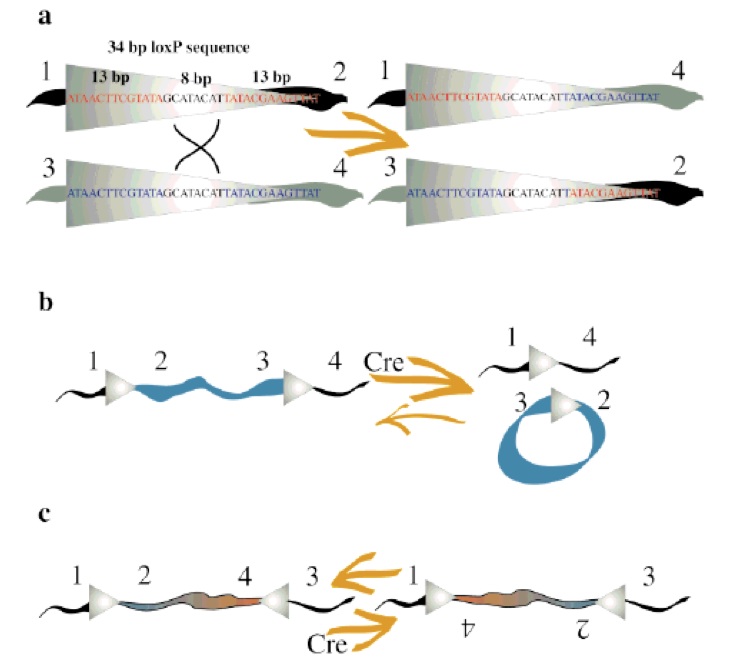
Cre Recombinase (38kDa) is a tyrosine recombinase from the P1 Bacteriophage (1). It is known to play important roles in this organism’s life cycle, such as cyclization of the linear genome when the phage infects the bacteria and resolution of dimeric chromosomes that form after DNA replication (7). The enzyme uses a topoisomerase I like mechanism to carry out site-specific recombination events between two DNA recognition sites (called loxP sites). Each loxP recognition site has 34pb, which consists of two 13bp palindromic sequences that flank an 8bp spacer region (ATAACTTCGTATA–GCATACAT–TATACGAAGTTAT).
The recombination result is dependent to location and relative orientation of the loxP sites, which can be in cis (same DNA strand) or trans (different DNA strands). The spacer sequence (8bp) found in each loxP site is also important for the outcome of the recombination process, it gives the orientation of one site in correlation to the other when both are in cis position. When DNA is found between two loxP sites oriented in the same direction this DNA would be excised as a circular loop, when these two loxP sites are in opposite directions the DNA between them will be inverted (5) (Fig. 1). The enzyme requires no additional cofactors (such as ATP) or accessory proteins for its function (1).
Concerning the molecular mechanism of recombination, a single recombinase molecule binds to each palindromic half of a loxP site, then the recombinase molecules form a tetramer, thus bringing two loxP sites together (8). The recombination occurs within the spacer area of the loxP sites. The post-recombination loxP sites are formed from the two complementary halves of the pre-recombination sites (Fig. 1). This mechanism was further improved for science research purposes, and nowadays, lots of tools have been made based on it. The best-known example is the Nobel Prize winner experiment of knockout on rats using the Cre-lox recombination (4).
Now we will talk about DNA integration or insertion. It is another way of working using Cre-lox recombination between two different DNA fragments. It has already been extensively explored and is the key mechanism of our experiment. Using two DNA fragments, each one with one loxP site, is possible to fuse both into one larger fragment.
However, insertion of a circular DNA carrying a loxP into a loxP site on a chromosome (integrative recombination) is quite inefficient because unimolecular reactions are kinetically favored over bimolecular reactions, causing that the inserted DNA will often be excised (6) (Fig. 2a). To tackle this problem we have used loxP mutant sites (2). These sites help to maintain the inserted DNA in the chromosome (Fig. 2b).In our project we used one loxP site and two loxP mutant sites (lox71 and lox66) (Fig. 2c).
The first recombination consists in a circularization of the linearized PCR product (target-gene flanked by one loxP site upstream and one lox66 site downstream, both in the same orientation) in order to form a plasmid. The result of this step is one 8bp loxP fragment that is released and one circular fragment with the target gene and one lox61 newly created (Fig. 3). The second recombination occurs between the circularized PCR product and the Plug&Play plasmid (containing the Cre recombinase gene, a T7 promoter, a lox71 site, a stop site and a ampicillin resistance gene), in an integrative recombination. As result, we will have one bigger plasmid with the target gene flanked by one loxP site and one double mutated site, reducing the chance of the fragment to be excised and locating the gene in a context ready to express it (Fig 3).
This project aims to reduce the expression of any gene to two steps; PCR and transformation. The linear DNA, from the PCR, is inserted in electro-competent cells (BL21(DE3)), the electro-competent cells already have the plug&play plasmid producing Cre recombinase for the circularization and the integration. Issues like the linear DNA degradation, integration and circularization rates were explored using mathematical modeling, which showed the viability of the project even before beginning to work in the bench.
BIBLIOGRAFIA:
1. ABREMSKI & HOESS (1984). "Bacteriophage P1 Site Specific Recombination. Purification and Properties of the Cre Recombinase Protein". Journal of Biological Chemistry 259: 1509–1514.
2. ALBERT H., DALE E.C., LEE E., OW D.W. (1995) Site-specific integration of DNA into wild-type and mutant lox sites placed in the plant genome. Plant J.7:649–659.
3. HOESS, R.H., ZIESE, M. AND STERNBERG, N. (1982) P1 site-specific recombination: nucleotide sequence of the recombining site. Proc. Nat/Acad. Sci. USA, 79, 3398-3402.
4. MANIS JP. Knock out, knock in, knock down – Genetically manipulated mice and the Nobel Prize. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:2426
5. NAGY A. 2000. Cre recombinase: the universal reagent for genome tailoring. Genesis 26:99-109.
6. SUZUKI N, INUI M, YUKAWA H (2007) Site-directed integration system using a combination of mutant lox sites for Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77: 871-878
7. VAN DUYNE G (2001). "A Structural View of Cre-loxP Site Specific Recombination". Annual Reviews Biophysics Biomolcular Structures 30: 87–104. 8. VOZIYANOV Y, PATHANIA S, JAYARAM M. 1999. A general model for sitespecific recombination by the integrase family recombinases. Nucleic Acids Res 27:930–941
 "
"