Team:MIT/Results
From 2012.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
$window = $(window); | $window = $(window); | ||
| - | + | ||
$window.scroll(function() { | $window.scroll(function() { | ||
if ($window.scrollTop() > offset.top - topPadding) { | if ($window.scrollTop() > offset.top - topPadding) { | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
} | } | ||
}); | }); | ||
| - | |||
| + | |||
| + | /* | ||
$window.scroll(function() { | $window.scroll(function() { | ||
if ($window.scrollTop() > offset.top - topPadding) { | if ($window.scrollTop() > offset.top - topPadding) { | ||
$sidebar.stop().animate({ | $sidebar.stop().animate({ | ||
marginTop: $window.scrollTop() - offset.top + topPadding, | marginTop: $window.scrollTop() - offset.top + topPadding, | ||
| - | }, | + | }, 200); |
} else { | } else { | ||
$sidebar.stop().animate({ | $sidebar.stop().animate({ | ||
marginTop: 0 | marginTop: 0 | ||
| - | }, | + | }, 200); |
} | } | ||
}); | }); | ||
| - | + | */ | |
}); | }); | ||
Revision as of 03:24, 29 September 2012
RNA Strand Displacement In Vitro
Previously:
In 2011, Lulu Qian and Erik Winfree of Caltech, published a paper "Scaling Up Digital Circuit Computation with DNA Strand Displacement cascades." This paper demonstrated how scalable DNA strand displacement based logic circuits are capable of processing functions as difficult as square roots. See MOTIVATION for more details
MIT iGEM 2012:
Before our team attempted to bring the mechanism of strand displacement into an in vivo context, we first decided to try assaying strand displacement in vitro using RNA. We used 2'-O-Methyl RNA strands that have never been proven before to strand displace in vitro. Before creating our own constructs, we decided to use sequences from Qian/Winfree and adapt them to RNA.
Our Foundational Experiment:
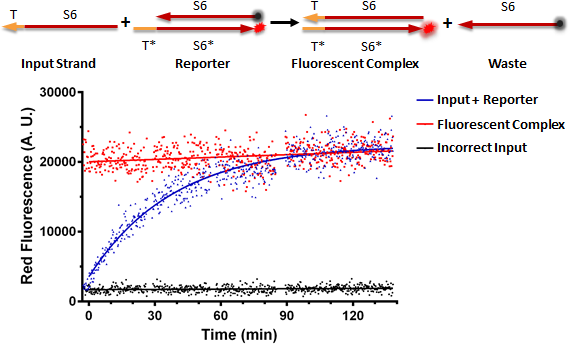
Figure A shows a foundational experiment with RNA strand displacement in vitro, performed on a plate reader. The negative control, in black, is a well that receives just an anneal reporter complex. This reporter has gate strand T*S6* that is tagged with a fluorophore, 3' ROX. The top strand of the complex, the output strand, S6 which is complementary to S6*, is tagged with a quencher, that absorbs fluorescence from the fluorophore. When the two strands of the reporter are annealed, no fluorescence should be observed. The positive control, in red, is the input strand, TS6, annealed to the gate strand, T*S6* tagged with ROX. This is what we would expect the product of a strand displacement reaction to behave like. We can see that in the experimental well when the input is present, it can bind to the exposed T* domain of the reporter and displace the output, S6-quencher, strand yielding a fluorescent complex and waste.
Figure A
Previously:
In 2011, Lulu Qian and Erik Winfree of Caltech, published a paper "Scaling Up Digital Circuit Computation with DNA Strand Displacement cascades." This paper demonstrated how scalable DNA strand displacement based logic circuits are capable of processing functions as difficult as square roots. See MOTIVATION for more details
MIT iGEM 2012:
Before our team attempted to bring the mechanism of strand displacement into an in vivo context, we first decided to try assaying strand displacement in vitro using RNA. We used 2'-O-Methyl RNA strands that have never been proven before to strand displace in vitro. Before creating our own constructs, we decided to use sequences from Qian/Winfree and adapt them to RNA.
Our Foundational Experiment:
Figure A shows a foundational experiment with RNA strand displacement in vitro, performed on a plate reader. The negative control, in black, is a well that receives just an anneal reporter complex. This reporter has gate strand T*S6* that is tagged with a fluorophore, 3' ROX. The top strand of the complex, the output strand, S6 which is complementary to S6*, is tagged with a quencher, that absorbs fluorescence from the fluorophore. When the two strands of the reporter are annealed, no fluorescence should be observed. The positive control, in red, is the input strand, TS6, annealed to the gate strand, T*S6* tagged with ROX. This is what we would expect the product of a strand displacement reaction to behave like. We can see that in the experimental well when the input is present, it can bind to the exposed T* domain of the reporter and displace the output, S6-quencher, strand yielding a fluorescent complex and waste.
Figure A

Nucleic Acid Delivery
To be able to achieve RNA strand displacement logic cascades in vivo, first our team had to ensure that we are capable to delivering nucleic acid to Mammalian Cells. We have achieved the delivery of plasmid DNA, single stranded modified RNA and double stranded modified RNA to mammalian cells through both lipofection and nucleofection.
(1) Delivery of Plasmid DNA to Mammalian Cells
Through the Gateway method, we have assembled many promoter-gene constructs as detailed on our Parts Page. After construction, we deliver the plasmid DNA to Mammalian Cells through the use of transient transfection, lipofection with Lipofectamine 2000 reagent. Figure A shows:
Figure A will go here.
(2) Delivery of 2'-O-Me RNA to Mammalian Cells
Since our modified reporter constructs use 2'-O-Methyl RNA, we must be able to deliver 2'-O-Me RNA into Mammalian Cells.
The movie below shows HEK293 cells expressing constitutive eYFP with a 2'-O-Methyl-RNA strand labeled with ROX (5-carboxy-x-rhodamine) on the 3' end. As time passes, the complex/vesicles are uptaken by the cell, releasing their payload resulting in whole cell fluorescence. Each frame is 5 minutes, movie encompasses 200 minutes in 9 seconds.
Figure B shows time point images taken at t = 0, 2, 3, and 4 hours post-transfection. Images taken at 10X on Zeiss microscope
Figure B

Once we demonstrated ability to deliver 2'-O-Me RNA to mammalian cells, we ran optimization experiments to optimize the ratio of RNA delivered to transfection reagent used. 2'-O-Me RNA to transfection reagent.
15,20,25,30 pmol ratio DATA from FACS .
(3) Inducible Control of Protein Expression
Figure C

Figure D

Delivery of Plasmid DNA which transcribes short RNA Inputs
FF1 Knockdown Data with triplicate data from nathan
To be able to achieve RNA strand displacement logic cascades in vivo, first our team had to ensure that we are capable to delivering nucleic acid to Mammalian Cells. We have achieved the delivery of plasmid DNA, single stranded modified RNA and double stranded modified RNA to mammalian cells through both lipofection and nucleofection.
(1) Delivery of Plasmid DNA to Mammalian Cells
Through the Gateway method, we have assembled many promoter-gene constructs as detailed on our Parts Page. After construction, we deliver the plasmid DNA to Mammalian Cells through the use of transient transfection, lipofection with Lipofectamine 2000 reagent. Figure A shows:
Figure A will go here.
(2) Delivery of 2'-O-Me RNA to Mammalian Cells
Since our modified reporter constructs use 2'-O-Methyl RNA, we must be able to deliver 2'-O-Me RNA into Mammalian Cells.
The movie below shows HEK293 cells expressing constitutive eYFP with a 2'-O-Methyl-RNA strand labeled with ROX (5-carboxy-x-rhodamine) on the 3' end. As time passes, the complex/vesicles are uptaken by the cell, releasing their payload resulting in whole cell fluorescence. Each frame is 5 minutes, movie encompasses 200 minutes in 9 seconds.
Figure B shows time point images taken at t = 0, 2, 3, and 4 hours post-transfection. Images taken at 10X on Zeiss microscope
Figure B

Once we demonstrated ability to deliver 2'-O-Me RNA to mammalian cells, we ran optimization experiments to optimize the ratio of RNA delivered to transfection reagent used. 2'-O-Me RNA to transfection reagent.
15,20,25,30 pmol ratio DATA from FACS .
(3) Inducible Control of Protein Expression
Figure C

Figure D

Delivery of Plasmid DNA which transcribes short RNA Inputs
FF1 Knockdown Data with triplicate data from nathan
In Vivo RNA Strand Displacement
Strategy 1: Lipofectamine 2000 Transfection of RNA version of Reporter from Winfree/QIan 2011 Paper

Images will go here from April 24th experiment - display red fluorescence in all wells, including those that only got reporter or the wrong input - also see red vesicles indicating reporter comes apart inside the vesicles
Strategy 2: Switch Transfection reagent to RNAiMAX
RNAiMAX is supposed to be a better transfection reagent for double stranded RNA
Images will go here from experiment from June 13th onward where we do not see red vesicles, however we still see whole cell red fluorescence
Strategy 3: Tag RNA strand with an Alexa Fluorophore to act as a transfection marker
Strategy 4: Create DNA plasmids driving transcription of RNA inputs, while transfecting RNA Reporter
Strategy 4: Nucleofect RNA reporter, RNA inputs
[Strategy 5]: Redesign RNA Reporter
Strategy 1: Lipofectamine 2000 Transfection of RNA version of Reporter from Winfree/QIan 2011 Paper

Images will go here from April 24th experiment - display red fluorescence in all wells, including those that only got reporter or the wrong input - also see red vesicles indicating reporter comes apart inside the vesicles
Strategy 2: Switch Transfection reagent to RNAiMAX
RNAiMAX is supposed to be a better transfection reagent for double stranded RNA
Images will go here from experiment from June 13th onward where we do not see red vesicles, however we still see whole cell red fluorescence
Strategy 3: Tag RNA strand with an Alexa Fluorophore to act as a transfection marker
Strategy 4: Create DNA plasmids driving transcription of RNA inputs, while transfecting RNA Reporter
Strategy 4: Nucleofect RNA reporter, RNA inputs
[Strategy 5]: Redesign RNA Reporter
Not Gate
 "
"

