Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/project2.3
From 2012.igem.org
AleAlejandro (Talk | contribs) (→Membrane Accelerator - PAH degradation & DBT desulfurization) |
AleAlejandro (Talk | contribs) (→Membrane Accelerator - PAH degradation & DBT desulfurization) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
To accelerate desulfurization of Dibenzothiophene (DBT) | To accelerate desulfurization of Dibenzothiophene (DBT) | ||
| - | To show the superiority of membrane scaffold in organizing enzymes | + | To show the superiority of membrane scaffold in organizing enzymes into two dimensional pattern |
*'''Achievements''' | *'''Achievements''' | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
===Background=== | ===Background=== | ||
| - | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which consist of two or more fused aromatic rings, are widespread in the environment and persist for a very long time. Some PAHs are toxic, mutagenic and carcinogenic and therefore are health hazards. Efforts have been made to screen bacteria strains that could degrade PAH. Moreover, many researchers focused on studying the mechanism of PAH biodegradation. But the rate of natural biodegradation is relatively slow. | + | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which consist of two or more fused aromatic rings, are widespread in the environment and persist for a very long time. Some PAHs are toxic, mutagenic and carcinogenic and therefore are health hazards. Efforts have been made to screen bacteria strains that could degrade PAH. Moreover, many researchers focused on studying the mechanism of PAH biodegradation. But the rate of natural biodegradation is relatively slow. We are trying to build a Membrane Accelerator to speed up proceeding rate of PAH biodegradation process. Naphthalene degradation pathway in ''Pseudomonas'' species is well studied and thus recruited in our project to build PAH-degrading ''Membrane Accelerator''. This is the very first time that scaffold system has been applied in accelerating Biodegradation pathway. |
| - | + | == Degradation Pathway== | |
We recruited naphthalene degradation pathway in ''Pseudomonas'' species, which has been well characterized. Six crucial enzymes are involved in naphthalene degradation pathway. | We recruited naphthalene degradation pathway in ''Pseudomonas'' species, which has been well characterized. Six crucial enzymes are involved in naphthalene degradation pathway. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
In the first catabolic step, an oxygen molecule is introduced at the 1,2-position of the aromatic nucleus to produce cis-1,2-dihydroxy-1,2-dihydronaphthalene by naphthalene dihydrodiol dioxygenase(NahA). cis-1,2-Dihydroxy-1,2-dihydronaphthalene is then dehydrogenated to 1,2-dihydroxynaphthalene by cis-naphthalene dihydrodiol dehydrogenase(NahB). 1,2-Dihydroxynaphthalene is cleaved by 1,2-dihydroxynaphthalene dioxygenase(NahC), and the resulting ring-cleavage product spontaneously cyclizes to form 2-hydroxy-2H-chromene-2-carboxylic acid. Enzymatic reactions by an isomerase(NahD) and a hydratase-aldolase(NahE) result in the production of salicylaldehyde, which is then transformed to salicylate by salicyladehyde dehydrogenase(NahF). | In the first catabolic step, an oxygen molecule is introduced at the 1,2-position of the aromatic nucleus to produce cis-1,2-dihydroxy-1,2-dihydronaphthalene by naphthalene dihydrodiol dioxygenase(NahA). cis-1,2-Dihydroxy-1,2-dihydronaphthalene is then dehydrogenated to 1,2-dihydroxynaphthalene by cis-naphthalene dihydrodiol dehydrogenase(NahB). 1,2-Dihydroxynaphthalene is cleaved by 1,2-dihydroxynaphthalene dioxygenase(NahC), and the resulting ring-cleavage product spontaneously cyclizes to form 2-hydroxy-2H-chromene-2-carboxylic acid. Enzymatic reactions by an isomerase(NahD) and a hydratase-aldolase(NahE) result in the production of salicylaldehyde, which is then transformed to salicylate by salicyladehyde dehydrogenase(NahF). | ||
| - | === Design=== | + | === Design of Experiment=== |
| - | To test whether Membrane Accelerator could accelerate naphthalene biodegradation pathway, we are trying to link six enzymes | + | To test whether Membrane Accelerator could accelerate naphthalene biodegradation pathway, we are trying to link six crucial enzymes (NahA, B, C, D and E) to orderly organized membrane anchors and expressed them in ''E.coli''. ''E.coli'' expressing the same type and amount of cytoplasmic enzymes is set as control group. |
[[File:12SJTU_PAHconstruction.png|thumb|600px|center|Demonstration of Membrane Accelerator designed for speeding naphthalene biodegradation process]] | [[File:12SJTU_PAHconstruction.png|thumb|600px|center|Demonstration of Membrane Accelerator designed for speeding naphthalene biodegradation process]] | ||
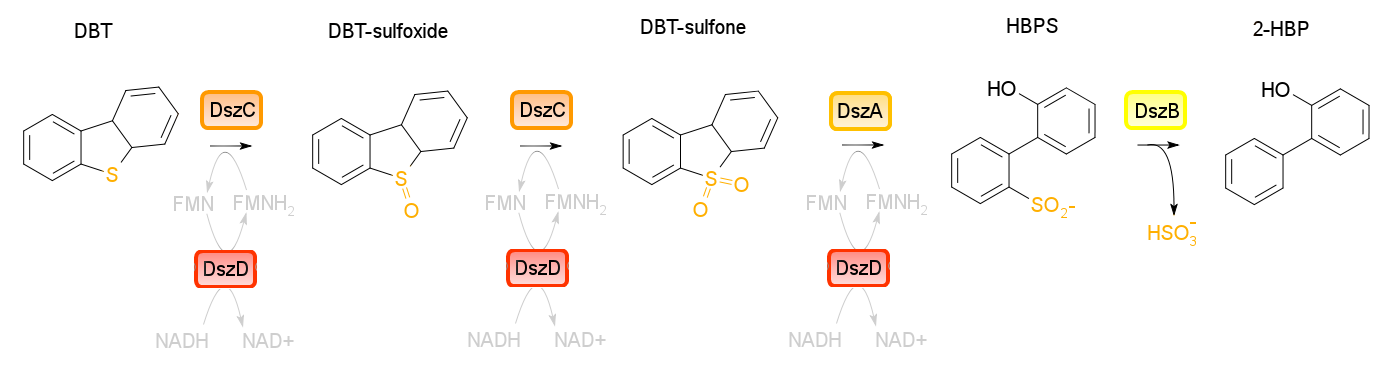
==Biodesulfurization of Dibenzothiophene (DBT) == | ==Biodesulfurization of Dibenzothiophene (DBT) == | ||
| - | |||
===Background=== | ===Background=== | ||
| - | We found that many iGEM teams wanted to express enzymes of biodegradation pathway in ''E.coli''. However, it doesn't have significant superiority compared to traditional strain screening. The power of synthetic biology is not fully demonstrated here. | + | We found that many iGEM teams wanted to express enzymes of biodegradation pathway in ''E.coli''. However, it doesn't have significant superiority compared to traditional strain screening strategy. The power of synthetic biology is not fully demonstrated here. |
We got inspired by project of 2012 iGEM team Calgary. One of their goals is to achieve desulfuration of dibenzothiophene in ''E.coli''. To improve the system, we aimed to link those enzymes to orderly organized membrane anchors, which would enhance desulfurization pathway remarkably. | We got inspired by project of 2012 iGEM team Calgary. One of their goals is to achieve desulfuration of dibenzothiophene in ''E.coli''. To improve the system, we aimed to link those enzymes to orderly organized membrane anchors, which would enhance desulfurization pathway remarkably. | ||
Sulfur in crude oil could contribute to global warming, acid rain, and various health issues. Biodesulfurization of fossil fuel could help upgrade the quality of fossil fuel and thus the whole environment. | Sulfur in crude oil could contribute to global warming, acid rain, and various health issues. Biodesulfurization of fossil fuel could help upgrade the quality of fossil fuel and thus the whole environment. | ||
| Line 77: | Line 76: | ||
For more information, click [https://2012.igem.org/Team:Calgary/Project/OSCAR/Desulfurization Wiki of team Calgary] | For more information, click [https://2012.igem.org/Team:Calgary/Project/OSCAR/Desulfurization Wiki of team Calgary] | ||
| - | === Design=== | + | === Design of Experiment=== |
We are trying to link DszA, DszB, DszC and DszD to orderly organized membrane anchor to accelerate Desulfurization process in ''E.coli''. Due to decreased distance between those enzymes, the proceeding speed could increase sharply. | We are trying to link DszA, DszB, DszC and DszD to orderly organized membrane anchor to accelerate Desulfurization process in ''E.coli''. Due to decreased distance between those enzymes, the proceeding speed could increase sharply. | ||
Revision as of 10:20, 26 October 2012
| ||
|
 "
"