Team:Tianjin/Modeling/Regulation
From 2012.igem.org

Contents |
Background
Metabolic Regulation
Cell metabolism is the foundation of cell growth, secretion, differentiation, etc. as well as the core process of the modern fermentation technology that can make large impact on the quality and output of product.
However the modern metabolic regulation of strains has a large amount of areas for improvement. Take the most common E. coli as example. At present, most of the regulation means is to use a single promoter to construct specific operon gene cluster to achieve the regulation with the addition of certain inducers induction of a specific protein. But this induced expression is typically unidirectional, irreversible and it needs to build many complex operons’ gene structure to construct multiple logical regulation, this will produce a plenty of limitation.
If we add our O-Key into the expression system, a novel regulation means will exist on the level of translation. Meanwhile, we can combine O-Key with the traditional transcription regulation to create logic gate regulation structure like “AND” gate. The logic gate working with normal close and normal open promoter can constitute multiple “AND/OR/NOR” logic gate control system which has more simple structure compared to traditional regulation.
The Difficulty of Large Fragments Assembly
The general digestion connection will leave scar and will be limited by the specific cleavage sequences.
Long PCR fragment will suffer the decline of success rate and distortion, etc.
However, the construction of some large fragments cannot be avoided, so the development of a low-cost, simple operation, good fidelity, a little limiting factor large DNA fragment assembly method is particularly important.
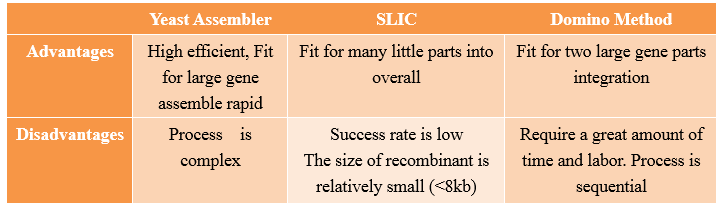
Yeast Assembler
History
Yeast Assembler is based on in vivo homologous recombination in yeast. As for its high efficiency and ease to work with, in vivo homologous recombination in yeast has been widely used for gene cloning, plasmid construction and library creation. In the early of 2008, Zengyi Shao from University of lllinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, used such a method to construct biochemical pathways. Such a method, for its high efficiency in assembling multiple genes, received great popularity since its appearance.
Principles
One step assembly into a vector.
When parts are transformed all parts into Yeast, homologous recombination occurs at the site “x”, and then all little parts are integrated into a vector.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Compared with other methods,the “Yeast assembler” are more efficient and useful for large gene assemble.
Completely Synthesizing the Genome of Mycoplasma Genitalium using Yeast Assembler
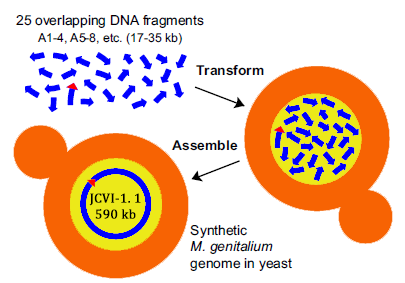
In 2008, Gibson from the J. Craig Venter Institute, published an article “one-step assembly in Yeast of 25 overlapping DNA fragments to form a complete synthetic Mycoplasma genitalium genome”. In the article, the author transformed 25 overlapping DNA fragments into Yeast, homologous recombination occurs, and then the whole genome is synthesized.
Construction of a synthetic M. genitalium genome in yeast. Yeast cells were transformed with 25 different overlapping A-series DNA segments (blue arrows; ~17 kb to35 kb each) composing the M. genitalium genome. To assemble these into a complete genome, a single yeast cell (tan) must take up at least one representative of the 25 different DNA fragments and incorporate them in the nucleus (yellow), where homologous recombination occurs. This assembled genome, called JCVI-1.1, is 590,011 bp, including the vector sequence (red triangle) shown internal to A86 – 89.
Synthesizing the Pathway Needed for Synthesizing Violacein
Background
In order to verify the abilities of orthogonal system to adjust metabolism, we chose the metabolic pathway of Violacein. The reason why we chose this one are based on the facts that the pathway is suitable to adjust, and has been deeply learned.
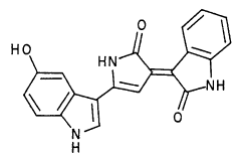
Violacei, the major pigment produced by Chromobacterium violaceum, is a bactericide, a trypanocide, a tumoricide and in addition it has anti-viral activity.
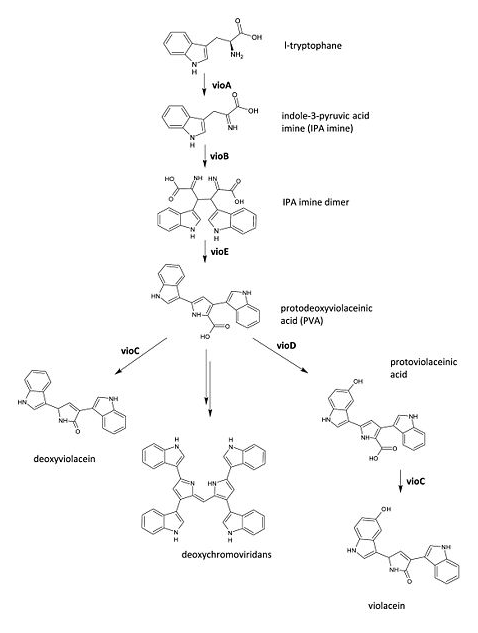
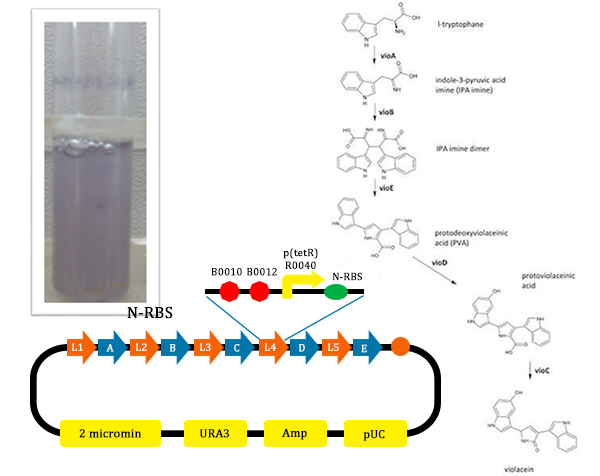
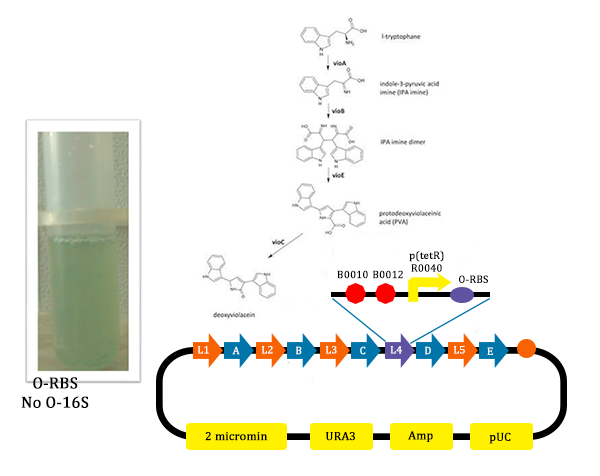
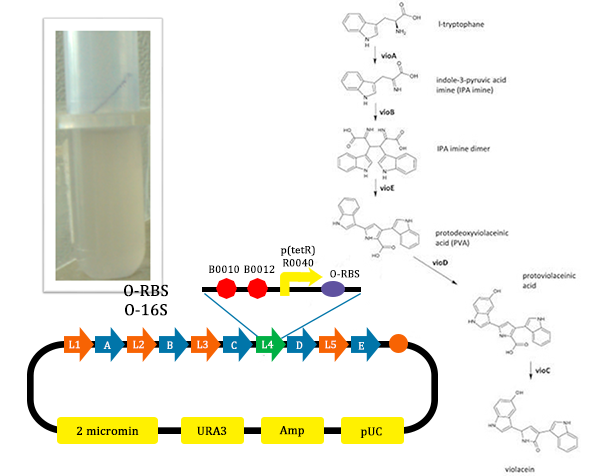
The metabolic pathways to produce Violacein are revealed in the following picture.
From the pathway, we can know that except for the desire product, Violacein, the pathway will also produce side product, deoxyviolacein.
Principle
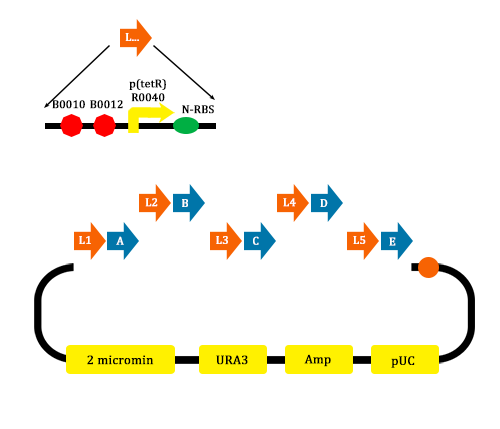
In order to verify the feasibility of the orthogonal system in adjusting metabolism, we mutated the RBS of the gene encoding VioD by MAGE, and assembled in Yeast Assembler. The VioD gene and the O-Key gene with pBad promoter were finally transformed into the cell. Because the cell itself doesn’t have the O-Key, the gene is stringently shut down. When we added Ala to induce pBad, the O-Key were produced to open the O-Lock, so the cell could produce violacin.
Experiment
- MAGE mutate the RBS of the gene coding VioD to o-RBS
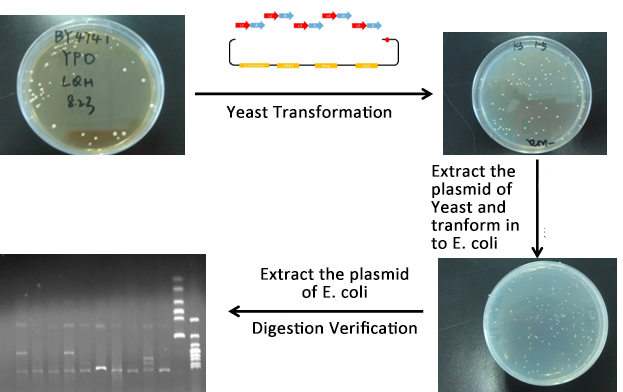
- We construct different parts of Vio operons, and transformed into yeast for assembly(In this part, we also assembly the original genes without mutation)
- Extracted the plasmid of Yeast and then transformed into our O-E.coli on LB plates.
- Verify through Cpcr and inculcated the right colony into liquid LB overnight.
- Extracted the plasmid of E.coli and verified through digestion of ligase.
Results and Analysis
- From the above picture, the process is finished smoothly and the result of Digested verification is right.
- From this picture, we could find that the test tube with the normal pathway, the liquid is purple. In such condition, for PVA have the larger potential to turn into violacein, violacein stand for a large part and liquid is purple.
- In this picture, we could find that liquid is blue. As we didn’t add Ala into the liquid, the cells didn’t produce O-ribosome, then the vioD could not be expressed. The PVA could only become deoxyviolacein, which is blue. Therefore the liquid is blue.
- In this picture, the liquid is lavender. For this tube, we added Ala, which could induce the production of O-ribosome, then PVA could turn into violacein, then the liquid is lavender.
- From the results of this experiment, we could find that the orthogonal system could work well when used to adjust metabolism, and the effect is satisfied. In the fourth part, we will further discuss the application of the orthogonal system in regulating the metabolism.
 "
"