Team:SEU O China/Project
From 2012.igem.org


Project
Background
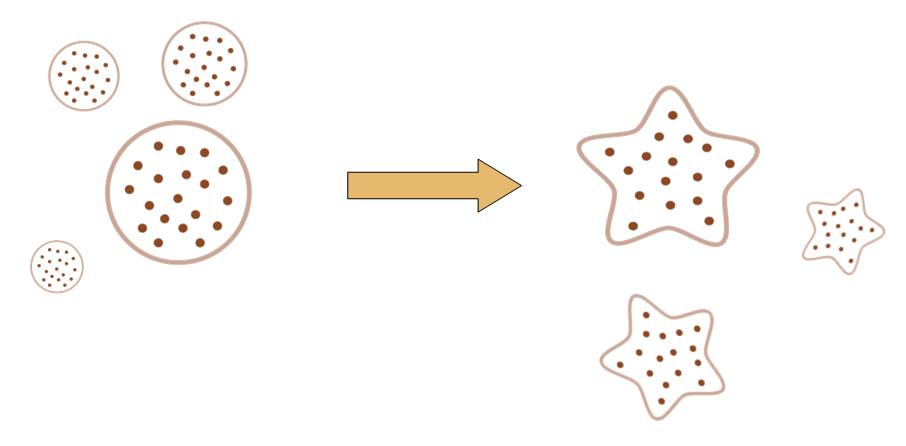
The original idea of this project is really simple. Getting bored of the indifferent, round round colony on the culture dish, we wish to make the bacteria grow into the form of a star, a smiling face, or any other patterns we desire.
Instead of the traditional method of painting a star on the culture dish, and let the colony grow into this pattern, we try to design a biobrick system which let the bacteria take the irregular shape all by itself, despite external conditions.
That means, not only the colony can grow into to shape of a star, but also, even if you pick one cell from the colony, and incubate it on another clean culture medium. That cell will also grow into a colony, which has the shape of a star.
Although the idea is like some kind of bio-game, our project is not that meaningless. Comparing the single cell organism like Escherichia coli, and some simplest multicellular organism like Slime which can act like a whole body in tough environment, we notice that a significant difference between them is that the cells of a multicellular organism can act as a whole, and construct a certain structure.
That is to say, the biobrick system we are constructing is meant to make the single cell bacteria grow into a colony which can act like a multicellular organism. To perform gene manipulation on a multicellular level would be a promising and interesting task.
Story
At first, the cells in a colony are all indifferent, and the toggle switches in cell are on the same status.
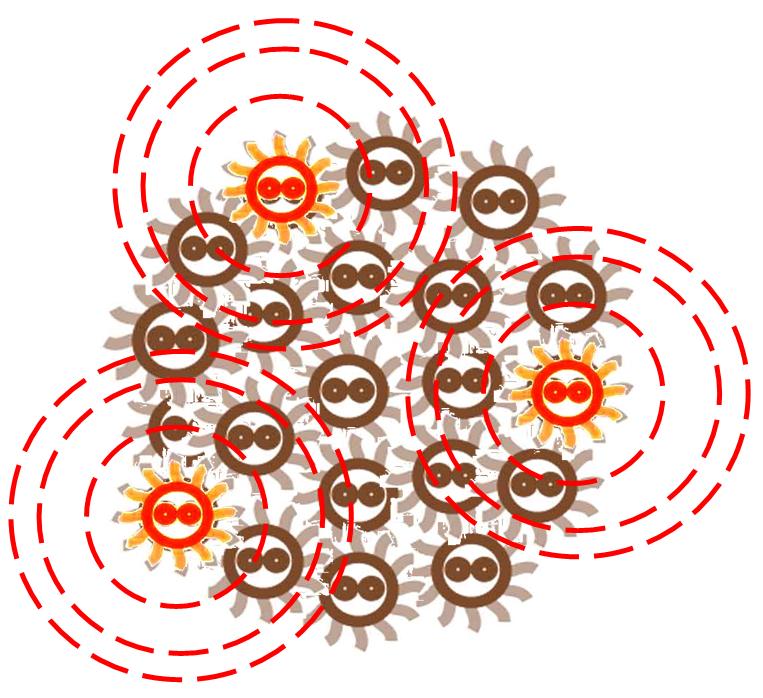
After some events, some of the cells become special. The switch is turned on, and the differentiation happens. The special cells can act like a 'brain', and control the behavior of other cells.
The special cells generate signal molecular which affect the nearby cells in the colony.
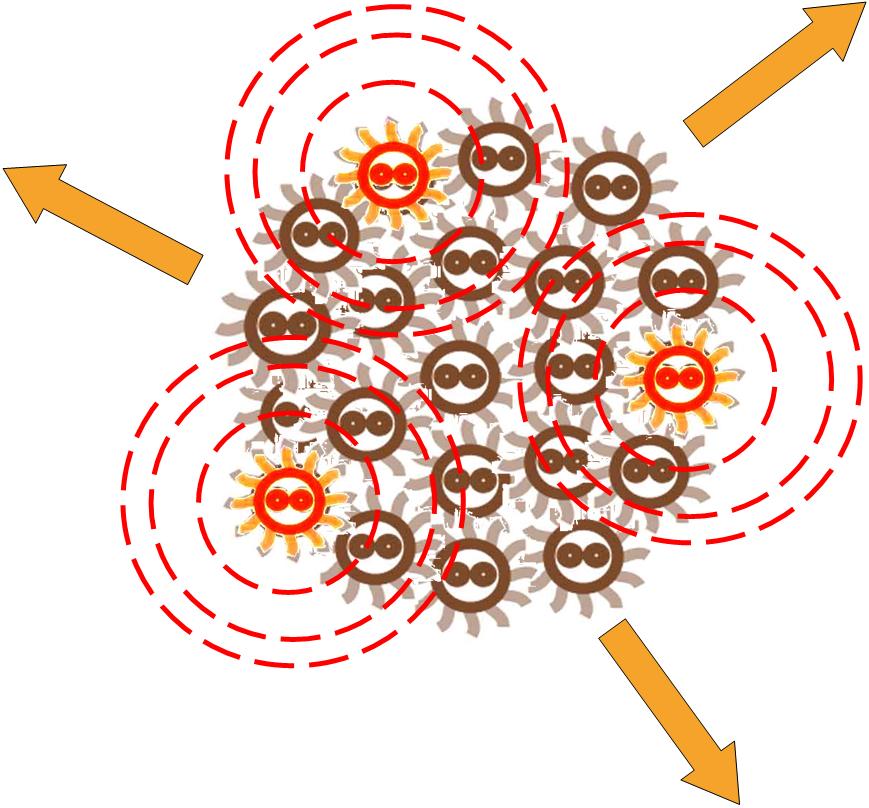
Responding to the density of signal molecular, the division rate of cells in the colony changes differently. Bacteria tend to divide slower in the place where the signal density is higher.
After some time, the Bacteria colony would grow into a certain pattern like this.
By controlling related parameters, it would be possible to create different shapes with bacteria colony.
The very idea of this process (and even the name of our project) comes from the slime's fruit body generation, which include the formation of special regions inside colony, the intercellular communication, and control of cell movement[1]. Special thanks to those one-level monsters we have fought in so many games for years....
[1] Oleg A. Igoshin et al. Breaking symmetry in myxobacteria, Curr Biol. 2004 Jun 22;14(12):R459-62.
System
In order to construct a multicellular system, several vital parts must be taken into consideration. We use a toggle switch to save a status, which simulates the cell differentiation, a AHL generate-receive system for intercelluar communication, an antisense mRNA biobrick as cell division inhibitor, in order to control the shape of bacteria colony. We designed a cell movement control device to start the differentiation automatically, as well as a light sensor system to start it artificially for easier control and further application.
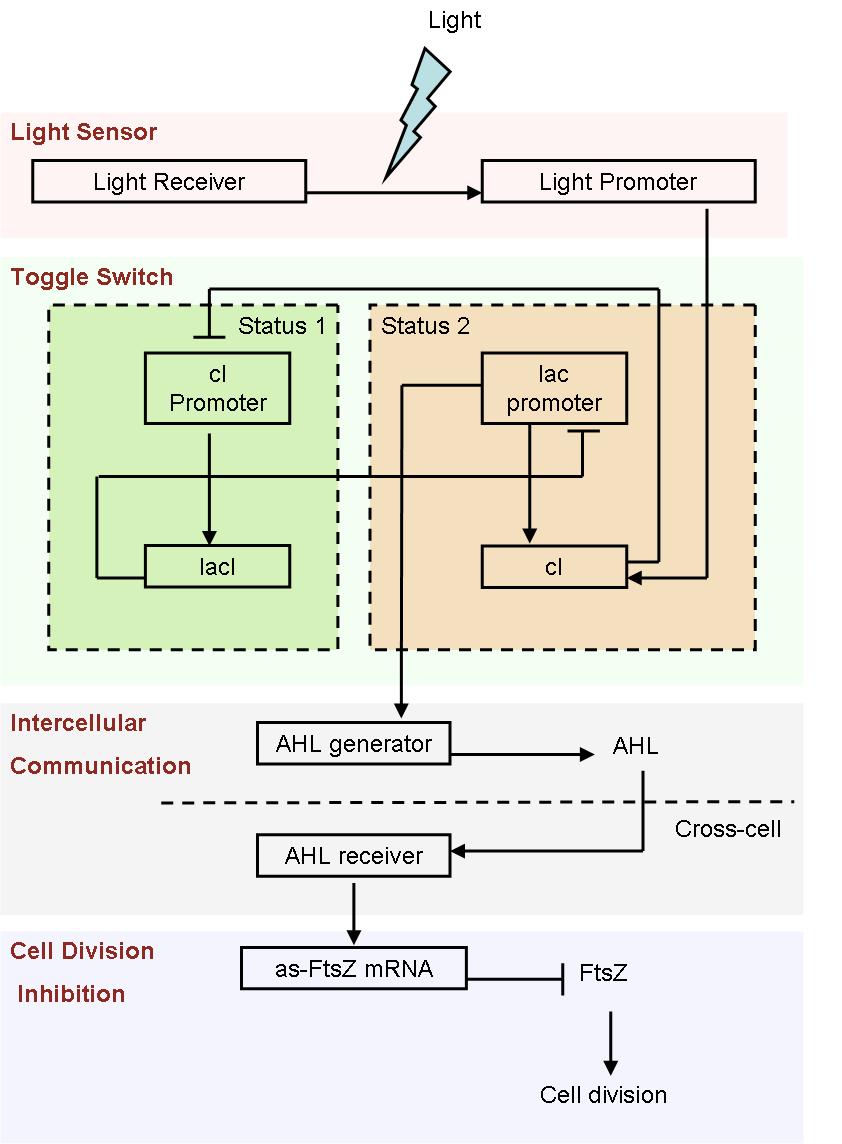
Since it is not easy to create a auto-differentiation system from scratch, we decide to start from a light induced system. That means, the first special cells are triggered artificially by light.
- Fig1. Scheme of light induced differentiation system:
At the beginning, we can set all the cells are on status 1 by exposure of UV light. Thus, the cI promoter is switched on and lacI protein is produced. So, at this time, the lac promoter is inhibited and the signal molecular is not generated.
When a cell gets a light signal, the light sensor system will be triggered, and a small amount of cI protein will be produced, which can repress the cI promoter. Then, the toggle switch will be set to status 2, in which the lac promoter is active. Promoted by the lac promoter, AHL molecules are generated from those special cells.
Receiving the AHL molecules, cells start their division inhibition system. An antisense mRNA is transcript, which can bind the mRNA of an essential cell division protein, FtsZ, and thus inhibit its expression and repress the growth of that part of colony. As a result, by controlling the position of light signal, we could create an unsymmetrical colony.
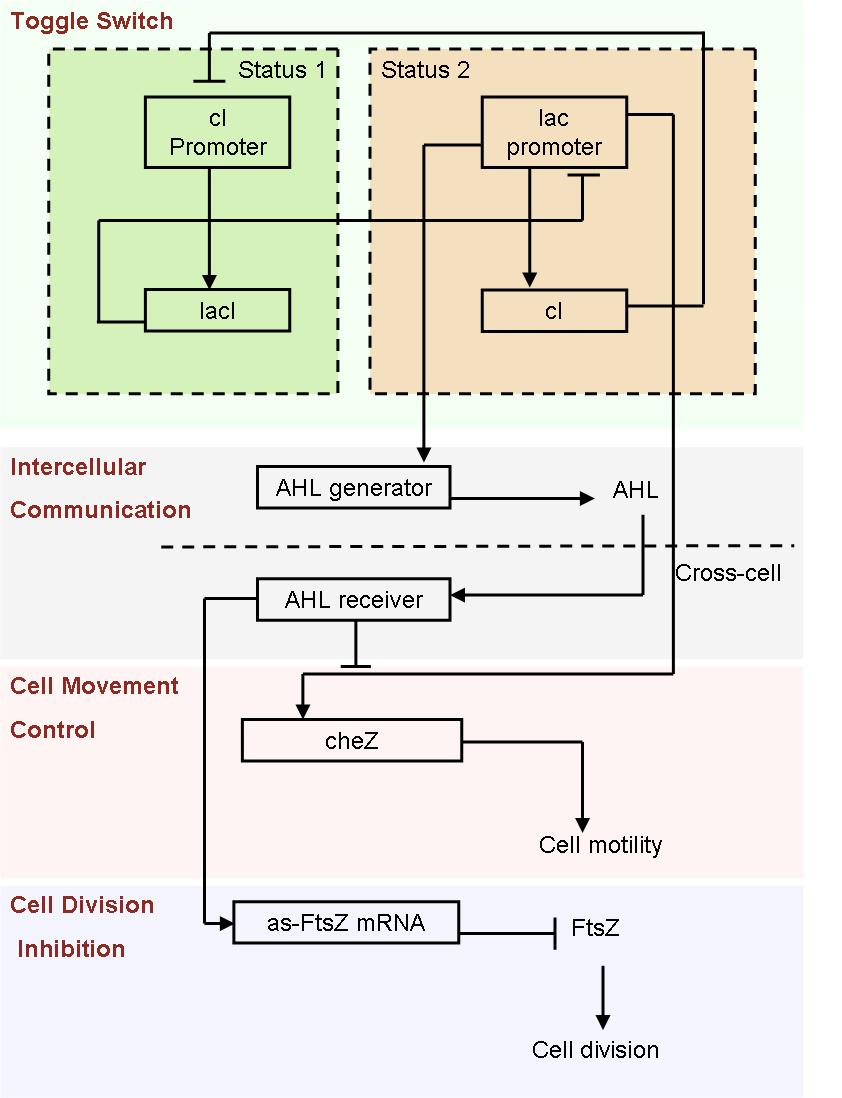
Based on the light induced system, we started to design an auto-differentiation system.
- Fig2. Scheme of auto-differentiation system:
Without external control, the toggle switches in cells start on random status and the rate between status 1 cells (green cells) and status 2 cells (red cells) is certain.
Same as the light induce system, the red cells start to produce AHL molecules. However, the difference is that, in this system, red cell tend to move while the AHL density is high, and stand still while low. Thus, the red cells can move toward the high AHL density region. Since the red cells themselves are AHL sources, this behavior leads red cells gather into several clusters inside the colony.
These red cell clusters, just like the light induced cells in the last system, generate signal molecules and control the division rate of other cells nearby. In the same way, an unsymmetrical pattern may appear on the culture dish.
Light Sensor
Light sensor is one of prime parts in our whole project and is constructed by two different scheme,considering the multiple choices of light source and reliablity of those two scheme.
Red light
This functional device,allowing the expression of a certain gene to be regulated by red light, consists of two main parts: phytochrome part and regulation part. phytochrome part is responsible for light sensing and regulation part converts the light signal in gene regulational signal.
- Fig1. Red light receptor system
Phytochrome part is a two-component system that consists of a membrane-bound, extracellular sensor (PCB) and an intracellular response-regulator (Cph1). Phycocyanobilin, abbreviated as PCB,is conversed from haem through a series of biological reactions that are catalyzed by heme oxygenase (ho1, BBa_I15008) and ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA,I15009). It acts like an antenna and responds to light as many other members in the phytochrome family. However,phytochromes usually lack DNA-binding domains and cannot regulate gene expression, which requires Cph1 to response and pass on the light signal to regulation part. Cph1, also known as synechocystis phytochrome, is combined with the histidine kinase domain of EnvZ which is one of the key components in EnvZ-OmpR system. The chimaera of Cph1 and EnvZ is named as Cph8(BBa_I15010) that is marked in yellow in Fig.1.
Regulation part is mainly based on EnvZ-OmpR systems. Once activated by the light signal from Cph1, the EnvZ in Cph8 phosphorylates the endogenous OmpR, a transcription factor that results in the expression of the gene after the OmpC promoter. It is noteworthy that endogenous EnvZ should be knocked off from the E.coli strains, which ,if not,may cause the continuous expression of gene after OmpC.
BBa_M30109 is expected to be a reliable kit while on the contrary, we failed to get the correct sequencing report of BBa_M30109. It also reminds us there might be some unsure problems like plasmid size causing the failure of BBa_M30109. As a result,we started constructing two relatively small plasmids: RSB, consisting of BBa_R0010, BBa_S03419 and BBa_B0015, and JIK, consisting of BBa_J13002, BBa_I15008 and BBa_K081024.
Up to now,after combined BBa_S03419 with BBa_B0015 and K081024 with I13507 (a report protein,RFP), we unexpectedly found that the strains of E.coli we use has endogenous EnvZ and until now we realized that EnvZ commonly exists in the genome of most E.coli strains. That's why we emphasize the importance of lack of endogenous EnvZ in the above.
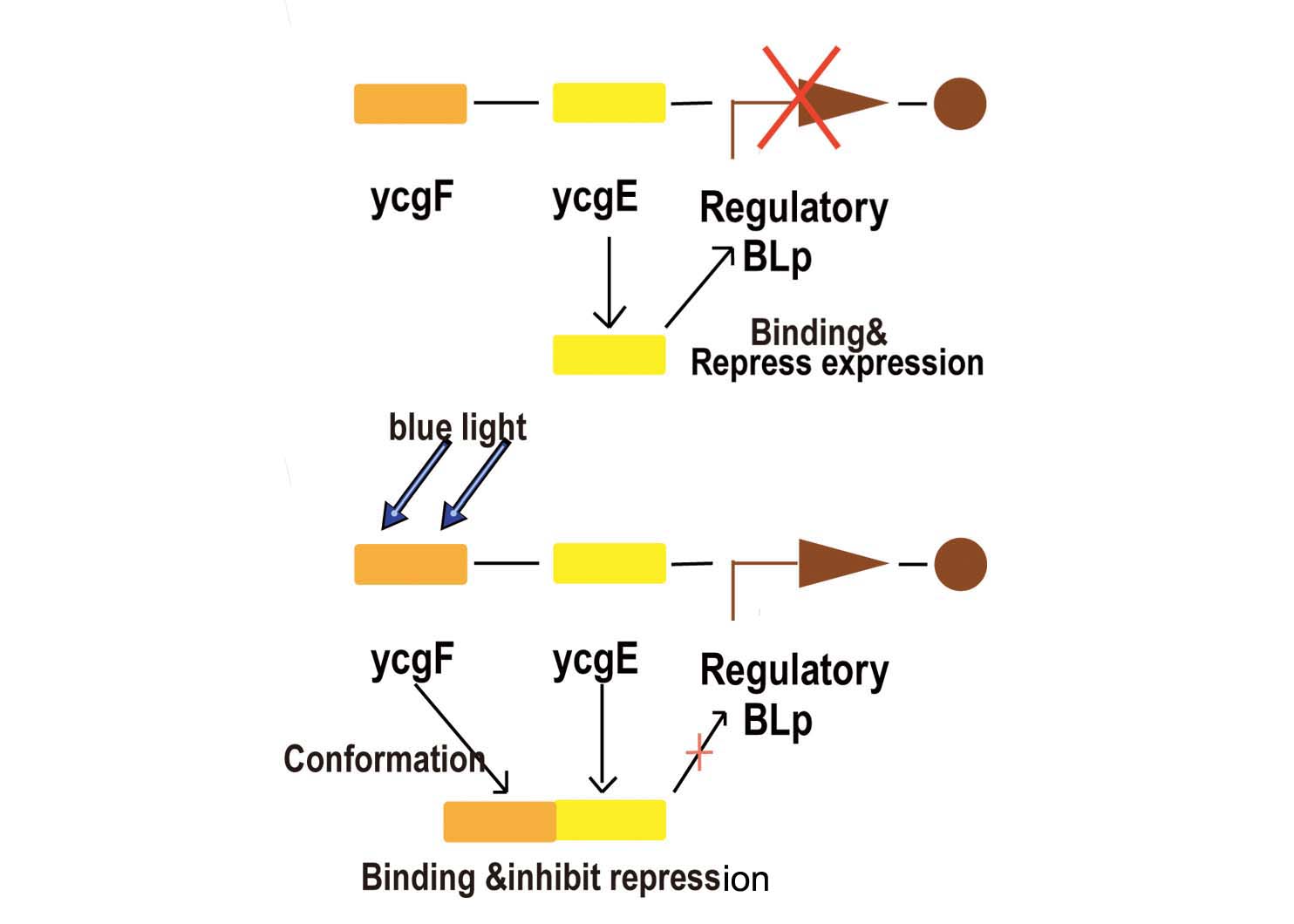
Blue light
Blue light sensor is relatively more simple but more reliable compared with red light sensor. We now start explaining how it works from the key promoter:BBa_K238013.
- Fig2. Blue light receptor system
Part BBa_K238013 is a promoter which normally lies before the ycgZ gene, a part of an operon consisting of several genes used by E.coli for regulating e.g. biofilm production. It is regulated by the ycgF/E system. This system consists of a receptor, ycgF, which is responsive to blue light. When blue light strikes, the receptor changes conformation and dimerizes. This allows it to bind to the ycgE repressor through its EAL-domain, releasing the repressor from the promoter region. The inverted repeats shown here are expected to represent the binding site for ycgE. YcgE binding results in transcription repression.
As the experiments done by team iGEM09_KULeuven shown, aside from light, temperature is a very important influence (if not a bigger one). for instance when working in low copy plasmids temperature will influence the promoter/repressor ratio. Cells are grown at 37°C will have too much promoter resulting in constitutive activity. At 16°C, there will be more repressor and receptor but the low temperature will put the receptor in its active state thus inhibiting the repressor from doing its job. When grown at 25°C the ratio is better and the receptor/repressor are still in there ground state leading to a good repression of the promoter.
Most fortunate for normal transgenic work of this light sensing part is that the ycgF/E system is a necessary for competent cells like BL21 or DH5α, which means extra implant of the ycgF/E system into competent cells is unnecessary.
We, by now in our project, have tried to use this blue light sensing system as a switch in the first step. Once triggered, it would lead to the execution of continual procedures.
Moreover, in an effort to improve biosafety standards in modern synthetic biology research, we have been working to construct a new biobrick that functions as a light-sensitive division repression tool. So long as the culture dish is kept under normal light condition, the implanted genes would not express at high colony densities.
Toggle Switch
Intercelluar Communication
Cell Division Inhibitor
Aiming at creating an asymmetric colony, we use the antisense FtsZ sequence to silent the FtsZ gene and control the self-renewal and differentiation of E.coli. We create a kit which can receive AHL signaling and promote the antisense sequence to repress the division of prokaryotes.
FtsZ To fabricate this part, we decided to utilize the FtsZ gene to manipulate the division of E.coli. Cell wall division in E. coli involves a complex series of events with the involvement of at least eight different proteins. One of the first steps in bacterial cell wall division involves the formation of the Z-ring, a circular polymeric structure formed by the cytosolic protein FtsZ.
FtsZ is a prokaryotic homologue of and - and -tubulin in E.coli. And like tubulin, it conducts GTPase and polymerization activities in vitro. The exact structure of the Z ring in vivo is not known, but there has been evidence proving that it is highly dynamic, being continuously remodeled, whose frequency is almost proportional to the amount of its GTPase activities . And FtsZ can assemble into the Z-ring without the assistance of any protein so far identified.
It has been demonstrated that FtsZ has a precise localization within the bacterium. Immuno-gold electron microscopy showed a diffuse localization in most cells but the Z ring of concentrated FtsZ near the membrane in cells that were about to divide. As division proceeded, the FtsZ ring constricted and remained at the tip of the invaginating membrane.
In conclude, FtsZ is one of the best conserved division proteins in its family and its role in cell division traces back very early in evolution.
Antisense RNA In order to inhibit the cell division, we synthesize the right antisense fragments with gene silencing effects targeting ftsZ in E.coli. Antisense RNA and DNA approaches have recently attracted much interest, particularly for biomedical and biotechnologic applications. (to be continued)
The paired termini
It is known that naturally occurring antisense RNA are complicated folded structures whose efficiency depends on binding rate rather than the stability of a complex with its target. (to be continued)
A paired termini (PT) design, where flanking inverted repeats create paired asRNA termini, was proved can produce effective gene silencing. (to be continued)
Design scheme
In order to interfere with the cell division, we synthesize the right antisense fragments with gene silencing effects targeting ftsZ in E.coli. A vector with paired termini was constructed to constantly express different asRNAs of ftsZ in E.coli, and the gene-silencing effects were observed by morphological observation on-plate,microscope and liquid culture. This part has been found inhibiting cell division considerbly.After that, we ligated it after the AHL receiver F2620 and let the AHL signaling promote it. Meanwhile, to witness the function of the paired termini, we also constructed series of kits only with the target fragments.

 "
"