Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus Introduction
From 2012.igem.org
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
<p align="justify"> | <p align="justify"> | ||
There are two major differences between ''B. subtilis'' and ''E. coli'' that are of interest to us: | There are two major differences between ''B. subtilis'' and ''E. coli'' that are of interest to us: | ||
| + | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
'''1) Transformation of ''B. subtilis''''' | '''1) Transformation of ''B. subtilis''''' | ||
| Line 93: | Line 94: | ||
<font color="#000000"; size="2"><p align="justify">Fig. 2: Exogenous DNA is shown in red while the bacterial genome is black a) The propagation of exogenous DNA if brought in as replicative plasmid. The number of plasmids per cell can vary. b) The propagation of exogenous DNA if it is able to integrate into the genome via homologous recombination</p></font> | <font color="#000000"; size="2"><p align="justify">Fig. 2: Exogenous DNA is shown in red while the bacterial genome is black a) The propagation of exogenous DNA if brought in as replicative plasmid. The number of plasmids per cell can vary. b) The propagation of exogenous DNA if it is able to integrate into the genome via homologous recombination</p></font> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | + | |} | |
| - | + | |} | |
Revision as of 22:18, 26 September 2012

The LMU-Munich team is exuberantly happy about the great success at the World Championship Jamboree in Boston. Our project Beadzillus finished 4th and won the prize for the "Best Wiki" (with Slovenia) and "Best New Application Project".
[ more news ]


Bacillus subtilis - a new chassis for iGEM
We chose to work with Bacillus subtilis to set new horizons and offer tools for this model organism to the Escherichia coli-dominated world of iGEM. To introduce B. subtilis, we want to highlight some important aspects of this organism, which are listed in the table below.
| Organism | B. subtilis | E. coli |
|---|---|---|
| Type | gram-positive rod | gram-negative rod |
| Motility | + | + |
| Transformation | natural competence | artificial competence |
| Vectors | integrative & replicative | replicative |
| Sporulation | + | - |
| Differentiation | + | - |
| Safety | [http://www.fda.gov/Food/FoodIngredientsPackaging/GenerallyRecognizedasSafeGRAS/default.htm GRAS] | [http://www.fda.gov/Food/FoodIngredientsPackaging/GenerallyRecognizedasSafeGRAS/default.htm GRAS] |
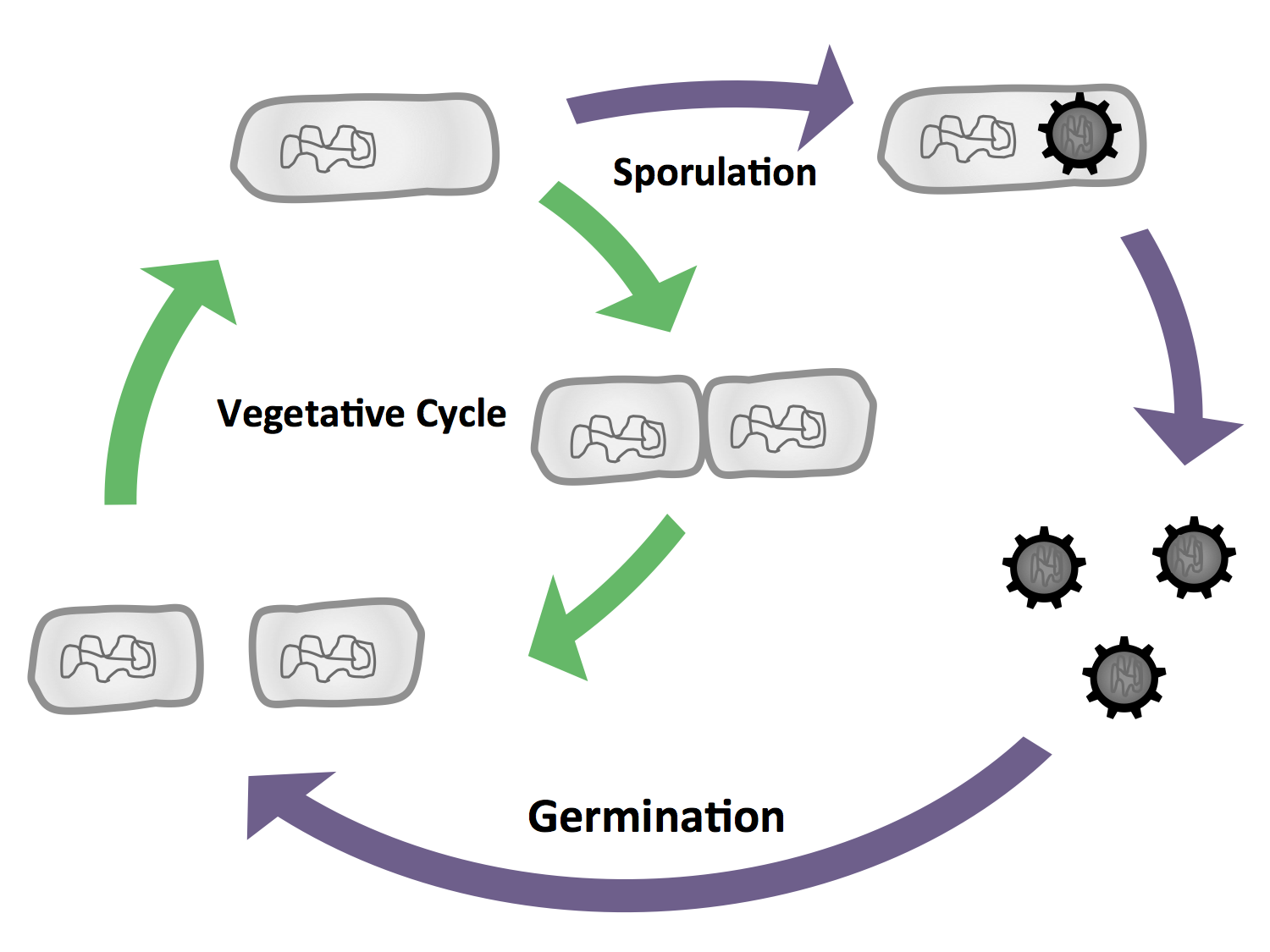
In general, bacteria can be divided into two groups that differ in essential characteristics: gram-positive and gram-negative. Escherichia coli is a model organism for the gram-negative bacteria. A model organism for the gram-positive microorganisms is B. subtilis, which we work with. The natural habitat of B. subtilis is soil, so it is forced to adapt to environmental changes. Hence B. subtilis is very complex. There are many differentiations and survival strategies that B. subtilis can engages (Fig. 1): Due to its natural competence it can uptake DNA and integrate it into its genome. To be flexibel to the environment and move towards nutrients or avoid toxics it is motile with the aid of its peritrich flagella. There is even cannibalism as one differentation form. If the conditions get to bad for living cells, B. subtilis can form spores. These are very stable vehicles where bacteria are resistant towards e.g. desiccation, heat and pressure. If these spores sense better conditions they are able to germinate again.
|
There are two major differences between B. subtilis and E. coli that are of interest to us:
1) Transformation of B. subtilis
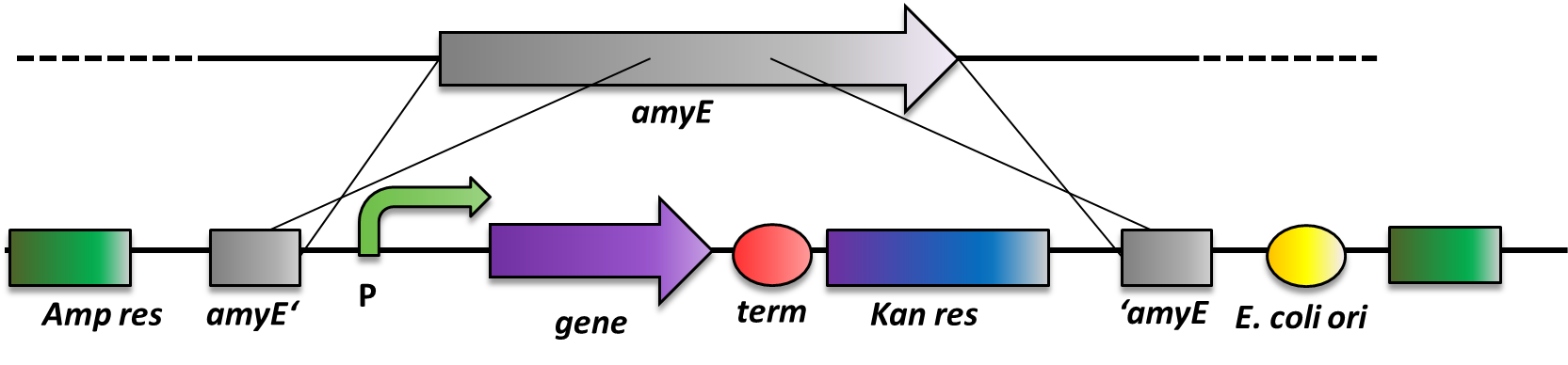
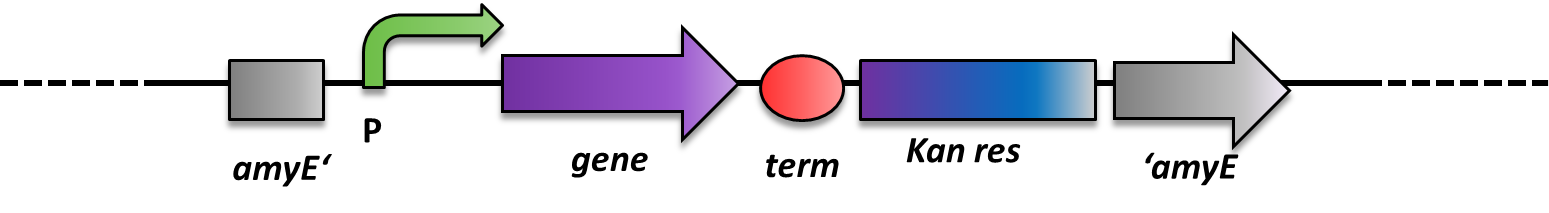
B. subtilis can replicate exogenous DNA via an origin of replication on a plasmid as E. coli does, but there is a much more elegant way of bringing in exogenous DNA stretches. When flanked by homologous regions to the bacterial genome, it will integrate at high efficiency via homologous recombination at this locus and furthermore be replicated with the genome. This has the advantage that if comparing different variables, not only the enviroment is always the same, but also the copy number is from cell to cell and from strain to strain the same, which is not always the case for replicative plasmids. This integrative way of bringing in exogenous DNA was exploited by us when producing the BioBrick compatible Bacillus vectors. The comparision between these two ways of bringing in exogenous DNA is depicted in Fig. 2.
For these reasons, in some cases B. subtilis can be the chassis of choice. Unfortunately, very few iGEM teams have worked with this model organism, and there is at this time no established BioBrick system to use B. subtilis as a chassis.
</p>
2) Integration of DNA B. subtilis is able to differentiate into cells with different morphology and function (Fig. 3), the most severe form being the endospore which is produced under stress conditions. We will exploit the production of endospores in our project Beadzillus. The life cycle of B. subtilis is depicted in Fig. 2.
In contrast to E. coli, the model organism B. subtilis is a gram-postivite rod. It is a facultatively aerobic soil bacterium which can move with its peritrichous flagella. Under ideal conditions, it has a doubling time of 45 minutes. B. subtilis is, in contrast to E. coli, naturally competent, which means that e.g. under nutrient limitation, 10% of cells in a populaton get competent and take up DNA. Also unique for B. subtilis is that the vegetative cells can differentiate under nutrient limitations into spores, which we use in our project Beadzillus. Concerning working with B. subtilis, it is important to know that there are integrative vectors which can integrate into the genome of the organism, in contrast to E. coli, for which there are only replicative vectors. Also both organisms have [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Generally_recognized_as_safe GRAS] state.
|
 "
"