Team:Penn/Targeting
From 2012.igem.org
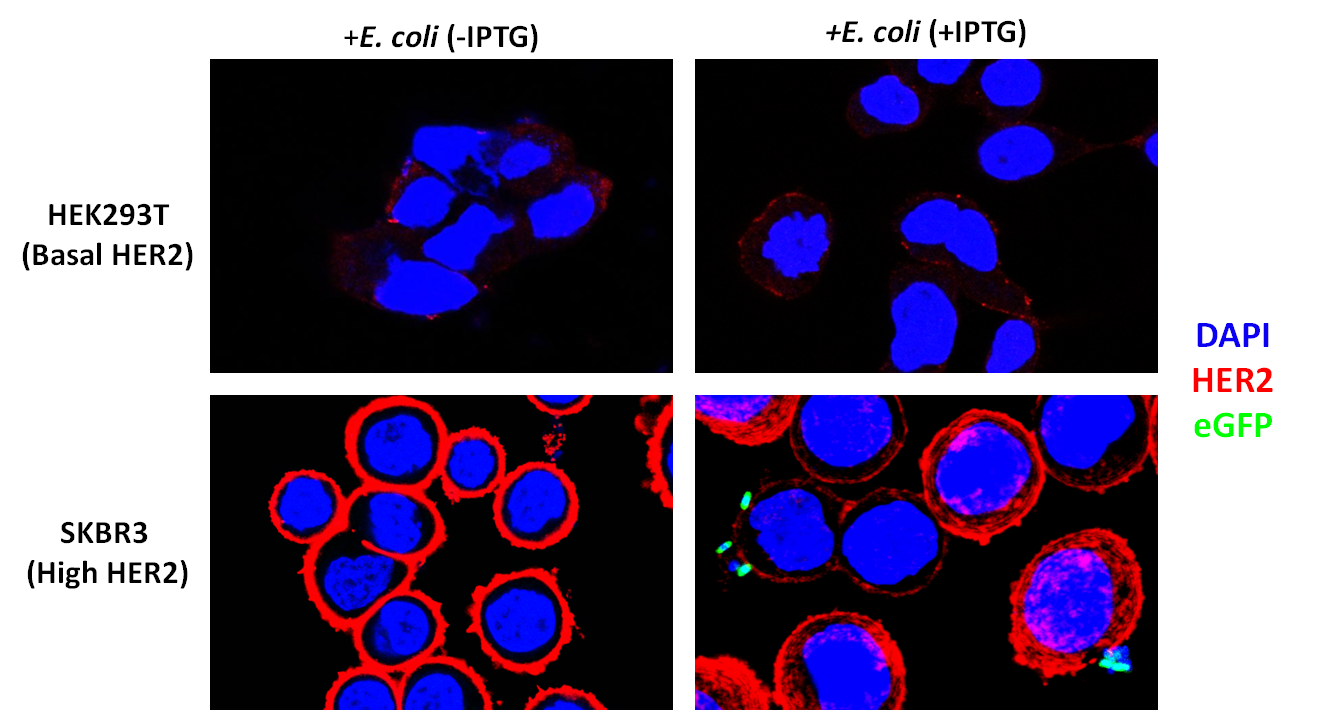
After verifying that the DARPin was displayed on the cell surface, we sought to test whether it could allow binding to HER2-overexpressing cancer cells. We were generously provided SKBR3 cells by the lab of Matthew Lazzara. These cells are derived from breast cancer cells and over-express HER2. We also obtained Human Embryonic Kidney (HEK) 293T cells, which express a low amount of HER2, to act as controls.
To verify that our SKBR3 cells overexpressed HER2, we immunostained for HER2 (primary anti-Neu Mouse Igg, Santa Cruz Biotechnology and secondary donkey anti-mouse Alexa-Fluor 647 conjugate, Jackson Immunoresearch) and visualized the cells on a confocal microscope. As expected, HER2 was overexpressed in SKBR3 cells (Figure 1).

Figure 1

Figure 2
To assay whether our DARPin-displaying E. coli bound to SKBR3 cells preferentially, we conducted experiments in which our bacteria were co-incubated with SKBR3 or HEK293T cells. The DARPin-displaying bacteria were co-transformed with constitutively expressed eGFP (pACBB-eGFP plasmid) for easy visualization. The goal was to show SKBR3-specific binding of eGFP labeled bacteria, and only when they were induced with IPTG to produce INPNC-DARPin. Preliminary results are exciting and show preferential binding to SKBR3 cells. In culture plates with low-HER2 HEK293T cells, no green bacteria were observed bound to the cells. IPTG-induced bacteria bound selectively to SKBR3 cells and we visualized this binding by confocal microscopy (Figure 3).
 "
"

