Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/project2.3
From 2012.igem.org
AleAlejandro (Talk | contribs) |
AleAlejandro (Talk | contribs) (→Biodesulfurization of Dibenzothiophene (DBT)) |
||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
===Background=== | ===Background=== | ||
| - | We found that many iGEM teams wanted to express enzymes of biodegradation pathway in ''E.coli''. However, it doesn't have significant superiority compared to traditional strain screening strategy. The power of synthetic biology is not fully demonstrated here. | + | We found that many iGEM teams wanted to express enzymes of biodegradation pathway in ''E.coli''. However, it doesn't have significant superiority compared to traditional strain screening strategy. The power of synthetic biology is not fully demonstrated here. |
| - | We got inspired by project of 2012 iGEM team Calgary. One of their goals is to achieve desulfuration of dibenzothiophene in ''E.coli''. | + | |
| - | Sulfur in crude oil could contribute to global warming, acid rain, and various health issues. Biodesulfurization of fossil fuel could help upgrade the quality of fossil fuel and thus the whole environment. | + | We got inspired by project of 2012 iGEM team Calgary. One of their goals is to achieve desulfuration of dibenzothiophene in ''E.coli''. Sulfur in crude oil could contribute to global warming, acid rain, and various health issues. |
| + | |||
| + | Biodesulfurization of fossil fuel could help upgrade the quality of fossil fuel and thus the whole environment. To upgrade this system, we aimed to link related enzymes to orderly organized membrane anchors, which would accelerate desulfurization pathway remarkably. | ||
| + | |||
===Desulfurization Pathway=== | ===Desulfurization Pathway=== | ||
| - | Four enzymes are involved in Desulfurization pathway. Dibenzothiophene monooxygenase (DszC) is responsible for converting DBT to DBT-sulfoxide and finally to DBT-sulfone (DBTO2). DBT-sulfone monooxygenase (DszA) then carries out the next step in the pathway, producing 2-hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinic acid (HBPS). HBPS is then converted to the final product by HBPS desulfinase (DszB), producing 2-HBP. The sulfur is released from the hydrocarbon in the form of sulfite. | + | Four enzymes are involved in Desulfurization pathway. Dibenzothiophene monooxygenase (DszC) is responsible for converting DBT to DBT-sulfoxide and finally to DBT-sulfone (DBTO2). DBT-sulfone monooxygenase (DszA) then carries out the next step in the pathway, producing 2-hydroxybiphenyl-2-sulfinic acid (HBPS). HBPS is then converted to the final product by HBPS desulfinase (DszB), producing 2-HBP. The sulfur is released from the hydrocarbon in the form of sulfite. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | Note that the first three steps of the this Desulfurization pathway require FMNH<sub>2</sub> as a reductant. In order to regain this power an Oxidoreductase (DszD) uses NADH to recycle the FMNH2, allowing the reaction to proceed. For more information, click [https://2012.igem.org/Team:Calgary/Project/OSCAR/Desulfurization Wiki of team Calgary] | |
| - | + | ||
| + | [[File:12SJTU desulconstruction.png|thumb|700px|center|The 4S Desulfurization Pathway, showing the desulfurization of the model compound DBT by DszA, DszB, DszC, and DszD. Credits to 2012 iGEM team Calgary]] | ||
| + | |||
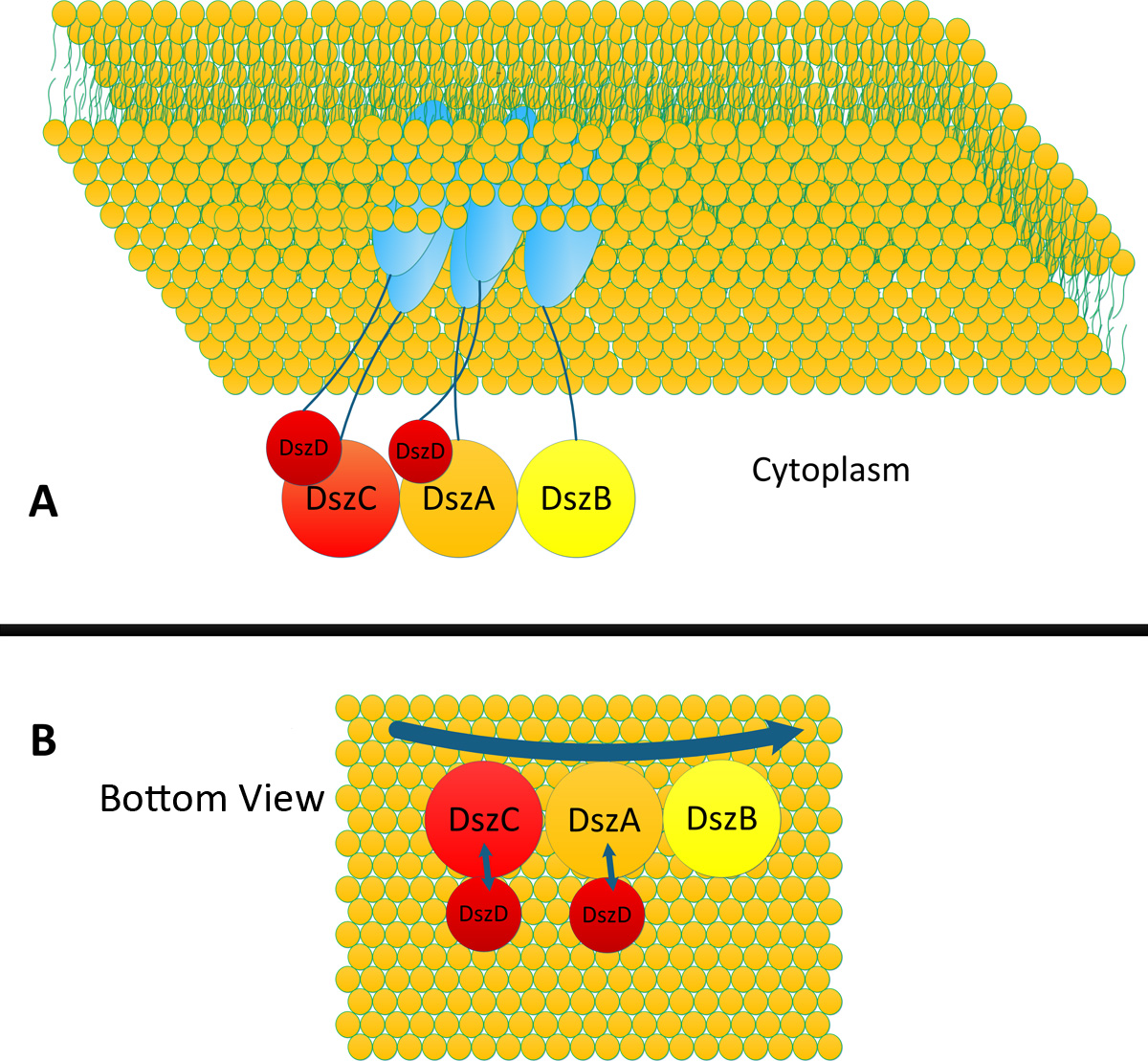
| + | === Design of Experiment=== | ||
| + | We are trying to link DszA, DszB, DszC and DszD to orderly organized membrane anchor to accelerate Desulfurization process in ''E.coli''. Due to decreased distance between those enzymes, the proceeding speed could increase sharply. | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
Revision as of 10:58, 26 October 2012
| ||
|
 "
"