Team:Tokyo Tech/Experiment/PHB
From 2012.igem.org
Contents |
PHB production by E.coli & Confirmation of PHB
To synthesize PHB by E.coli, we transformed E.coli JM109 with the constructed PHAC1-A-B1 part on pSB1C3 ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001]). E.coli JM109 is used to synthesize PHB, because it tends to have a high density accumulation of PHB([5] ). As a negative control, we transformed E.coli JM109 with PlasI-gfp on pSB1C3.
4-1 Confirmation of PHB synthesized on colonies
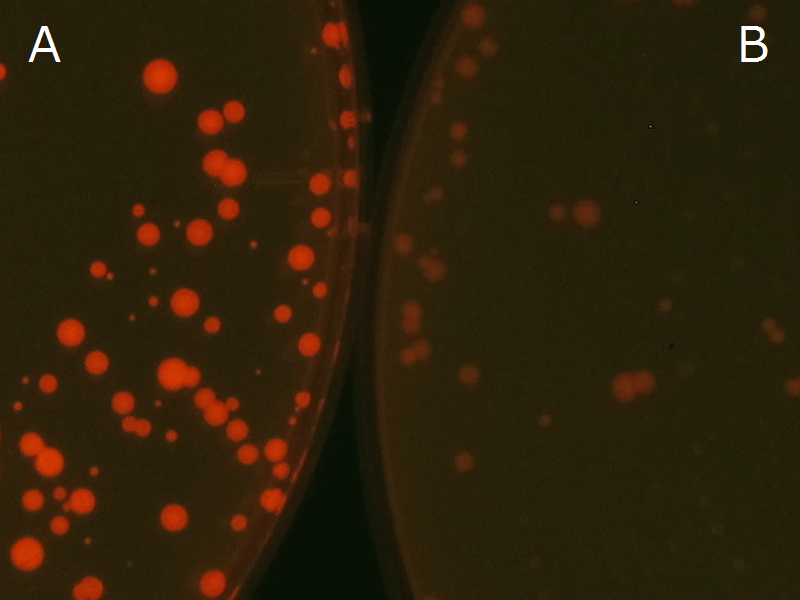
We observed the accumulation of PHB in the E.coli colonies on Nile red positive medium under UV. Nile red has been widely used to stain colonies and distinguish between PHA-accumulating and non-accumulating colonies. Nile red in the agar medium doesn’t affect the growth of the cells, and the accumulation of PHAs in the colonies can be directly monitored([3][4][5] ). We cultured the transformant on LB agar medium plates with Nile red. After several days, colonies storing PHB were stained orange by Nile red when observed under UV. This result indicates that transformant synthesized and stored PHB. Fig2-2-4-1 is the photographs of E.coli colonies on Nile red positive medium taken under UV. The orange colonies in Fig2-2-4-1A show that the accumulated PHB in cells was stained by Nile red. This result indicates that part [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001] synthesized PHB. Fig2-2-4-1B is the photograph of negative control cells. In this figure we observed that there were no remarkable colored colonies. Fig2-2-4-1-2 shows the difference between cells storing PHB and those not storing PHB on one plate. The cells in blue rectangle area are the cells with PHB synthesis gene and the cells in green rectangle area are the cells with PlasI-gfp gene as a negative control. Using the cells storing PHB, we drew a rose silhouette on the LB agar plate containing Nile red (Fig2-2-4-1-3).[Protocol]
Confirmation of PHB accumulated in cells
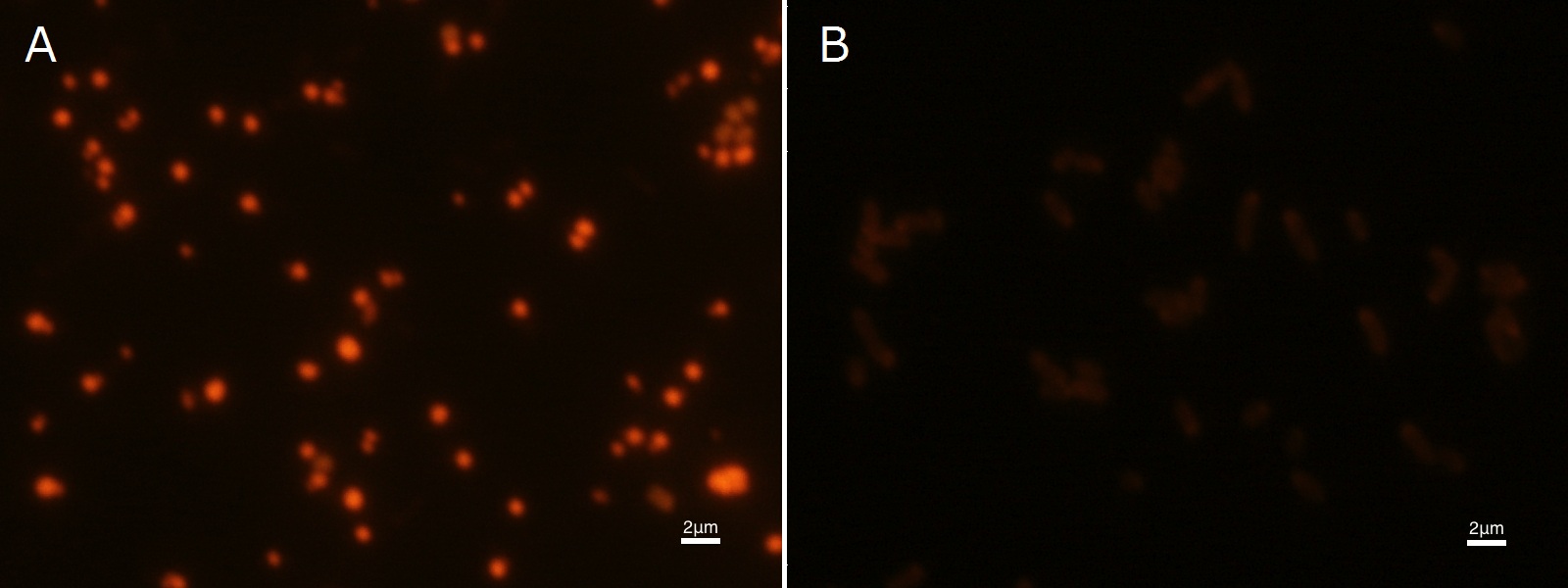
To confirm the accumulation condition of PHB in E.coli with a microscope, we stained the PHB with Nile blue A reagent. Nile blue A is also used to detect the existence of PHB and has no toxicity to the cells([5]). Before the observation, we stained the dried cells with Nile blue A solution. We then took photographs of the sample under fluorescence microscope. Fig2-2-4-2-1 is the photograph of dried E.coli (with PHAC1-A-B1 gene) cells dyed with Nile blue A solution taken by fluorescence microscope. The fluorescent areas in Fig2-2-4-2-1A are the accumulated PHB in the cells. This result also indicates that part [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001] synthesized PHB. In the photograph of negative control (Fig2-2-4-2-1B), no remarkable fluorescent area was observed.[Protocol]
Construction of pha-C1-A-B1 in Biobrick format
[Back to "Construction of phaC1-A-B1 in Biobrick format"]
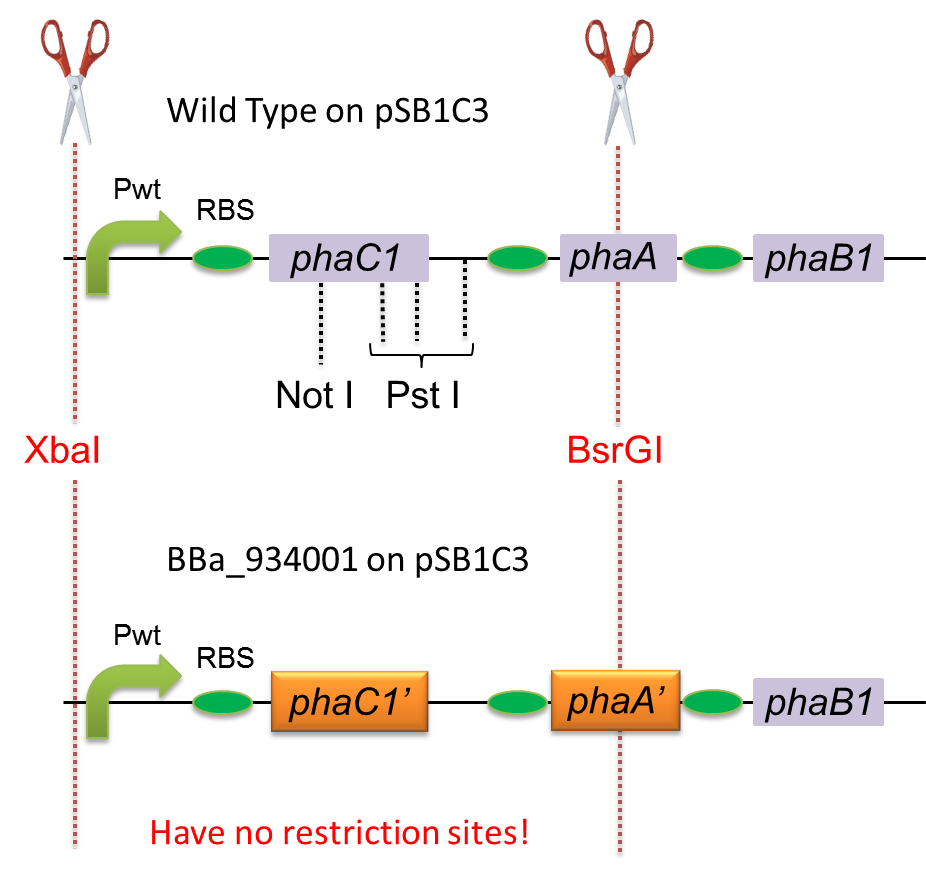
To construct a part that meets Biobrick format, we have modified the phaC1-A-B1 operon not to contain forbidden restriction enzyme sites. First, we cloned the wild type gene phaC1-A-B1 from R.eutropha H16 by using PCR and inserted the gene into pSB1C3. However, wild type phaC1-A-B1 gene sequence contains one NotI and three PstI recognition sites that are not allowed in Biobrick format. To get phaC1-A-B1 sequence without these recognition sites, we ordered the chemically synthesized DNA from IDT/MBL. In this chemically synthesized DNA, coding is optimized for E.coli. We used restriction enzyme XbaI (on pSB1C3) and BsrGI (on phaC1-A-B1) to insert sequence. That is to say, we got Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] synthesizing gene in Biobrick format ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001]).
[Back to "Construction of phaC1-A-B1 in Biobrick format"]
Protocol
A .PHB production on colonies and preparation before confirmation with Nile red under UV
[Back to "4-1 Confirmation of P(3HB) synthesized on colonies"]
1 Preparation of LB agar medium plate containing Nile red and Glucose
1.1 Autoclave a LB agar(final 40g/L) solution at 120 ° C
1.2 After the autoclave, add Chloramphenicol(final 25ug/ml), Nile red and glucose(final 20g/L) to the LB agar solution when it cools down.
1.3 Make LB agar medium plates with the mixture.
2 Transformation of E.coli strain JM109 with pSB1C3 plasmid containing phaC1-A-B1 into strain JM109
2.1 Thaw the competent cells JM109 at 4° C
2.2 Add the target DNA 3ul into 1.5ml tube, then add in 50ul the thawed competent cells.
2.3 Put the tube into ice for 15mins
2.4 42° C,30secs, heatshock
2.5 Add 160ul of SOC into the tube
2.6 Incubate the the cells at 37° C for 30mins
2.7 Spread the resulting culture on LB agar medium plate with a large cone rod.
2.8 Incubate the plate at 37° C for 36hrs then cells the plate into 4° C room for 2-3 days.
[Back to "4-1 Confirmation of P(3HB) synthesized on colonies"]
B.PHB production in cells and preparation before the confirmation with Nile blue A
[Back to "4-2 Confirmation of P(3HB) accumulated in cells"]
1 Production of PHB
1.1 Acquire one colony of the transformed strains (JM109) with a platinum loop
1.2 Culture the colony in LB solution for 16hrs at 37 ° C
1.3 Measure LB medium (final 2.5%) and add it to each Erlenmeyer flask inside clean bench.
1.4 Add distilled water(final 95%) to each Erlenmeyer flask and cover the flasks with four-folded aluminum foil.
1.5 Set all flasks into autoclave
1.6 Add Chloramphenicol(final 25ug/ml) and glucose solution (50%) (final 20g/L) after the medium is completely cooled.
1.7 Add the solution of cultured cells into each flasks and shaking culture with air permeable lids at 37 ° C for 96 hours.
2 Preparation before the confirmation (with Nile blue A) under fluorescent microscope
2.1 Collection of PHBs in JM109
2.1.1 Weigh empty 50ml falcon tube without lid and make a record.
2.1.2 Add some culture solution into each tube.
2.1.3 Set the tubes into centrifuge and make sure that the label faces outside.
2.1.4 4 ° C, 5000G, 10mins in centrifuge.
2.1.5 Remove the supernatant with electric pipettor then add culture solution and set in centrifuge again.
2.1.6 After adding all the culture solution and setting in centrifuge, remove the supernatant and add water, set in centrifuge again.
2.1.7 Remove the supernatant and add a little amount of water
2.1.8 Cover the tubes with double layers of parafilms and fully freeze them.
2.2 Freeze drying (lyophilization)
2.2.1 Poke several holes on the tubes’ parafilm with toothpick.
2.2.2 Set the tubes on the freeze drying machine.
2.2.3 Freeze dry for 3 days.
2.3 Stain PHB accumulated dried cells with Nile blue A before observation
2.3.1 Acquire dried cells after freeze drying
2.3.2 Put a small amount of cells on the slide glass
2.3.3 Add water on the cells and heat the slide glass immobilize the cells
2.3.4 Stain the cells with 1% Nile blue A solution (water) for 8 minutes
2.3.5 Wash excess Nile blue A with 8% acetic acid solution
 "
"