Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project
From 2012.igem.org
(→Introduction) |
AleAlejandro (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
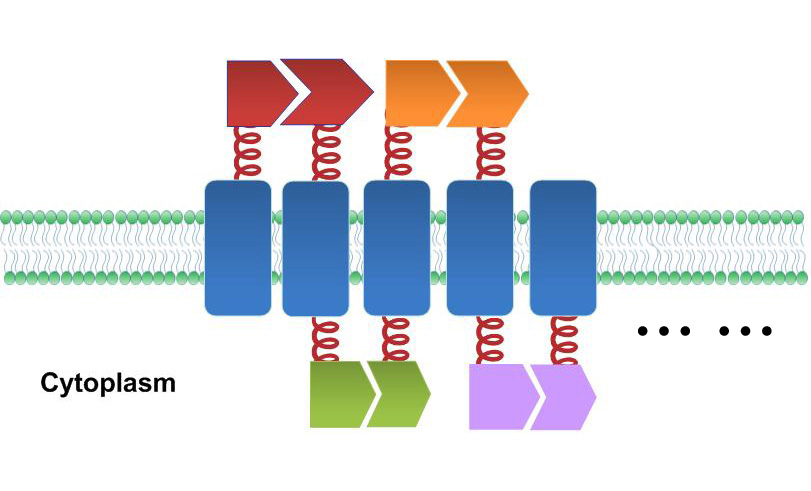
1. '''Natural Scaffold: ''' Different from previous synthesized scaffold, membrane scaffold is an innate one. Besides, there is no limitation on scaffold amount. | 1. '''Natural Scaffold: ''' Different from previous synthesized scaffold, membrane scaffold is an innate one. Besides, there is no limitation on scaffold amount. | ||
| - | [[File:12SJTU Why membrane1.png|400px|center|thumb|Natural Scaffold]] | + | [[File:12SJTU Why membrane1.png|400px|center|thumb|''Fig.3:'' Natural Scaffold]] |
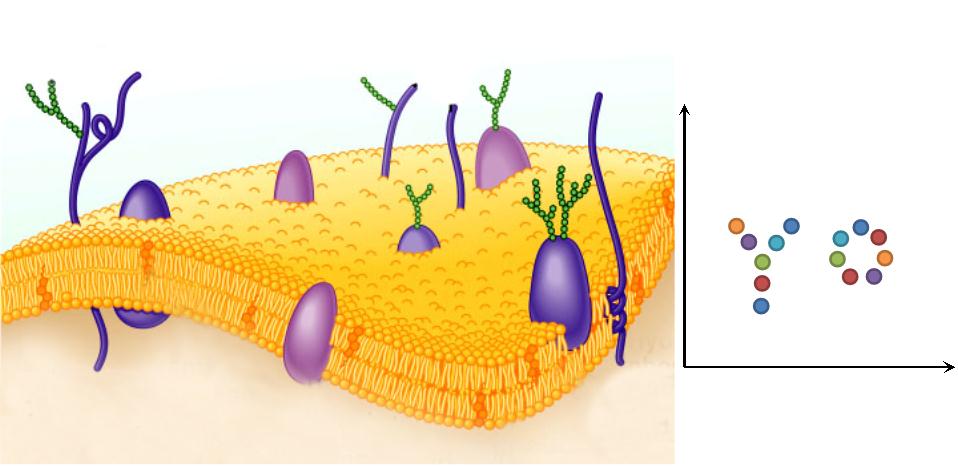
2. '''Two-Dimensional Plane: ''' Membrane Scaffold changes restricted the reaction space to a two-dimensional plane, which has been proved to accelerate reaction more sharply than one-dimensional and discrete scaffold. | 2. '''Two-Dimensional Plane: ''' Membrane Scaffold changes restricted the reaction space to a two-dimensional plane, which has been proved to accelerate reaction more sharply than one-dimensional and discrete scaffold. | ||
| - | [[File:12SJTU Why membrane2.jpg|400px|center|thumb|Two-Dimensional Plane]] | + | [[File:12SJTU Why membrane2.jpg|400px|center|thumb|''Fig.4:'' Two-Dimensional Plane]] |
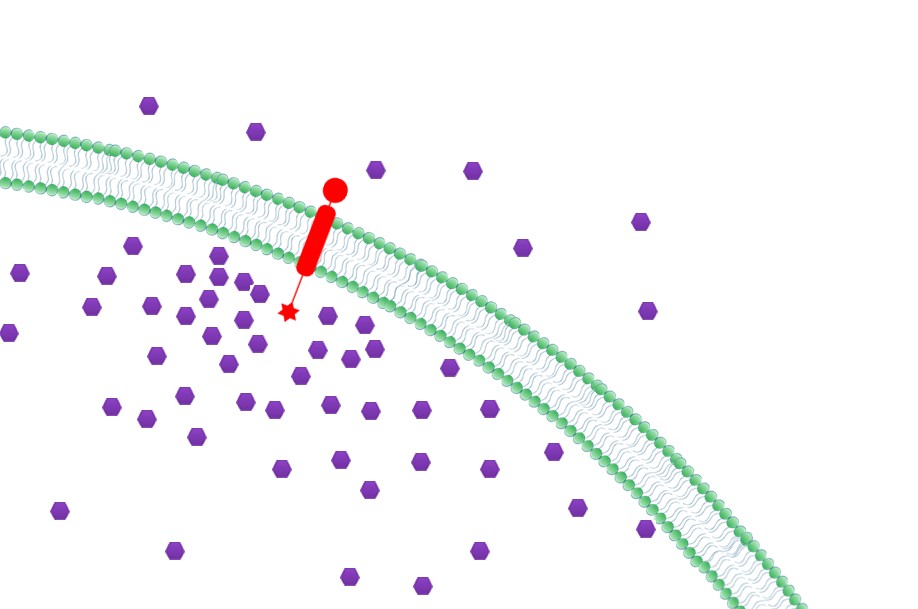
3. '''Priority to Exportation: ''' Concentration of final products could be effectively increased near the membrane with Membrane Scaffold, which in turn, facilitates the transmembrane transportation. So final products would be more readily to be exported to extracellular media. | 3. '''Priority to Exportation: ''' Concentration of final products could be effectively increased near the membrane with Membrane Scaffold, which in turn, facilitates the transmembrane transportation. So final products would be more readily to be exported to extracellular media. | ||
| - | [[File:12SJTU Why membrane3.jpg|400px|center|thumb|Priority to Exportation]] | + | [[File:12SJTU Why membrane3.jpg|400px|center|thumb|''Fig.5:'' Priority to Exportation]] |
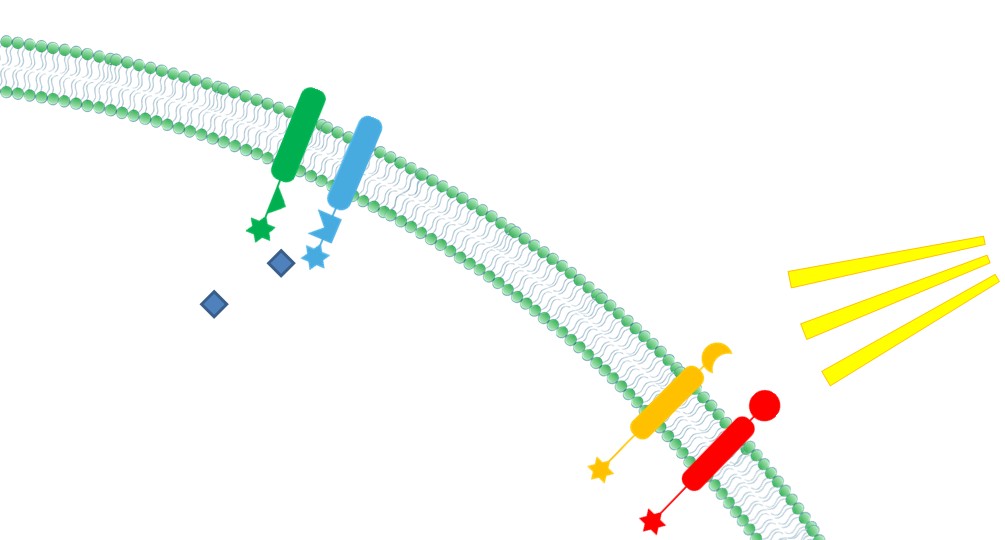
4. '''Ability to Sense Signals''' Membrane Scaffold provides a platform to directly receive environmental and internal signal. Thus reactions could be dynamically controlled through those signals. | 4. '''Ability to Sense Signals''' Membrane Scaffold provides a platform to directly receive environmental and internal signal. Thus reactions could be dynamically controlled through those signals. | ||
| - | [[File:12SJTU Why membrane4.jpg|400px|center|thumb|Ability to sense signals]] | + | [[File:12SJTU Why membrane4.jpg|400px|center|thumb|''Fig.6:'' Ability to sense signals]] |
| + | ==Reference== | ||
| + | Delebecque, C. J., A. B. Lindner, et al. (2011). "Organization of intracellular reactions with rationally designed RNA assemblies." Science 333(6041): 470. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dueber, J. E., G. C. Wu, et al. (2009). "Synthetic protein scaffolds provide modular control over metabolic flux." Nature biotechnology 27(8): 753-759. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Conrado, R. J., G. C. Wu, et al. (2012). "DNA-guided assembly of biosynthetic pathways promotes improved catalytic efficiency." Nucleic acids research 40(4): 1879-1889. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 01:28, 26 October 2012
| ||
|
 "
"